-
Views
-
Cite
Cite
Islam M D Alrazi, Tomisin H Ogunwa, Ayodele O Kolawole, Olusola O Elekofehinti, Olaposi I Omotuyi, Takayuki Miyanishi, Shinsaku Maruta, Kolaflavanone, a biflavonoid derived from medicinal plant Garcinia, is an inhibitor of mitotic kinesin Eg5, The Journal of Biochemistry, Volume 170, Issue 5, November 2021, Pages 611–622, https://doi.org/10.1093/jb/mvab083
Close - Share Icon Share
Abstract
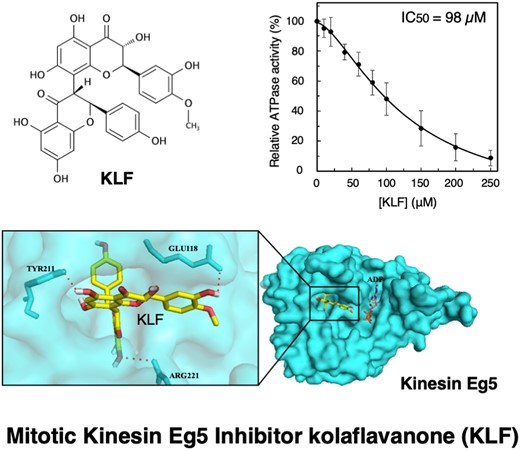
Mitotic kinesin Eg5 remains a validated target in antimitotic therapy because of its essential role in the formation and maintenance of bipolar mitotic spindles. Although numerous Eg5 inhibitors of synthetic origin are known, only a few inhibitors derived from natural products have been reported. In our study, we focused on identifying novel Eg5 inhibitors from medicinal plants, particularly Garcinia species. Herein, we report the inhibitory effect of kolaflavanone (KLF), a Garcinia biflavonoid, on the ATPase and microtubule-gliding activities of mitotic kinesin Eg5. Additionally, we showed the interaction mechanism between Eg5 and KLF via in vitro and in silico analyses. The results revealed that KLF inhibited both the basal and microtubule-activated ATPase activities of Eg5. The inhibitory mechanism is allosteric, without a direct competition with adenosine-5′-diphosphate for the nucleotide-binding site. KLF also suppressed the microtubule gliding of Eg5 in vitro. The Eg5–KLF model obtained from molecular docking showed that the biflavonoid exists within the α2/α3/L5 (α2: Lys111–Glu116 and Ile135–Asp149, α3: Asn206–Thr226; L5: Gly117–Gly134) pocket, with a binding pose comparable to known Eg5 inhibitors. Overall, our data suggest that KLF is a novel allosteric inhibitor of mitotic kinesin Eg5.