-
Views
-
Cite
Cite
Norihisa Yasui, Kazuaki Nakamura, Atsuko Yamashita, A sweet protein monellin as a non-antibody scaffold for synthetic binding proteins, The Journal of Biochemistry, Volume 169, Issue 5, May 2021, Pages 585–599, https://doi.org/10.1093/jb/mvaa147
Close - Share Icon Share
Abstract
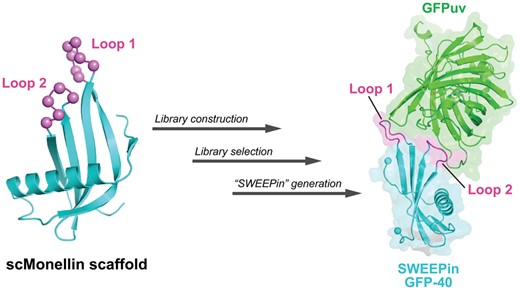
Synthetic binding proteins that have the ability to bind with molecules can be generated using various protein domains as non-antibody scaffolds. These designer proteins have been used widely in research studies, as their properties overcome the disadvantages of using antibodies. Here, we describe the first application of a phage display to generate synthetic binding proteins using a sweet protein, monellin, as a non-antibody scaffold. Single-chain monellin (scMonellin), in which two polypeptide chains of natural monellin are connected by a short linker, has two loops on one side of the molecule. We constructed phage display libraries of scMonellin, in which the amino acid sequence of the two loops is diversified. To validate the performance of these libraries, we sorted them against the folding mutant of the green fluorescent protein variant (GFPuv) and yeast small ubiquitin-related modifier. We successfully obtained scMonellin variants exhibiting moderate but significant affinities for these target proteins. Crystal structures of one of the GFPuv-binding variants in complex with GFPuv revealed that the two diversified loops were involved in target recognition. scMonellin, therefore, represents a promising non-antibody scaffold in the design and generation of synthetic binding proteins. We termed the scMonellin-derived synthetic binding proteins ‘SWEEPins’.