-
Views
-
Cite
Cite
Tao Wu, PSVIII-18 Dietary supplementation with trihexanoin enhances intestinal function of weaned piglets, Journal of Animal Science, Volume 97, Issue Supplement_3, December 2019, Pages 302–303, https://doi.org/10.1093/jas/skz258.611
Close - Share Icon Share
Abstract
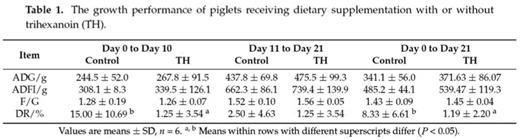
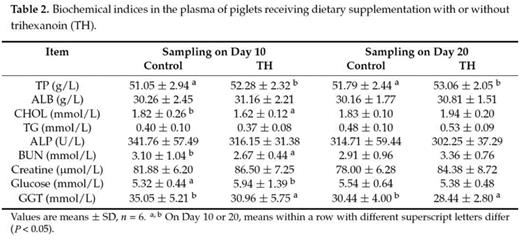
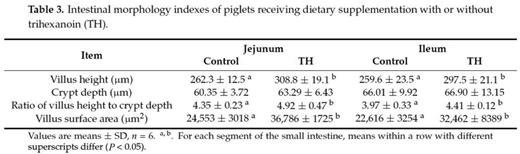
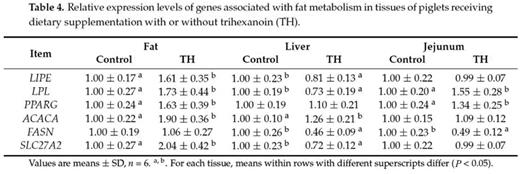
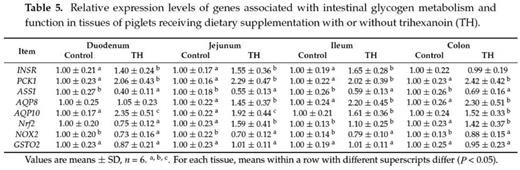
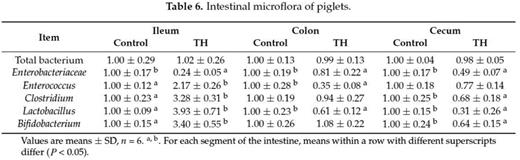
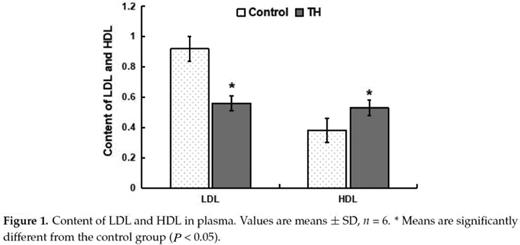
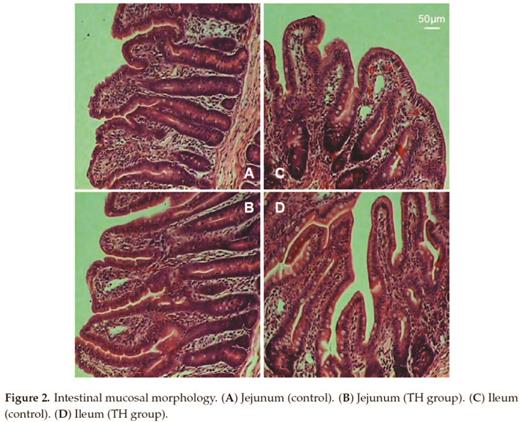
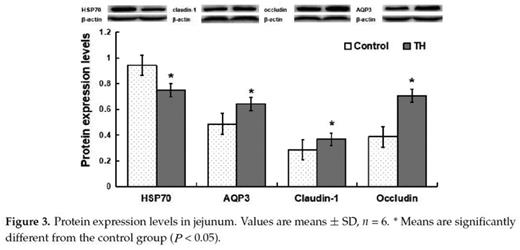
Trihexanoin is a short-chain triglyceride (SCT). Many studies have reported that SCTs play important roles in the maintenance of intestinal epithelial structure and function. The present work was to investigate the effects of trihexanoin on growth performance, carbohydrate and fat metabolism, as well as intestinal morphology and function in weaned piglets. Twenty weaned piglets (21 ± 2 d) were randomly allocated to one of two treatment groups: the control group (basal diet supplemented with 0.5% soya oil); the TH group (basal diet supplemented with 0.5% trihexanoin). Dietary trihexanoin supplementation significantly reduced diarrhea rate (P < 0.05); increased the concentrations of LDL, HDL and total protein, decreased cholesterol concentrations (CHOL) and glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT) activity in plasma (P < 0.05); increased villus height, surface area, and the ratio of villus height to crypt depth (P < 0.05); altered the mRNA levels and abundances of proteins related to glycogen and fat metabolism (gene LIPE, LPL, PPARG, ACACA, FASN, SLC27A2, INSR, PCK1 and ASS1), mucosal barrier function (protein claudin-1, and occludin), antioxidant capacity (protein HSP70 and gene Nrf2, NOX2 and GSTO2) and water transport capacity (protein AQP3 and gene AQP8 and AQP10) (P < 0.05); altered the gene abundance of intestinal bacteria (Enterobacteriaceae, Enterococcus, Clostridium, Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium) (P < 0.05). In conclusion, dietary supplementation of trihexanoin improved the intestinal function and health of weaned piglets by regulating nutrient metabolism, improving intestinal function of mucosal barrier, transport, absorption and antioxidant, and altering the community of microbiota.