-
PDF
- Split View
-
Views
-
Cite
Cite
Keith A Crandall, Sammy De Grave, An updated classification of the freshwater crayfishes (Decapoda: Astacidea) of the world, with a complete species list, Journal of Crustacean Biology, Volume 37, Issue 5, September 2017, Pages 615–653, https://doi.org/10.1093/jcbiol/rux070
Close - Share Icon Share
Abstract
The freshwater crayfishes are a group of decapod crustaceans that have played a critical role in a diversity of biological studies, from physiology, to ecology, neurobiology, conservation, and evolution. Central to many of these fields of study is the dependence on a robust taxonomic framework for accurate communication relating to species diversity and associated attributes. Despite a huge body of taxonomic work since Linnaeus, there has never been a single, comprehensive taxonomic summary of all the species of crayfish of the world. There has also been an abundance of recent taxonomic work in terms of new species descriptions and taxonomic insights gained from a variety of phylogenetic studies. Here we gather diverse taxonomic and phylogenetic information into a single resource. We develop an updated classification system that includes all the crayfishes worldwide and taxonomic changes to better reflect the current phylogenetic knowledge of the group. We also include all the fossil crayfish taxa for a complete classification of extant and extinct crayfishes. Our classification results in two superfamilies (Astacoidea and Parastacoidea), five families, 38 genera, and 669 species (692 including distinct subspecies). We provide a checklist of all species and include validated taxonomic authorities, type localities, figure references, and synonyms. We also provide arguments for our revised classification. The updated and complete classification aims to provide a robust framework for future studies of the freshwater crayfishes of the world.
INTRODUCTION
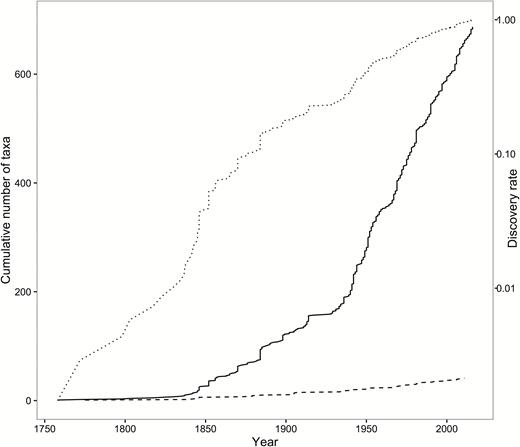
The freshwater crayfishes are a diverse group of decapod crustaceans that have played a central role in biology for over 130 years since being proposed as a model organism (Huxley, 1880). They have served as model organisms in vision research (Wald, 1967), physiology (Furshpan & Potter, 1959; Douglass et al., 1993; McMahon, 2001) and ecology (Stein, 1977). Crayfishes are keystone species in stream communities (Creed, 1994; Momot, 1995; Parkyn et al., 1997) and flagship species for conservation efforts in highly endangered freshwater habitats (Richman et al., 2015). All these research efforts, however, rely on a robust taxonomic underpinning for appropriate comparisons and inferences. There is unfortunately not a single, recent taxonomic summary of the freshwater crayfishes of the world. The closest summary is a checklist of American crayfishes (Hobbs, 1989). While an exceptional resource for those working in the Americas, this checklist is limited geographically and taxonomically to a subset (albeit a large one) of the world’s crayfish diversity. Furthermore, the crayfish taxonomic community has been very active with a large number of species described since 1989 (Fig. 1). A number of important and helpful regional assessments have been published more recently (e.g., Pflieger, 1996; Taylor & Schuster, 2004; Souty-Grosset et al., 2006). While these resources are extremely valuable for local and regional insights into the diversity of crayfishes, there is no single comprehensive resource that brings together all the taxonomic information of the world crayfishes. This is no doubt due to a number of outstanding taxonomic issues and confusions that have developed because of competing taxonomies and updated understanding of evolutionary relationships among the freshwater crayfishes illuminated by a number of recent phylogenetic studies on various groups.
Cumulative number of genera (dashed) and species (solid) described for the freshwater crayfish by year and their discovery rate (dotted) expressed as a fraction of those known to date on a logarithmic scale sensuDe Grave (2003).
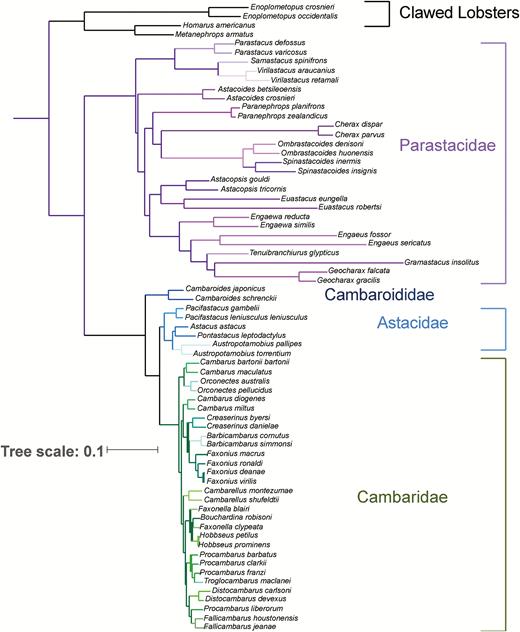
Phylogenetic estimate of the freshwater crayfishes based on a subset of data from Stern et al. (2017). Family clades of freshwater crayfish are shown in distinct colors with lobster outgroups shown in black.
While many new species have been described in recent years and regional faunal lists have been published, the backbone taxonomy has remained relatively unchanged with four notable exceptions. First is the discovery of much hidden diversity in Tasmania resulting in the description of two new genera and the synonymization of another (Hansen & Richardson, 2006). Second was the revision of East European and Asian taxa by Starobogatov (1996), which was not well received and has been variously integrated (more often not) into regional taxonomies. Third was the discovery of a new fossil family from China (Taylor et al., 1999) and new fossil genera from British Columbia (Feldmann et al., 2011), Argentina (Aguirre-Urreta, 1992), and Australia (Martin et al., 2008). Two subgenera have been mentioned in the literature within the genus Cherax, namely Astaconephrops and Cherax. Because these subgenera have not been consistently used, we follow Davie (2002) and Ahyong (2014), supported by the recent phylogenetic analysis of Bláha et al. (2016), in not recognizing subgenera within the genus Cherax. Finally, CambaroidesFaxon, 1884 has been recently placed phylogenetically outside Astacidae Latreille, 1802 and Cambaridae Hobbs, 1942a on both morphological (Rode & Babcock, 2003; Kawai et al., 2013) and molecular phylogenetic (Crandall et al., 2000; Ahn et al., 2006; Braband et al., 2006; Bracken-Grissom et al., 2014) grounds. We therefore take this opportunity to raise an earlier subfamily rank name for this genus, but to family level. The remaining higher-level crayfish taxonomy has been reasonably stable over the last 50 years through the exceptional efforts of Horton H. Hobbs, Jr. (e.g., Hobbs, 1942a; 1972a, b; 1974a, b; 1981; 1989). Here we attempt to integrate, update, and revise crayfish taxonomy with insights gained through systematic and taxonomic studies. We identify a number of areas of controversy and justify our conclusions in the sections below before presenting the first comprehensive taxonomic summary for the freshwater crayfishes. Additionally, we integrate these results into the IUCN RedList (IUCN, 2016) and in the World Register of Marine Species (WoRMS, 2017) taxonomic database through the Freshwater Animal Diversity Assessment (FADA) Project (Lévêque et al., 2005).
SUMMARY OF TAXONOMY
The classification of the freshwater crayfish presented herein consists of five families and 38 genera. We outline our classification, including the two superfamilies (Northern and Southern hemispheres divisions). We also summarize the genera and numbers of extant species, additional subspecies, and fossil species within each genus. “AstacusFabricius, 1775 (3 + 2, 3††)” indicates that this genus contains 3 extant species with 2 subspecies additional to the nominotypical ones and an additional three fossil taxa. Only a single number is given if no subspecies are currently recognized; “†” refers to a species known from both fossil and extant material, whereas a “††” refers to species known only from fossil material. The summary hopes to orient the reader to both the phylogeny discussion as well as the overall checklist.
Infraorder Astacidea Latreille, 1802
Superfamily Astacoidea Latreille, 1802
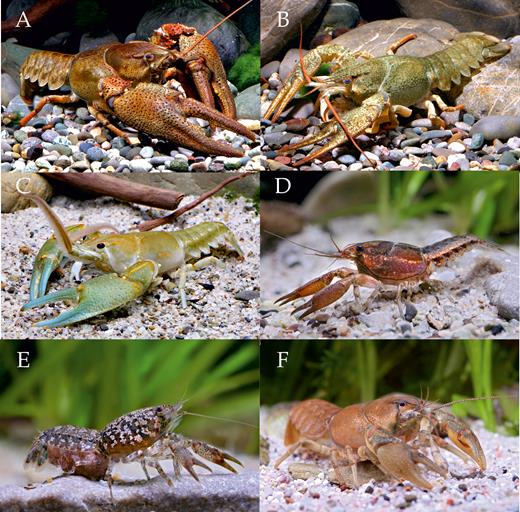
Family AstacidaeLatreille, 1802 (see Fig. 3A–B for examples)
Representatives of Astacidae: (A) Astacus astacus astacus (Linnaeus, 1758); (B) Pontastacus leptodactylus (Eschscholtz, 1823), Cambaridae: (C) Barbicambarus cornutus (Faxon, 1884); (D) Bouchardina robisoniHobbs, 1977a; (E) Cambarellus (Pandicambarus) puerHobbs, 1945; and Cambaroididae: (F) Cambaroides similis (Koelbel, 1892) (all photos by C. Lukhaup).
AstacusFabricius, 1775 (3 + 2, 3††)
AustropotamobiusSkorikov, 1907 (3 + 3, 1†)
PacifastacusBott, 1950 (5, 1††)
PontastacusBott, 1950 (9 + 1)
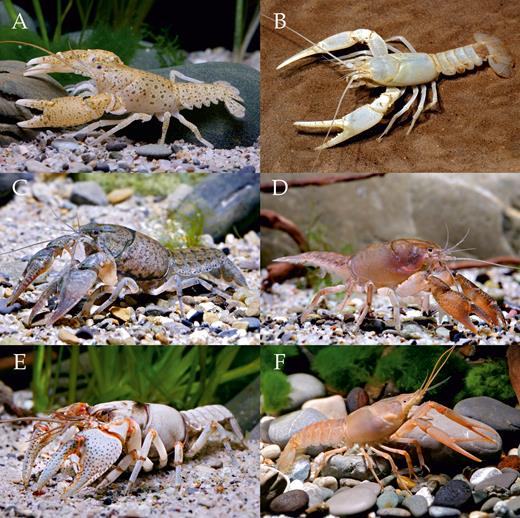
Family CambaridaeHobbs, 1942a (see Fig. 3C–E, Fig. 4A–F for examples)
Representatives of Cambaridae: (A) Cambarus maculatusHobbs & Pflieger, 1988; (B) Cambarus subterraneusHobbs, 1993; (C) Creaserinus fodiens (Cottle, 1863); (D) Distocambarus (Fitzcambarus) youngineriHobbs & Carlson, 1985; (E) Fallicambarus devastatorHobbs & Whiteman, 1987; (F) Procambarus niveusHobbs & Villalobos, 1964 (all photos by C. Lukhaup).
BarbicambarusHobbs, 1969a (2)
BouchardinaHobbs, 1977a (1)
CambarellusOrtmann, 1905a
Cambarellus (Cambarellus) Ortmann, 1905a (10)
Cambarellus (Pandicambarus) Fitzpatrick, 1983 (9)
CambarusErichson, 1846 (118 + 1)
CreaserinusHobbs, 1973a (9)
DistocambarusHobbs, 1981
Distocambarus (Distocambarus) Hobbs, 1981 (2)
Distocambarus (Fitzcambarus) Hobbs, 1983 (3)
FallicambarusHobbs, 1969a (12)
FaxonellaCreaser, 1933 (4)
FaxoniusOrtmann, 1905a (88 + 11)
HobbseusFitzpatrick & Payne, 1968 (7)
OrconectesCope, 1872 (7 + 1)
PalaeocambarusTaylor, Schram & Shen, 1999 (1††)
ProcambarusOrtmann, 1905b (167 + 6)
TroglocambarusHobbs, 1942a (1)
Family CambaroididaeVillalobos, 1955 (see Fig. 3F)
CambaroidesFaxon, 1884 (6)
Family CricoidoscelosidaeTaylor, Schram & Shen, 1999
CricoidoscelosusTaylor, Schram & Shen, 1999 (1††)
Superfamily Parastacoidea Huxley, 1879
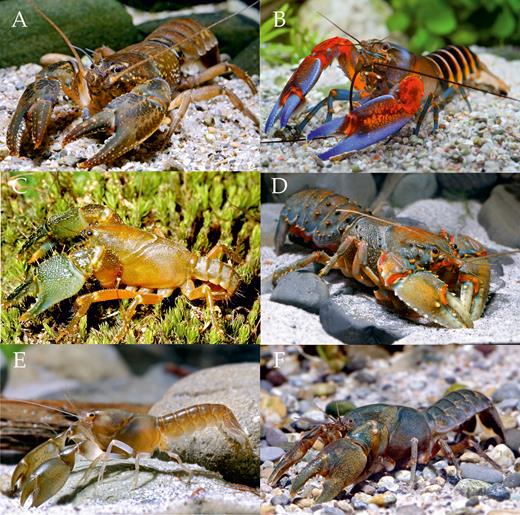
Family ParastacidaeHuxley, 1879 (see Fig. 5A–F for examples)
Representatives of Parastacidae: (A) Astacoides madagascarensis (H. Milne Edwards & Audouin, 1839); (B) Cherax peknyiLukhaup & Herbert, 2008; (C) Engaeus sp.; (D) Euastacus claytoniRiek, 1969; (E) Tenuibranchiurus glypticusRiek, 1951; (F) Virilastacus rucapihuelensisRudolph & Crandall, 2005 (all photos by C. Lukhaup).
AenigmastacusFeldmann, Schweitzer & Leahy, 2011 (1††)
AstacoidesGuérin-Méneville, 1839 (7)
AstacopsisHuxley, 1879 (2, 1†)
CheraxErichson, 1846 (52 + 3)
EngaeusErichson, 1846 (35)
EngaewaRiek, 1967a (5)
EuastacusClark, 1936 (53)
GeocharaxClark, 1936 (2)
GramastacusRiek, 1972 (2)
LammuastacusAguirre-Urreta, 1992 (1††)
OmbrastacoidesHansen & Richardson, 2006 (11)
PalaeoechinastacusMartin, Rich, Poore, Schultz, Austin, Kool & Vickers-Rich, 2008 (1††)
ParanephropsWhite, 1842 (2, 1††)
ParastacusHuxley, 1879 (11 + 1)
SamastacusRiek, 1971 (1)
SpinastacoidesHansen & Richardson, 2006 (3)
TenuibranchiurusRiek, 1951 (1)
VirilastacusHobbs, 1991a (4)
PHYLOGENY
Recent advances in morphological and molecular phylogenetic studies have impacted fundamentally our understanding of the evolutionary relationships among the species of freshwater crayfishes and their relationship to lobsters. Molecular (Crandall et al., 2000) and morphological (Scholtz & Richter, 1995) work supports the notion of the freshwater crayfishes as a monophyletic group. While Scholtz & Richter (1995) argued for Thalassinida to be more closely allied with the freshwater crayfishes than the clawed lobsters (homarids), recent work has clearly demonstrated the sister relationship between the clawed lobsters (Nephropidae and Enoplometopidae) and freshwater crayfishes with the divergence between freshwater and marine groups occurring approximately 330 mya (Bracken-Grissom et al., 2014). While freshwater crayfishes are clearly established as a monophyletic group, the monophyly of the families was questioned because the genus Cambaroides clusters consistently as a basal group to the family Astacidae (Bracken-Grissom et al., 2014) or basal to both the astacids and cambarids (Fig. 2) instead of within Cambaridae where it has been traditionally placed. Nevertheless, the Northern (Astacidae and Cambaridae) and Southern (Parastacidae) hemispheres families form reciprocally monophyletic clades with deep divergence (approximately 265 mya) (Bracken-Grissom et al., 2014). The divergence times across the Southern Hemisphere taxa are deep and the genera form monophyletic groups (Toon et al., 2010). On the other hand, multiple studies question the monophyly of many Northern Hemisphere genera and subgenera, especially in Orconectes (Crandall & Fitzpatrick, 1996; Fetzner, 1996), Cambarus (Breinholt et al., 2012), and Fallicambarus (Ainscough et al., 2013). Various studies have also made insights about the species status of individual taxa. All of these studies have made necessary suggestions for adjustments to taxonomy based on the results of the research. Here we strive to make these classification changes formal and detail the proposed changes and our justifications below.
FAMILY ADJUSTMENTS
The placement of Cambaroides has been the topic of discussion for a long time. The group was recognized as distinctive by Faxon (1884), who established Cambaroides as a subgenus within Astacus. The name was then raised to generic status and placed within its own subfamily (Cambaroidinae) within the family Astacidae by Villalobos (1955). The subfamily was subsequently transferred to Cambaridae by Hobbs (1974a). Phylogenetic studies had a similar difficulty in placing this genus, demonstrating that the inclusion of Cambaroides in either Cambaridae or Astacidae made those groups non-monophyletic, based on both molecular (Crandall et al., 2000) and morphological (Rode & Babcock, 2003) grounds. These studies also showed a closer affinity of Cambaroides to astacids rather than to cambarids. These early phylogenetic studies were nevertheless limited in their sampling of species from within Cambaroides. Two subsequent studies provided evidence with much more extensive sampling within Cambaroides for the monophyly of the group and basal and sister relationship to both Astacidae and Cambaridae (Ahn et al., 2006; Braband et al., 2006). Our phylogenetic estimate based on more extensive genetic sampling (three mitochondrial and three nuclear genes; Fig. 2) shows the genus to be basal and sister to both the astacids and cambarids, justifying the recognition of a further family for this genus and its six constituent species (Stern et al., 2017). We, therefore, elevate herein the subfamily Cambaroidinae Villalobos, 1955 to family level solely for the genus Cambaroides to recognize the phylogenetic, morphological, and geographical distinctiveness of this genus and to avoid paraphyly within the Astacidae and/or Cambaridae.
WESTERN PALEARCTIC CRAYFISHES
The species of western Palearctic crayfishes are in need of a comprehensive overhaul that takes advantage of recent molecular tools to diagnose species boundaries and establish relationships among populations and species. While there are many population genetic studies of particular species (e.g., Fratini et al., 2005; Cataudella et al., 2010), these studies have been focused regionally, for the most part, with the aim of aiding local and regional conservation issues and are not taxonomically focused as needed for taxonomic updates (as outlined in Manganelli et al., 2006). As a result, such studies are often missing important populations and taxa that might allow for a more comprehensive overview of the species within Astacus, Austropotamobius, and Pontastacus. Some more comprehensive studies have been attempted (e.g., Schrimpf et al., 2011), but still with limited sampling, especially in Eastern Europe and further east. Lacking data to the contrary, we follow the recommendation of Smietana et al. (2006) by recognizing the three genera supported by Brodsky (1983), including the somewhat controversial Pontastacus. As pointed out by Smietana et al. (2006), much more extensive work needs to be done on the Eastern European species before a reasonable picture of the western Palearctic fauna can be achieved. Similarly, we also largely adhere to the classification outlined in Starobogatov (1996), which has been somewhat conveniently overlooked by the majority of workers rather than rigorously tested. We nevertheless follow Smietana et al. (2006) and not Starobogatov (1996) in only recognizing three genera and follow the nomenclature outlined in Manganelli et al. (2006) for some taxa. We agree with the argument put forward by Manganelli et al. (2006) that the oldest available name for the Italian white-clawed crayfish is indeed Astacus pallipes var. FulcisianaNinni, 1886, which thus takes priority over Astacus pallipes italicusFaxon, 1914 (ICZN, 1999). As such, we list this taxon under the name Austropotamobius fulcisianus fulcisianus (Ninni, 1886).
NORTH AMERICAN GENERA AND SUBGENERA
We have revised the classification of the North American taxa, especially at both generic and subgeneric levels, based on recent phylogenetic results. For Cambarus, Orconectes, and Procambarus, we eliminate the subgeneric classifications. These classifications have been shown to have no phylogenetic validity in Cambarus (Breinholt et al., 2012) and Orconectes (Crandall & Fitzpatrick, 1996; Fetzner, 1996; Taylor & Knouft, 2006), and our preliminary data suggest the same is true for Procambarus. While we appreciate the desire to have these genera with large numbers of species divided into smaller, more digestible groupings, these assignments have not been based on cladistic characters (Fitzpatrick, 1987a) and do not support monophyletic groups. It is therefore difficult at times even to place new species in the appropriate subgenus. Cambarellus, however, has two subgenera that are reciprocally monophyletic (Cambarellus and Pandicambarus) (Pedraza-Lara et al., 2012) and we, therefore, retain these taxa. The subgenus Dirigicambarus nested within Pandicambarus in the analysis of Pedraza-Lara et al. (2012) and we therefore consider these species to be contained within this latter subgenus and eliminate the former subgenus. We also do not recognize the subfamily Cambarinae as a further distinction for this genus, as it seems unwarranted, especially without a reciprocal sister group.
Fallicambarus, on the other hand, has traditionally been divided into two subgenera (Fallicambarus and Creaserinus). While these two subgenera form monophyletic groups, each is more closely related to other genera than to each other (Ainscough et al., 2013), with the subgenus Fallicambarus more allied with members of Procambarus and the subgenus Creaserinus more closely allied with species of Faxonius (see below). We thus elevate the subgenus Creaserinus to full generic rank and retain the contained species. Similarly, the representatives of Orconectes form at least two distinct groups. The nominal group (the “cave Orconectes”) form a monophyletic group that is more closely related to members of Cambarus, while the remaining “Orconectes” are more closely related to Barbicambarus, Creaserinus, and other species of Cambarus (Crandall & Fitzpatrick, 1996; Fetzner, 1996). As the type species of Orconectes, Orconectes inermisCope, 1872, belongs to the cave-dwelling group, the genus is herein restricted to just those taxa. The surface-dwelling taxa now excluded from Orconectes sensu stricto are herein placed in the resurrected genus FaxoniusOrtmann, 1905a, the oldest available name previously considered to be a synonym of OrconectesCope, 1872.
At the species level, a few studies have suggested new generic allocations for certain species, including Cambarus pecki (Hobbs, 1967a) (not Procambarus (see Buhay & Crandall, 2009)), Fallicambarus tenuis (Hobbs, 1950a) (not Procambarus (see Ainscough et al., 2013)), and the synonymy of Procambarus ferrugineusHobbs & Robison, 1988 with Procambarus liberorumFitzpatrick, 1978a based on phylogenetic inferences (Crandall et al., 2009).
Some genera, such as Procambarus and Cambarus, are clearly still not monophyletic groups (Fig. 2). We nevertheless refrain from making further taxonomic changes until we achieve a more comprehensive sampling of species within such groups. Similarly, some relationships, such as the placement of the Australasian genus Cherax, are different compared to previous phylogenetic studies (Toon et al., 2010). There still remain a number of poorly-supported nodes in the overall phylogeny and we have attempted to make taxonomic revisions based only on the more well-supported aspects of the phylogeny. Phylogenetic studies seem to suggest that clades are more geographically than taxonomically affiliated. The present list provides a significant but first step in achieving a comprehensive phylogenetically based taxonomy of the freshwater crayfishes by making taxonomic changes suggested throughout the last twenty years of phylogenetic studies and bringing all information into a single resource.
LIST OF THE SPECIES OF FRESHWATER CRAYFISHES OF THE WORLD
For each of the herein recognized crayfish families (both extant and fossil), we list the currently recognized genera, species, and subspecies. For each genus, we provide a reference to the original description, their type species and method of designation, as well as their gender to facilitate future work. All known synonyms are also listed. For species and subspecies, we list their current bi/trinomen, original name combination (if different), as well as currently accepted synonyms. For each, we list the page number on which the original description starts, a reference to all figures or plates on which the original illustrations appear, and type locality information. As is traditional, we distinguish different species described by the same author(s) in the same year but in different publications by a letter following the year of publication, following the order in which they appear in the text, for example, Bouchardina robisoniHobbs, 1977a and Procambarus strenthiHobbs, 1977b. For type localities, we list the original information in the type description in quotation marks, with additional information and translations in brackets to distinguish it from the original description, as in “Cancer astacusLinnaeus, 1758: 631 (“Europae lacubus, fluviis” [= European lakes and rivers]).” The listing of type locality generally follows the rules laid down by De Grave & Fransen (2011) in their catalogue of shrimp names. Many of the early North American crayfish descriptions, like those by C. Girard and W. Faxon, however, had no circumscribed type localities, as often large, syntypic series were involved in the descriptions. W. Faxon, A. Ortmann, and especially H. H. Hobbs Jr. restricted many of these to more circumscribed localities, but often without the designation of lectotypes, all of which are listed in Hobbs (1974b, 1989). To avoid unnecessary confusion, we follow these traditional designations, but have clearly marked them as such. We have refrained from guessing in which country some type localities are located, reflecting the originally stated inaccuracy, for example “Potamobius pylzowiSkorikov, 1907: 117 (“oriental part of Zakavkazie” [= eastern part of Transcaucausia]), which spans several eastern European and western Asian countries. We also left, out of necessity, some older type localities simply as stated in the original descriptions. Lectotype and neotype designations are highlighted (when known), as well as additional comments when necessary, primarily those relating to ICZN rules.
We highlight fossil taxa with a dagger (†) following the convention of De Grave et al. (2009), with a single dagger meaning the species is known from both fossil and extant material, while a double dagger signifies a fully fossil taxon. For clarity, nomina dubia, nomina nuda, as well as unavailable names are included in the synonymies of species when known or discernible; the remainder are listed at the end of the compilation.
The cut-off date for inclusion of names was set at 11 June 2017, although we are very much aware that the description of several species are in press and the present compilation will be outdated as soon as it appears in print. The data will nevertheless be migrated to the WoRMS platform (www.marinespecies.org) on publication, where we will endeavor to keep the list current.
Ng (1994) laid down the foundation of author citation in decapod literature, which since has been followed in all major compilations of decapod higher level taxonomy (De Grave et al., 2009), brachyuran crabs (Ng et al., 2008), anomurans (Baba et al., 2008; McLaughlin et al., 2010a; 2010b), lobsters (Chan, 2010), and shrimps (De Grave & Fransen, 2011). This follows a strict interpretation of Article 50 (ICZN, 1999) in that merely citing an author’s name after a new species name does not make it explicit enough that the description is solely by that/those person(s). Rather, it requires either a specific statement to that effect, or as is common in older literature, a clear line of evidence that parts of the article were written by, and can thus be formally attributed to a person(s) other than the author(s) of the article. For example, we attribute Cambarus setosus to Faxon & Garman in Garman, 1889, rather than just Faxon alone, as listed in Hobbs (1974b). This problem is not restricted to older literature as often thought, with for example, Ribeiro, Buckup, Gomes & Araujo (2016) describing “Parastacus fluviatilis Ribeiro & Buckup sp. nov.” and “Parastacus caeruleodactylus Ribeiro & Araujo sp. nov.” By following Ng (1994), the citation of these names becomes far less cumbersome, for example P. fluviatilisRibeiro, Buckup, Gomes & Araujo (2016) rather than P. fluviatilis Ribeiro & Buckup in Ribeiro, Buckup, Gomes & Araujo (2016). We accept that this is not how Article 50 is uniformly interpreted across the zoological community and others may disagree. Because all other compilations in the taxonomy of decapods have followed this format, it seems logical to employ the same rule to bring the crayfish taxonomic literature in line with the prevailing viewpoint in decapod nomenclature. Various other conventions on spelling of authors and the argument that authors are “nomina” instead of “persona” (see Dubois, 2008) are as followed in Ng et al. (2008) and De Grave & Fransen (2011). We use, for example, Austropotamobius torrentium torrentium (von Paula Schrank, 1803), rather than only “(Schrank, 1803)” as used in previous compilations (e.g., Hobbs, 1974a). For the relative priority and publication dates of some names published by H.H. Hobbs Jr., we follow Reed & Manning (1998), whilst publication dates for other publications were verified and if necessary adjusted from a variety of sources. For example, the revision of Starobogatov was actually published on the 25 January 1996, rather than in 1995, according to the website of the journal, Arthropoda Selecta.
SYSTEMATICS FRESHWATER CRAYFISHES OF THE WORLD
Superfamily Astacoidea †Latreille, 1802
Family Astacidae †Latreille, 1802
= Astacini Latreille, 1802: 32 [invalid original spelling, corrected by Samouelle, 1819 to Astacidae, see Anonymous, 1955].
= Potamobiidae Huxley, 1879: 776.
= Pacifastacinae Starobogatov, 1996: 9.
Astacus †Fabricius, 1775
= AstacusFabricius, 1775: 413 [type species Cancer AstacusLinnaeus, 1758, designated in Direction 12, see Anonymous, 1955; gender masculine].
= PotamobiusSamouelle, 1819: 95 [type species Cancer AstacusLinnaeus, 1758, by monotypy; gender masculine].
= CarabisMarchand, Lamy & de Boisvillette, 1874: 55 [type species Cancer AstacusLinnaeus, 1758, by monotypy; gender masculine].
Astacus astacus astacus (Linnaeus, 1758)
= Cancer astacusLinnaeus, 1758: 631 (“Europae lacubus, fluviis” [= European lakes and rivers]).
= Astacus fluviatilisFabricius, 1775: 413 (“Europae lacubus, fluviis” [= European lakes and rivers]).
= Cancer nobilisvon Paula Schrank, 1803: 246 (“Boica” [= Bavaria, Germany]).
= Astacus fluviatilis communis Gerstfeldt, 1859: 554 [no type locality indicated].
Astacus astacus canadziaeStarobogatov, 1996: 14 (validation under Art. 10.2 (ICZN, 1999) of the unavailable name Astacus (Astacus) astacus natio čanadžiaeKaraman, 1963).
= Astacus astacus chanadzhiaeStarobogatov, 1996: 14 (unjustified emendation for Astacus astacus canadziaeStarobogatov, 1996; herein corrected under Art. 33.2.2 (ICZN, 1999)).
= Astacus (Astacus) astacus natio čanadžiaeKaraman, 1963: 116 (“Zuflüssen der Donau in Croatien, wahrscheinlich auch in Serbien und Rumänien verbreitet” [= tributaries of the Danube in Croatia, probably also distributed in Serbia and Romania]; not an available name under Art. 1.3.4 and 45.6.3 (ICZN, 1999)).
= Astacus (Astacus) astacus natio pretzmanniKaraman, 1963: 115 (“oberen Teil des Donausystems, einschliesslich der Drau” [= upper parts of the Danube Basin, including the Drava River]; not an available name under Art. 1.3.4 and 45.6.3 (ICZN, 1999)).
Astacus balcanicus balcanicus (Karaman, 1929)
= Potamobius fluviatilis balcanicusKaraman, 1929: 147, fig. 2 (“Vardar; Ohridsee” [= Vardar Basin and Lake Ohrid, Republic of Macedonia]).
Astacus balcanicus graecusStarobogatov, 1996: 14 (validation under Art. 10.2 (ICZN, 1999) of the unavailable name Astacus (Astacus) balcanicus natio graecaKaraman, 1963).
= Astacus (Astacus) balcanicus natio graecaKaraman, 1963: 117 [(“Janinasee, Griechenland” [= Lake Ioannina, Greece]; not an available name under Art. 1.3.4 and 45.6.3 (ICZN, 1999)].
Astacus colchicusKessler, 1876
= Astacus colchicusKessler, 1876: 2 (“Stromgebiete des Rion” [= Rioni River Basin, Georgia]).
Astacus edwardsii †† Van Straelen, 1928a: 4; pl. 1 (“Sézanne (Champagne)” [France]).
= Astacus Edwardsi Munier-Chalmas in Vélain, 1889: 870 [nomen nudum]
Astacus laevissimus †† Fritsch & Kafka, 1887: 49; pl. 10, fig. 4 (“Zbyslav” [Czech Republic]).
Astacus multicavatus †† Bell, 1863: 31; pl. 9, figs. 7, 8 (“Speeton Clay” [UK]).
Austropotamobius †Skorikov, 1907
= Potamobius (Austropotamobius) Skorikov, 1907: 116 [type species Cancer torrentiumvon Paula Schrank, 1803, by subsequent designation in Bott (1950); gender masculine].
= Austropotamobius (Atlantoastacus) Bott, 1950: 21 [type species Astacus pallipesLereboullet, 1858, by original designation; gender masculine].
Austropotamobius fulcisianus fulcisianus (Ninni, 1886)
= Astacus pallipes var. FulcisianaNinni, 1886: 326 (“trovo nel Bellunese” (= Province of Belluno]).
= Astacus pallipes italicusFaxon, 1914: 361; pl. 8, fig. 2 (“River Sarno, Pompeii, Italy”).
= Astacus fluviatilis lusitanicusMateus, 1934: 33 (“ribeiro de Angueira, affluent du Sabor, près de San-Martinho, arrondisement de Miranda-do-Douro, Province de Trás-os-Montes” [= tributary of Sabor River, near São Martinho de Angueira, Miranda-do Douro, NE Portugal]).
= Austropotamobius (Atlantoastacus) berndhauseriBott, 1972: 399; fig. 5; pl. 4 (“Schweiz: Tessin; Maggia-Tal, Roggio di Gordovio” [= Switzerland: Ticoni Canton; “Roggio di Gordovio”, Valle Maggia]).
Austropotamobius fulcisianus orientalis (Karaman, 1929)
= Potamobius pallipes orientalisKaraman, 1929: 148, fig. 4 (“in der Krka und Cetina; kleinen Abflusskanal der kleinen Seen der Niederung von Knin” [= Krka River; Cetina River; Knin Valley; all in Croatia]).
= Austropotamobius italicus carsicusKaraman, 1962: 180, figs. 2, 10, 17, 28 (“Sickelflüsse von Gacko, Nachbarfelder der Herzegowina; Gewässer, die unittelbar der Meeresküste entspringen: Ljuta und Konavle bei Dubrovnik”).
= Astacus pallipes var. carinthiacaAlbrecht, 1981: 270, fig. 2 (“Gitschtal, Seitental des Gailtales bei Hermagor” [= Gitschtal, side valley of Gailtal Valley near Hermagor, Austria]; not an available name under Art. 45.6.3 (ICZN, 1999)).
= Astacus pallipes var. dalmaticinusAlbrecht, 1982: 195 [(“Dalmatien (Jugoslawien)” [= Dalmatia, Croatia]; not an available name under Art. 45.6.3 (ICZN, 1999)).
? = Astacus pallipes var. lombardicusAlbrecht, 1982: 194 (“Tessin (Schweiz); Lombardei (Italien); nach Graubünden (Schweiz)” [= Ticoni Canton and Graubünden, Switzerland; Lombardy, Italy]; not an available name under Art. 45.6.3 (ICZN, 1999)).
? = Astacus pallipes var. trentinicusAlbrecht, 1982: 195 (“Südtirol und Trentino (Italien)” [= South Tyrol and Trentino provinces, Italy]; not an available name under Art. 45.6.3 (ICZN, 1999)].
= Atlantoastacus orientalis carinthiacusStarobogatov, 1996: 12 [nomen nudum].
Austropotamobius llopisi †† (Vía, 1971)
= Pseudoastacus llopisiVía, 1971: 607, fig. 2 (“cantera de Santa María de Moyá, en el Montsec (Lérida)” [=Santa María de Moyá quarry in the Serra del Montsec, Province of Lleida, Spain]).
Austropotamobius pallipes † (Lereboullet, 1858)
= Astacus pallipesLereboullet, 1858: 7; pl. 2; pl. 3, fig. 3–3d (as Astacus flavipes) (“nombreus canaux qui entourent Strasbourg et dans les fossés des fortifications [= Strasbourg, France]).
= Astacus pallipes var. flavusLereboullet, 1858: 9 [no type locality indicated].
= Astacus fontinalisCarbonnier, 1869: 8 (“France”).
Austropotamobius torrentium danubicusStarobogatov, 1996: 11 (validation under Art. 10.2 (ICZN, 1999) of the unavailable name Austropotamobius torrentium natio danubicusKaraman, 1962).
= Austropotamobius torrentium natio danubicusKaraman, 1962: 178 (“Kroatien (Gračane, Gerovo, Kostajevica, Sošice, Janesica, Dobra, Podsused)” [all localities in Croatia]; not an available name under Art. 1.3.4 and 45.6.3 (ICZN, 1999)).
Austropotamobius torrentium macedonicusKaraman, 1929: 149 (“Treskaschlucht bei Skoplje” [= Treska ravine near Skoplje, Republic of Macedonia]).
= Potamobius torrentium dalmatinusKaraman, 1929: 150; fig. 7 (“in der Krka und Cetina” [= Krka and Cetina rivers, Croatia]).
Austropotamobius torrentium torrentium (von Paula Schrank, 1803)
= Cancer Torrentiumvon Paula Schrank, 1803: 247 (“Boica; in steinigen Bächen und Flüssen; aber auch in Seen, namentlich im Würmsee” [= stony brooks and streams in Bavaria; Lake Standberg, Germany]).
= Astacus saxatilisKoch, 1837: 1; unnumbered pl. (“kleinen Bächen der bergigen Gegenden der Oberpflalz, auch in der Donau” [= Oberpfalz district, Bavaria and Danube River, Germany]).
= Astacus tristisKoch, 1837: 2; unnumbered pl. (“kleinen Bergbach bei Bodenstein in bayerischen Regenkreise” [= small mountain streams near Bodenstein, Bavaria, Germany]).
= Astacus longicornisLereboullet, 1858: 2; pl. 1; pl. 3, fig. 2–2d (“dans L’Ill et dans la Bruche” [= Ill and Bruche rivers, Strasbourg, France]).
Pacifastacus †Bott, 1950
= PacifastacusBott, 1950: 24 [type species Astacus klamathensisStimpson, 1857, by original designation; gender masculine].
= Pacifastacus (Hobbsastacus) Bouchard, 1977: 431 [type species Astacus [sic] GambeliiGirard, 1852, by original designation; gender masculine].
Pacifastacus chenoderma †† (Cope 1871)
= Astacus chenodermaCope 1871: 606 (“upper part of Castle Creek, Owyhee County” [Idaho, USA] according to Hobbs, 1974b).
? = Astacus subgrundialisCope, 1871: 605 (“freshwater deposit in the Territory of Idaho, near Hot Springs Mountain” [USA]).
? = Astacus breviforcepsCope, 1871: 606 (“upper part of Castle Creek, Owyhee County” [Idaho, USA] according to Hobbs, 1974b).
Pacifastacus connectens (Faxon, 1914)
= Astacus gambelii connectensFaxon, 1914: 360; pl. 7, figs. 6, 10; pl. 10, fig. 1 (“Snake River at Upper Salmon Falls” [Twin Falls County, Idaho, USA]).
Pacifastacus fortis (Faxon, 1914)
= Astacus nigrescens fortisFaxon, 1914: 360; pl. 7, figs. 5, 9; pl. 9, fig. 2 (“Fall River, Fall City Mills, Shasta County, California” [USA]).
Pacifastacus gambelii (Girard, 1852)
= Cambarus GambeliiGirard, 1852: 90 (“California” [USA]).
Pacifastacus leniusculus (Dana, 1852)
= Astacus oreganusRandall, 1840: 138; pl. 7 (“Columbia River, west coast of North America”;
suppressed under the plenary powers for the purposes of the Principle of Priority but not those of the Principle of Homonymy and placed on the Official Index of Rejected and Invalid Specific Names in Zoology in Opinion 855, see Anonymous, 1968).
= Astacus leniusculusDana, 1852: 524 (“flumine Columbia, Oregoniae” [= Columbia River, Oregon, USA]; placed on the Official List of Specific Names in Zoology in Opinion 855, see Anonymous, 1968).
= Astacus KlamathensisStimpson, 1857: 87 (“Klamath Lake” [Oregon, USA]).
= Astacus TrowbridgiiStimpson, 1857: 87 (“Columbia River, above Astoria” [Oregon, USA]).
= Cambaras [sic] americanusAnonymous, 1927: unnumbered figures [nomen nudum]
Pacifastacus nigrescens (Stimpson, 1857)
= Astacus nigrescensStimpson, 1857: 87 (“vicinity of San Francisco” [California, USA]).
PontastacusBott, 1950
= Astacus (Pontastacus) Bott, 1950: 12 [type species Astacus leptodactylusEschscholtz, 1823, by original designation; gender masculine].
= CaspiastacusStarobogatov, 1996: 14 [type species Astacus pachypusRathke, 1837, by original designation; gender masculine].
Pontastacus cubanicus (Birstein & Vinogradov, 1934)
= Astacus leptodactylus cubanicusBirstein & Vinogradov, 1934: 51 (“Kuban River bassin, part of the Azov Sea, Don River south of Rostov (Rostov-na-Donu), Sal River” [translated from the original; all locations in Russia]).
Pontastacus danubialisBrodsky, 1981
= Pontastacus eichwaldi danubialisBrodsky, 1981: 165, fig. 82 (validation under Art. 10.2 (ICZN, 1999) of the unavailable name Astacus leptodactylus caspius natio danubialisBrodsky, 1967).
= Astacus leptodactylus caspius natio danubialisBrodsky, 1967: 310, fig. 2 (“Danube lakes - Kitaï, Katlabukh, Yalpukh (above Kosa village), Kugurluï, Kartal, Saf’yan, Dolgoe, and others. Introduced to lakes of Pripyat’ and Prut rivers, and in ponds of Kiev and Vinnitsa regions, and in the Donbass reservoirs” [translated from the original; all localities in Ukraine]; not an available name under Art. 1.3.4 and 45.6.3 (ICZN, 1999)].
Pontastacus daucinusBrodsky, 1981
= Pontastacus cubanicus daucinusBrodsky, 1981: 161 (proposed replacement name for the unavailable name Pontastacus leptodactylus cubanicus natio danubialisBrodsky, 1967 (nec Astacus leptodactylus caspius natio danubialisBrodsky, 1967).
= Astacus leptodactylus cubanicus natio danubialisBrodsky, 1967: 309, fig. 1 (“Kili delta of the Danube, Repida waterway and associated lakes Yalpukh (below Kosa village) and Kugurlui, delta of Prut River and Manta Lake” [translated from the original; all localities in Ukraine]; not an available name under Art. 1.3.4 and 45.6.3 (ICZN, 1999)).
Pontastacus eichwaldi bessarabicusBrodsky, 1981: 169 (validation under Art. 10.2 (ICZN, 1999) of the unavailable name Astacus leptodactylus caspius natio bessarabicusBrodsky, 1967).
= Astacus leptodactylus caspius natio bessarabicusBrodsky, 1967: 311, fig. 3 (“Dniestr and Kuchurgan limans, eastern coast of Caspian Sea (Kianla region, Krasnovodskiy Bay), introduced into Kiev’s park pond, where it is now established” [translated from the original; all localities in Ukraine]; not an available name under Art. 1.3.4 and 45.6.3 (ICZN, 1999)).
Pontastacus eichwaldi eichwaldi (Bott, 1950)
= Astacus leptodactylus var. caspiaEichwald, 1838: 148 (“Tyrae ostio”; Caspian Sea, near Lenkoran according to Faxon, 1914 [= Lankaran, Azerbaijan]).
= Astacus (Pontastacus) leptodactyus eichwaldiBott, 1950: 16 (replacement name for Astacus leptodactylus var. CaspiaEichwald, 1838 nec Astacus caspiusEichwald, 1838).
Pontastacus kessleri (Schimkewitsch, 1886)
= Astacus kessleriSchimkewitsch, 1886: 20. (“nähe der Stadt Turkestan (Süürinsky, Karatschinyskym, Kutsch-atà und Tuka-tak” [all localities in Turkestan] according to Bott,1950).
Pontastacus leptodactylus (Eschscholtz, 1823)
= Astacus leptodactylusEschscholtz, 1823: 109; pl. 18 (“aquas dulces Tauriae” [= fresh water in Crimea]).
= Astacus angulosusRathke, 1837: 74; pl. 4, fig. 3 (“in der Krym an mehreren Orten” [= several localities in Crimea]).
= Astacus leptodactylus boreoorientalisBirstein & Vinogradov, 1934: 51 (“Kama River bassin, from which it migrated via a man-made canal (made during Ivan the Terrible) to Severnaya Dvina River, reaching Vologda and Arkhangelsk. Introduced to Ob’ River bassin, reaching Tobolsk, Omsk and upper Ishim River; from here introduced to the Nura River bassin (Akmolinsk)” [translated from the original; all localities in Russia]).
= Astacus (Pontastacus) leptodactylus leptodactylus natio intermediusKaraman, 1963: 122 (“Marmara Meers, in dem Maritza-Flusssystem sowie in Klein Asia” [= Sea of Marmara, Maritsa River system and Anatolia, Turkey]; not an available name under Art. 1.3.4 and 45.6.3 (ICZN, 1999)).
= Astacus (Pontastacus) leptodactylus leptodactylus natio caeareensisPretzmann, 1973: 331 [(“Teich bei Karpuzatan bei Kayseri” [= pond in Karpuzatan near Kayseri, Turkey]; not an available name under Art. 1.3.4 and 45.6.3 (ICZN, 1999)).
Pontastacus pachypus (Rathke, 1837)
= Astacus pachypusRathke, 1837: 365 (“umgegend von Nikolajew” [= around Mykolaiv, Ukraine]).
= Astacus caspiusEichwald, 1838: 149 (“in Caspio mari, prope Bacuam” [= Caspian Sea, near Baku, Azerbaijan]).
= Astacus pachypus var. lacustrisCzerniavsky, 1884: 94 (“locus montanus Abrau, haud procul ab opp. Novorossijsk” [= mountains around Abrau-Dyurso, near Novorossiysk, Russia]).
= Pontastacus pachypus notabilisBrodsky, 1981: 177, figs. 86, 87 (“Azov-Black Sea”).
Pontastacus pylzowi (Skorikov, 1907)
= Potamobius pylzowiSkorikov, 1907: 117 (“oriental part of Zakavkazie” [= eastern part of Transcaucausia]).
Pontastacus salinus (von Nordmann, 1842)
= Astacus salinusvon Nordmann, 1842: pl. 1 (“Black Sea” according to Faxon, 1914).
= Astacus leptodactylus sartoriusBirstein & Vinogradov, 1934: 51 (“mainly W Europe, in the USSR only in the Polesie region and W Ukraine, in the Shepetovka area” [translated from the original]).
Family Cambaridae †Hobbs, 1942a
= Cambarinae Hobbs, 1942a: 338
= Cambarellinae Laguarda, 1961: 69
BarbicambarusHobbs, 1969a
= BarbicambarusHobbs, 1969a: 98 [type species Cambarus cornutusFaxon, 1884; by original designation; gender masculine].
Barbicambarus cornutus (Faxon, 1884)
= Cambarus cornutusFaxon, 1884: 120 (“Green River near the Mammoth Cave, [Edmonson County], Kentucky” [USA]).
Barbicambarus simmonsiTaylor & Schuster, 2010: 325, figs. 1, 2, 3 (“Factory Creek at Hardin Loop Road, approximately 9.5 km WNW Loretto, Lawrence County, Tennessee (35.10109°N, -87.53994°W)” [USA]).
BouchardinaHobbs, 1977a
= BouchardinaHobbs, 1977a: 734 [type species Bouchardina robisoniHobbs, 1977a, by original designation; gender feminine].
Bouchardina robisoniHobbs, 1977a: 734, fig. 1 (“backwaters of Bayou Bodcaw (Red River Basin) in borrow ditch along Sunray Road, 4 miles (6.4 km) north of Lewisville, off State Route 29, Sec. 14, R. 24W, T. 15S, Lafayette County, Arkansas” [USA]).
CambarellusOrtmann, 1905a
Cambarellus (Cambarellus) Ortmann, 1905a
= CambarellusOrtmann, 1905a: 97 [type species Cambarus Montezumae de Saussure, 1867, by original designation; gender masculine].
Cambarellus (Cambarellus) alvareziVillalobos, 1952
= Cambarellus alvareziVillalobos, 1952: 525; pl. 1, 2 (“Potosí, Nuevo León, 23 km NO Galeana, parte norte del Valle Salado” [Mexico]).
Cambarellus (Cambarellus) areolatus (Faxon, 1885a)
= Cambarus Montezumae var. areolataFaxon, 1885a: 123 (“near Parras, Coahuila state, Mexico”).
Cambarellus (Cambarellus) chapalanus (Faxon, 1898)
= Cambarus chapalanusFaxon, 1898: 661; pl. 67, figs. 1, 2 (“Lake Chapala, State of Jalisco, Mexico”).
Cambarellus (Cambarellus) chihuahuaeHobbs, 1980
= Cambarellus chihuahuaeHobbs, 1980: 194, fig. 1 (“Ojo de Carbonera, 4.3 km south of Ejido Rancho Nuevo, approximately 36 airline km west of Villa Ahumada (106°51ʹ, 30°35ʹN), Chihuahua, Mexico”).
Cambarellus (Cambarellus) montezumae (de Saussure, 1857a)
= Cambarus Montezumaede Saussure, 1857a: 102 (“vallée de Mexico” (= Valley of Mexico).
= Cambarus Montezumae var. tridensvon Martens, 1872: 130 (“Puebla” [Mexico]).
= Cambarus montezumae dugesiiFaxon, 1898: 660; pl. 66, fig. 1 (“State of Guanajuato, Mexico”).
= Cambarellus montezumae forma lermensisVillalobos, 1943: 603; pl. 2, figs. 3, 5, 8, 11, 18, 20 (“Lerma, Estado de Mexico, Mexico” according to Hobbs, 1989).
Cambarellus (Cambarellus) occidentalis (Faxon, 1898)
= Cambarus montezumae occidentalisFaxon, 1898: 661; pl. 66, figs. 3, 4 (“Mazatlan, Mexico”).
Cambarellus (Cambarellus) patzcuarensisVillalobos, 1943
= Cambarellus montezumae patzcuarensisVillalobos, 1943: 607; pl. 2, figs. 1, 6, 9, 10, 12, 15, 19, 21, 23 (“Lago de Patzcuaro, State of Michoacán, Mexico” according to Hobbs, 1989).
Cambarellus (Cambarellus) prolixusVillalobos Figueroa & Hobbs, 1981
= Cambarellus (Cambarellus) prolixusVillalobos Figueroa & Hobbs, 1981: 492, figs. 1, 2 (“Lago de Chapala, 500 m from the north levee at Ajijic, State of Jalisco, Mexico”).
Cambarellus (Cambarellus) zacapuensisPedraza-Lara & Doadrio, 2015: 590, fig. 4. (“Zacapu Lake, in the town of the same name, state of Michoacán, Mexico, 19º49.336ʹN, 101º47.306ʹW”).
Cambarellus (Cambarellus) zempoalensisVillalobos, 1943
= Cambarellus montezumae forma zempoalensisVillalobos, 1943: 601; pl. 2, figs. 2, 4, 7, 13, 16, 17, 22 (“Llagunas de Zempoala, State of Morelos Mexico” according to Hobbs, 1989).
Cambarellus (Pandicambarus) Fitzpatrick, 1983
= Cambarellus (Pandicambarus) Fitzpatrick, 1983: 268 [type species Cambarellus schmittiHobbs, 1942b, by original designation; gender masculine].
= Cambarellus (Dirigicambarus) Fitzpatrick, 1983: 267 [type species Cambarus ShufieldtiiFaxon, 1884, by original designation; gender masculine].
Cambarellus (Pandicambarus) blackiHobbs, 1980
= Cambarellus blackiHobbs, 1980: 201, fig. 2 (“small cypress pond at Oak Grove, Escambia County, Florida” [USA]).
Cambarellus (Pandicambarus) diminutusHobbs, 1945
= Cambarellus diminutusHobbs, 1945: 467, figs. 1, 2, 5, 6, 10, 12, 13, 17, 18, 25, 26 (“sand-bottomed stream, 3.5 miles south of Irvington, Mobile County, Alabama” [USA]).
Cambarellus (Pandicambarus) leslieiFitzpatrick & Laning, 1976
= Cambarellus leslieiFitzpatrick & Laning, 1976: 138, fig. 1 (“0.5 mi S of Alabama Port, Mobile County, Alabama” [USA]).
Cambarellus (Pandicambarus) ninaeHobbs, 1950b
= Cambarellus ninaeHobbs, 1950b: 89; pl. 8 (“borrow ditches in the Aransas Refuge (along East Shore Road), Aransas County, Texas” [USA]).
Cambarellus (Pandicambarus) puerHobbs, 1945
= Cambarellus puerHobbs, 1945: 469, figs. 7, 8, 9, 11, 14, 16, 19, 21, 22, 24 (“seven miles west of Dayton, Liberty County, Texas, on U.S. Highway 90” [USA]).
Cambarellus (Pandicambarus) rotatusSchuster & Kendrick, 2017: 376, figs. 1, 2, 3, 4A–C (“Hale County, tupelo swamp, 1.8 mi NW of Stewart, along White Rd.” [Alabama, USA]).
Cambarellus (Pandicambarus) schmittiHobbs, 1942b
= Cambarellus schmittiHobbs, 1942b: 149; pl. 10, figs. 176–180; pl. 19 (“small spring flowing into the Suwannee River at Branford, Suwannee County, Florida” [USA]).
Cambarellus (Pandicambarus) shufeldtii (Faxon, 1884)
= Cambarus ShufeldtiiFaxon, 1884: 134 (“near New Orleans, La.” [Louisiana, USA]).
Cambarellus (Pandicambarus) texanusAlbaugh & Black, 1973
= Cambarellus texanusAlbaugh & Black, 1973: 177, fig. 1 (“ditch beside Farm Road 521, 1.5 mi S, 1 mi W of Wadsworth, 12 mi S of Bay City, Matagorda County, Texas” [USA]).
CambarusErichson, 1846
= CambarusErichson, 1846: 95 [type species Astacus BartoniiFabricius, 1798, by subsequent designation in Faxon (1898); gender masculine].
= Cambarus (Bartonius) Ortmann, 1905a: 97 [type species Cambarus bartoni [sic] Fabricius, 1798, by original designation; gender masculine].
= Cambarus (Aviticambarus) Hobbs, 1969a: 99 [type species Orconectes hamulatusCope & Packard, 1881, by original designation; gender masculine].
= Cambarus (Depressicambarus) Hobbs, 1969a: 102 [type species Astacus latimanusLe Conte, 1856, by original designation; gender masculine].
= Cambarus (Erebicambarus) Hobbs, 1969a: 99 [type species Cambarus bartoni tenebrosusHay, 1902a, by original designation; gender masculine].
= Cambarus (Hiaticambarus) Hobbs, 1969a: 105 [type species Cambarus longulusGirard, 1852, by original designation; gender masculine].
= Cambarus (Jugicambarus) Hobbs, 1969a: 106 [type species Cambarus bartonii asperimanusFaxon, 1914, by original designation; gender masculine].
= Cambarus (Lacunicambarus) Hobbs, 1969a: 110 [type species Cambarus diogenesGirard, 1852, by original designation; gender masculine].
= Cambarus (Puncticambarus) Hobbs, 1969a: 101 [type species Cambarus extraneusHagen, 1870, by original designation; gender masculine].
= Cambarus (Tubericambarus) Jezerinac, 1993: 534 [type species Cambarus acanthuraHobbs, 1981, by original designation; gender masculine]
= Cambarus (Veticambarus) Hobbs, 1969a: 96 [type species Cambarus pristinusHobbs, 1965, by original designation; gender masculine].
= Cambarus (Glareocola) Bouchard & Bouchard, 1995: 1 [type species Cambarus (Glareocola) williamiBouchard & Bouchard, 1995, by original designation; gender masculine].
Cambarus acanthuraHobbs, 1981
= Cambarus (Lacunicambarus) acanthuraHobbs, 1981: 215, figs. 25g, 84c, 85, 86, 220 (“field on west side of Holly Creek (farm of Homer Robison), about one mile northeast of Chatsworth, Murray County, Georgia” [USA]).
Cambarus aculabrumHobbs & Brown, 1987
= Cambarus (Jugicambarus) aculabrumHobbs & Brown, 1987: 1040, figs. 1, 2a–c, e, j, n (“Logan Cave, about 11 km east of Shiloam Springs, Benton County, Arkansas [USA] (Gallatin Quadrangle T. 18N, R. 32W, Sec. 33; 36°11ʹ50ʺN, 94°22ʹ 50ʺW)”).
Cambarus acuminatusFaxon, 1884: 113 (“Saluda River, at Farr’s Mills, west of Greenville, Greenville County, South Carolina” [USA] according to Hobbs, 1974b).
Cambarus adustusThoma, Fetzner, Stocker & Loughman, 2016
= Cambarus (Jugicambarus) adustusThoma, Fetzner, Stocker & Loughman, 2016: 176, figs. 2, 3, 4 (“roadside ditch serving as a tributary to Big Branch of Salt Lick Creek adjacent KY Rt. 898 just N of Hatcher Branch, 4.67 km SW of Charters, 3.60 km NE of Glen Springs, (38.53930, -83.46565, WGS84), Lewis County, Kentucky” [USA]).
Cambarus aldermanorumCooper & Price, 2010
= Cambarus (Puncticambarus) aldermanorumCooper & Price, 2010: 336, fig. 1 (“South Carolina, Chester County, South Fork Fishing Crk (trib. Catawba River, Santee River drainage), 1.2 km upstream from SR 496, ca. 3.2 air km NNW of Rodman (34.79736N, -81.09698W)”[USA]).
Cambarus andersoniJones & Eversole, 2015
= Cambarus (Hiaticambarus) andersoniJones & Eversole, 2015: 160, figs. 7(partim), 8(partim), 9, 10 (“Cox Creek upstream and downstream of Alabama State Route 17 crossing, 0.12 km north of junction with Alabama State Route 133, Florence, Lauderdale County, Alabama, 34.8436 degrees north latitude, -87.6744 degrees west” [USA]).
Cambarus angularisHobbs & Bouchard, 1994
= Cambarus (Cambarus) angularisHobbs & Bouchard, 1994: 2, fig. 1 (“Caney Valley Creek, 6.1 miles (9.8 km) southeast of Tazewell, Claiborne County, Tennessee, on U.S. Highway 25E” [USA]).
Cambarus appalachiensisLoughman, Welsh & Thoma, 2017
= Cambarus (Cambarus) appalachiensisLoughman, Welsh & Thoma, 2017: 435, figs. 2, 3 (“Pipestem Creek at intersection of Tom-Honaker Road (CR 20-3) and State Route 20, 3.3 km (2.04 mi) north-east of Pipestem, Summers County, West Virginia” [USA]).
Cambarus asperimanusFaxon, 1914
= Cambarus bartonii asperimanusFaxon, 1914: 391 (“Flat Creek, near Montreat, Buncombe Co., N. C.” [North Carolina, [USA]).
Cambarus bartonii bartonii (Fabricius, 1798)
= Astacus BartoniiFabricius, 1798: 407 (“America Boreali”; probably neighborhood of Philadelphia, Pa. [Pennsylvania, USA] according to Faxon, 1914).
= Astacus ciliarisRafinesque, 1817: 42 (“brooks near Fishkill, Newburg, &c” [all localities in New York state, USA]).
= Astacus pusillusRafinesque, 1817: 42 [(“brooks near Saratoga, Lake George, Lake Champlain, Utica, Oswego, &c” [all localities in New York state, USA]).
= Cambarus montanusGirard, 1852: 89 (“tributary of James River, Rockbridge Co., Virginia” [USA] according to Ortmann, 1931]).
= Cambarus bartoni typicusOrtmann, 1906a: 450 [no type locality indicated].
Cambarus bartonii cavatusHay, 1902b: 435 (“Powell River, Tazewell, Tennessee” [USA]).
Cambarus batchiSchuster, 1976
= Cambarus (Jugicambarus) batchiSchuster, 1976: 225, fig. 1 (“burrows around ponds in the Central Kentucky Wildlife Management Area, off U.S. 421, approximately two and one-half miles SE of Kingston, Madison Co., Kentucky” [USA]).
Cambarus bouchardiHobbs, 1970a
= Cambarus (Veticambarus) bouchardiHobbs, 1970a: 245, fig. 1 (“Perkins Creek, 6.9 miles north of Oneida, Scott County, Tennessee on U.S. Highway 27” [USA]).
Cambarus brachydactylusHobbs, 1953a: 20; pl. 1 (“Louise Creek, 13.9 miles south of Clarksville, Montgomery County, Tennessee on State Highway 48” [USA]).
Cambarus brimleyorumCooper, 2006a
= Cambarus (Puncticambarus) brimleyorumCooper, 2006a: 82, fig. 1 (“North Carolina, Cherokee Co., Valley River (Hiwassee River basin) at SR 1390 bridge, just N of junction SR 1420, ENE of Andrews (Andrews 7.5ʹ USGS quadrangle, UTM zone 17, coordinates 243439E/3899484N)” [USA]).
Cambarus buntingiBouchard, 1973a
= Cambarus (Puncticambarus) buntingiBouchard, 1973a: 407, fig. 1 (“Elk Creek, a tributary of Clear Fork Creek (Cumberland River system) at Co. Rd. 2345, approximately 1 mile S of Newcomb, Campbell County, Tennessee” [USA]).
Cambarus callainusThoma, Loughman & Fetzner, 2014
= Cambarus (Puncticambarus) callainusThoma, Loughman & Fetzner, 2014: 543, figs. 1, 2, 4 [partim] (“Russell Fork adjacent to VA Rt. 605 at county line of Dickenson and Buchanan counties, 3.79 air km NW of Davenport, 14.2 air km SE of Haysi, VA, 37.11954 N, -82.17185 W” [Virginia, USA]).
Cambarus carinirostrisFaxon, 1914
= Cambarus bartonii carinirostris (Hay MS) Faxon, 1914: 384 (“Gandy Creek, Oceola, Randolph County, West Virginia” [USA]; lectotype designated by Thoma & Jezerinac, 1999: 99).
Cambarus carolinus (Erichson, 1846)
= Astacus (Cambarus) CarolinusErichson, 1846: 96 (“Greenville, Greenville County, South Carolina” [USA] according to Hobbs, 1974b; but see Hobbs & Bouchard, 1973).
Cambarus catagiusHobbs & Perkins, 1967: 141, figs. 1–11 (“lawn at East Whittington Street, in the southeastern section of Greensboro, Guildford County, North Carolina” [USA]).
Cambarus causeyiReimer, 1966: 9, figs. 1–8 (“four miles west of Sandgap, Pope County, Arkansas, on State Highway 124” [USA]).
Cambarus chasmodactylusJames, 1966
= Cambarus longulus chasmodactylusJames, 1966: 14, fig. 1 (“East Fork of the Greenbrier River 9.7 mi. W. of Virginia state line on U.S. Highway 250, Pocahontas County, West Virginia” [USA]).
Cambarus chaugaensisPrins & Hobbs, 1972
= Cambarus (Puncticambarus) chaugaensisPrins & Hobbs, 1972: 413, fig. 1 (“Chauga River at Cassidy Bridge (off County Road 290), Oconee County, South Carolina” [USA]).
Cambarus clairitaeSchuster & Taylor, 2016
= Cambarus (Depressicambarus) clairitaeSchuster & Taylor, 2016: 333, figs. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5A–D, 6A, 7A, 8A, 9A (“Gurley Creek, a tributary of Locust Fork in the Black Warrior River drainage, in a long riffle approximately 100 meters upstream of the State Route 79 bridge, Jefferson County, Alabama (33.7942N; -86.6867)” [USA]).
Cambarus clivosusTaylor, Soucek & Organ, 2006: 31, figs. 2, 3 (“seep-fed tributary of Dry Creek at Pea Ridge Wildlife Management Area, approximately 11.5 km WSW Smithville, De Kalb County, Tennessee (35.9205°N, -85.9271°W)” [USA]).
Cambarus conasaugaensisHobbs & Hobbs, 1962
= Cambarus (Jugicambarus) conasaugaensisHobbs & Hobbs, 1962; 41, figs. 1–10 (“small tributary of the Conasauga River, two miles east of Chatsworth, Murrray County, Georgia on U.S. Rte. 76” [USA]).
Cambarus coosaeHobbs, 1981
= Cambarus (Puncticambarus) coosaeHobbs, 1981: 230, figs. 21c, 89a, 90, 223 (“Spring Creek, 8 miles east-southeast of Rome, Floyd County, Georgia, on U.S. Highway 411” [USA]).
Cambarus coosawattaeHobbs, 1981
= Cambarus (Hiaticambarus) coosawattaeHobbs, 1981: 150, figs. 22b, 58a, 59, 207 (“Cartecay River, 6 miles east southeast of Ellijay, just off Route S1010, near Flint Hill Church, Gilmer County, Georgia” [USA]).
Cambarus cracensBouchard & Hobbs, 1976
=Cambarus (Exilicambarus) cracensBouchard & Hobbs, 1976: 2, figs. 1, 2 (“Short Creek at State Route 75, 1.1 miles southwest of the junction with State Route 68 (T.8S, R.4E, Sec. 36), Marshall County, Alabama” [USA]).
Cambarus crinipesBouchard, 1973b
= Cambarus (Jugicambarus) crinipesBouchard, 1973b: 106, fig. 1 (“White Oak Creek, a tributary of Clear Fork Creek (Big South Fork of the Cumberland River system) at U.S. 27 in Sunbright, Morgan County, Tennessee” [USA]).
Cambarus cryptodytesHobbs, 1941a
= Cambarus (Cambarus) cryptodytesHobbs, 1941a: 110, figs. 2, 3, 7, 11, 13, 15, 18, 21, 24, 28, 29 (“two miles south of Graceville, Jackson County, Florida” [USA]).
Cambarus cumberlandensisHobbs & Bouchard, 1973
= Cambarus (Puncticambarus) cumberlandensisHobbs & Bouchard, 1973: 42, fig. 1 (“Poplar Cove Creek (a tributary to the East Fork of the Obey River), 5.8 miles west of Jamestown, Fentress County, Tennessee, USA, off State Route 52, just east of Helena” [USA]).
Cambarus cymatilisHobbs, 1970a
= Cambarus (Depressicambarus) cymatilisHobbs, 1970a: 251, fig. 3 (“near the western city limits of Chatsworth, Murray County, Georgia [USA], in lawn and rose garden of Mr. Charles S. Dunn, off Chestnut Street”).
Cambarus davidiCooper, 2000a
= Cambarus (Cambarus) davidiCooper, 2000a: 431, fig. 1 ([USA] “North Carolina, Wake County, small intermittent stream entering cove along western shore of Falls Lake (impoundment of Neuse River), ca. 1.4 air km NW of western end of NC 98 bridge and ca. 2.6 air km W of Stony Hill (Bayleaf 5.5ʹ USGS quadrangle, UTM zone 17, 3984850/712190)”).
Cambarus deweesaeBouchard & Etnier, 1979
= Cambarus (Depressicambarus) deweesaeBouchard & Etnier, 1979: 589, fig. 1 (“seepage area near east bank of Poplar Creek at Tennessee State Highway 61 (south side of highway) in Anderson County, Tennessee” [USA]).
Cambarus diogenesGirard, 1852
= Astacus fossorRafinesque, 1817: 42 (“Virginia, Pennsylvania, and New York” [USA]; name suppressed for the purposes of the Law of Priority but not those of the Law of Hononymy in Opinion 522, see Anonymous, 1958a).
= Cambarus diogenesGirard, 1852: 88 (“neighbourhoods of the city of Washington” [D.C., USA]).
= Cambarus nebrascensisGirard, 1852: 91 (“Fort Pierre, Nebraska”; locality now in “Stanley County, South Dakota” [USA] according to Hobbs, 1967b).
= Cambarus obesusHagen, 1870: 81; pl. 1, figs. 39–42; pl. 3, fig. 163 (“Lawn Ridge, Illinois” [USA] according to Hobbs, 1974b).
Cambarus distansRhoades, 1944a: 136, fig. 9 (“Cumberland River and a small tributary, just above Cumberland Falls, McCreary County, Kentucky” [USA]).
Cambarus diupalmaJones & Eversole, 2015
= Cambarus (Hiaticambarus) diupalmaJones & Eversole, 2015: 167, figs. 12, 13 (“Mountain Fork at Old Mountain Fork Road, 2.6 air km northeast of New Market, Madison County, Alabama, 34.9180 degrees north latitude, 86.4012 degrees west longitude” [USA]).
Cambarus doughertyensisCooper & Skelton, 2003
= Cambarus (Depressicambarus) doughertyensisCooper & Skelton, 2003: 828, fig. 1 ([USA] “Georgia, Dougherty County, burrows in wetland just south of access road near western boundary Albany Nursery Wildlife Management Area, ca. 12.8 km W of Albany (Pretoria 7.5ʺ USGS quadrangle, UTM Zone 16, coord. 751779E, 3496706N”).
Cambarus dubiusFaxon, 1884: 114 (“Terra Alta (Cranberry Summit), Preston County, West Virginia” [USA] according to Hobbs, 1974b).
Cambarus eeseeohensisThoma, 2005
= Cambarus (Cambarus) eeseeohensisThoma, 2005: 795, fig. 1 ([USA] “North Carolina Avery County, Linville River at Tanglewood Cemetery Road, off Rt. 105, 0.6 miles N of U.S. Rt. 221; 0.8 miles NW of Linville, 3.0 miles ESE of Newland; 36°04ʹ45ʺN 81°52ʹ08ʺW”).
Cambarus elkensisJezerinac & Stocker, 1993
= Cambarus (Hiaticambarus) elkensisJezerinac & Stocker, 1993: 346, fig. 1 (“Laurel Fork of the Left Fork of the Holly River at Holly River State Park campground, Webster County, Hacker Valley District, West Virginia (1.1 (air) km NNE of Hacker Valley)” [USA]).
Cambarus englishiHobbs & Hall, 1972
= Cambarus (Depressicambarus) englishiHobbs & Hall, 1972: 151, fig. 1 (“Tallapoosa River, in riffle area immediately downstream from City of Tallapoosa water intake, 1 mile north of Tallapoosa, Haralson County, Georgia, a few hundred yards east of bridge on State Route 100” [USA]).
Cambarus erythrodactylusSimon & Morris, 2014
=Cambarus (Lacunicambarus) erythrodactylusSimon & Morris, 2014: 573, figs. 1, 3, 4 (“USA: Alabama: Fayette County: Section 18, Range 12W (3.2 air km S of Fayette; 8.9 air km ENE of Belk); a roadside ditch at the intersection of State Route (St. Rte.) 171, 0.5 mi S of St. Rte. 159 (33°40ʹ8.7ʺN, 87°50ʹ7.5ʺW)”).
Cambarus extraneusHagen, 1870: 73; pl. 1, figs. 88–89; pl. 3, fig. 156 (“Tennessee River, Georgia” [USA], see Hobbs, 1974b).
Cambarus fasciatusHobbs, 1981
= Cambarus (Hiaticambarus) fasciatusHobbs, 1981: 156, figs. 22e, 58b, 61, 208 (“Etowah River, 0.2 mile west of State Route 52 on an unpaved road near Davis Chapel, Lumpkin County, Georgia” [USA]).
Cambarus friaufiHobbs, 1953a: 24; pl. 2 (“small stream tributary of the Cumberland River at Elmwood, Smith County, Tennessee” [USA]).
Cambarus gentryiHobbs, 1970b
= Cambarus (Jugicambarus) gentryiHobbs, 1970b: 163, fig. 1 (“boggy area below seepage along a small tributary to Turnbull Creek (Harpeth-Cumberland drainage system), one mile west of Kingston Springs, Cheatham County, Tennessee” [USA]).
Cambarus georgiaeHobbs, 1981
= Cambarus (Puncticambarus) georgiaeHobbs, 1981: 251, figs. 21g, 87, 89d, 96, 225 (“Little Tennessee River at U.S. Highway 441 south of Dillard, Rabun County, Georgia” [USA]).
Cambarus girardianusFaxon, 1884: 117 (“Cypress Creek, Lauderdale Co., Ala.” [Alabama, USA]).
Cambarus graysoniFaxon, 1914: 393 (“Bear Creek, a tributary of Green River, Grayson Springs, Grason Co., Ky.” [Kentucky, USA]).
Cambarus guenteriLoughman, Henkanaththegedara, Fetzner & Thoma, 2017
= Cambarus (Puncticambarus) guenteriLoughman, Henkanaththegedara, Fetzner & Thoma, 2017: 468, figs. 3, 4 (“Silver Creek at Hagan Mill Road Crossing, 5.5 km (3.4 mi) southwest of Richmond, Madison County, KY, 37.69196/-84.36081” [Kentucky, USA]).
Cambarus halliHobbs, 1968
= Cambarus (Depressicambarus) halliHobbs, 1968: 269, figs. 12–22 (“small tributary of the Tallapoosa River, 1.3 miles south of the River on U.S. Rte. 27, Haralson County, Georgia” [USA]).
Cambarus hamulatus (Cope & Packard, 1881)
= Orconectes hamulatusCope & Packard, 1881: 881; pl. 7, figs.1–1b (“Nickajack Cave, Tennessee” [USA]).
Cambarus hartiHobbs, 1981
= Cambarus (Depressicambarus) hartiHobbs, 1981: 104, figs. 23e, 38b, 41, 45, 201 (“seepage and wooded area adjacent to the National Fish Hatchery at Warm Springs, Meriwether County, Georgia” [USA]).
Cambarus hatfieldiLoughman, Fagundo, Lau, Welsh & Thoma, 2013
= Cambarus (Cambarus) hatfieldiLoughman, Fagundo, Lau, Welsh & Thoma, 2013: 224, figs. 1, 2, 4A (“Mate Creek at CR 6 crossing in Red Jacket, Mingo County, West Virginia (37.64807ºN, -82.13524ºW)” [USA]).
Cambarus hazardiLoughman, Henkanaththegedara, Fetzner & Thoma, 2017
= Cambarus (Puncticambarus) hazardiLoughman, Henkanaththegedara, Fetzner & Thoma, 2017: 477, figs. 6, 7 (“Red River at KY 77 crossing in Red River Gorge National Geologic Area at the Powell/Menifee county line, KY, 37.83376/-83.65990” [Kentucky, USA]).
Cambarus hiwasseensisHobbs, 1981
= Cambarus (Puncticambarus) hiwasseensisHobbs, 1981: 256, figs. 21e, 89f, 97, 226; frontispiece (“tributary to Peachtree Creek, 0.8 miles north of Peachtree School on U.S. Alternate Highway 64, Cherokee County, North Carolina” [USA]).
Cambarus hobbsorumCooper, 2001
= Cambarus (Puncticambarus) hobbsorumCooper, 2001: 153, fig. 1 (“North Carolina, Union Co., Bearskin Creek (tributary Richardson Creek, Rocky River subdrainage, Yadkin-Pee Dee River basin) near NC 200 bridge, about 2.4 air km NE of center of Monroe (Monroe 7.5ʹ USGS quadrangle, UTM zone 17, coordinates 3872500/543500)” [USA]).
Cambarus howardiHobbs & Hall, 1969
= Cambarus (Cambarus) howardiHobbs & Hall, 1969: 281, figs. 1–12 (“Sope Creek, tributary to the Chattahoochee River at Paper Mill Road 1.5 miles above mouth, Cobb County, Georgia” [USA]).
Cambarus hubbsiCreaser, 1931
= Cambarus (Bartonius) hubbsiCreaser, 1931: 4; pls. 3, 4 (“Little Creek, tributary to the St. Francis River, one mile northeast of Chloride, Iron County, Missouri” [USA]).
Cambarus hubrichtiHobbs, 1952a: 689, figs. 1–8 (“stream in Lewis Cave, 15 miles northwest of Doniphan, Ripley County, Missouri” [USA]).
Cambarus hystricosusCooper & Cooper, 2003
= Cambarus (Puncticambarus) hystricosusCooper & Cooper, 2003: 921, fig. 1 (“North Carolina, Hoke County, Puppy Creek at SR 1409, ca. 2.4 air km E of Wayside (Nicholson Creek 7.5ʹ USGS quadrangle, UTM Zone 17, coordinates 670662E/3876690N)” [USA]).
Cambarus jezerinaciThoma, 2000
= Cambarus (Jugicambarus) jezerinaciThoma, 2000: 731, fig. 1 (“Virginia, Lee Co., unnamed tributary of Dry Branch, a tributary of Indian Creek of the Powell River drainage, 0.2 miles (0.32 km) east of Chadwell Gap Trail, 1.4 miles (2.25 km) north of Caylor (36°39ʹ16ʺN, 83°29ʹ55ʹʹW)” [USA]).
Cambarus johniCooper, 2006b
= Cambarus (Puncticambarus) johniCooper, 2006b: 67, fig. 1 (“North Carolina, Wilkes County, Stone Mountain State Park, East Prong Roaring River (Yadkin-Pee Dee River basin) at SR 1739, ca. 1.2 air km N of Joynes (Glade Valley 7.5ʹ USGS quadrangle, UTM zone 17, coordinates 493837E/4026042N)” [USA]).
Cambarus jonesiHobbs & Barr, 1960: 19, figs. 11–20 (“Cave Spring Cave, 12.1 miles northwest of Valhermosa, Morgan County, Alabama” [USA]).
Cambarus laconensisBuhay & Crandall, 2009
= Cambarus (Aviticambarus) laconensisBuhay & Crandall, 2009: 128, figs. 5, 6 (“Lacon Exit Cave (ACS #3343), Morgan County” [= Alabama, USA]).
Cambarus latimanus (Le Conte, 1856)
= Astacus latimanusLe Conte, 1856: 402 (“Georgia superiore”; “Athens, Clarke County, Georgia” [USA] according to Hobbs, 1974b).
= Cambarus JordaniFaxon, 1884: 119 (“Etowah River near Rome, Georgia” [USA]).
Cambarus lenatiCooper, 2000b
= Cambarus (Cambarus) lenatiCooper, 2000b: 2, fig. 1 (“North Carolina, Rutherford Co., Brier Crk at SR 1735, ca. 11.2 air km NE of town of Lanes Store (Benn Knob 7.5ʹ USGS quadrangle; WGS 84: N35.31.388, W81.43.130)” [USA]).
Cambarus lentiginosusJones & Eversole, 2016
= Cambarus (Hiaticambarus) lentiginosusJones & Eversole, 2016: 45, figs. 4a, 5a, 6, 7 (“Fowler Creek at Elkwood Section Road crossing, 1.5 km (0.9 mi) W of junction with US 231/ 431, north of Fisk, Alabama, 34.9765 degrees north latitude, 86.5857 degrees west longitude” [= Madison County, Alabama,USA]).
Cambarus longirostrisFaxon, 1885a
= Cambarus Bartonii var. longirostrisFaxon, 1885a: 64 [“Eastern Tennesse and West Virginia”; restricted to “Doe River, Carter Co., Tennessee” [USA] by Ortmann, 1931).
Cambarus longulusGirard, 1852: 90 [“middle states of the Union”; restricted to “Rockfish River, south of Afton, Nelson County, Virginia” [USA] by Hobbs, 1967b).
Cambarus ludovicianusFaxon, 1884
= Cambarus Diogenes var. LudovicianaFaxon, 1884: 144 (“New Orleans, Louisiana” [USA]).
Cambarus maculatusHobbs & Pflieger, 1988
= Cambarus (Erebicambarus) maculatusHobbs & Pflieger, 1988: 644, figs. 1, 2 (“Hazel Creek at Route C, 8 miles (12.8 km) northeast of Courtois, Washington County, Missouri (T. 36N, R. 1 W, SE¼ Sec. 24)” [USA]).
Cambarus mageraeThoma & Fetzner, 2015
= Cambarus (Jugicambarus) mageraeThoma & Fetzner, 2015: 13, fig. 1 (“South Fork Powell River, at bridge crossing on Cracker Neck Road (SSR 616) adjacent to the Big Stone Gap Water Treatment Plant, 6.14 km SE of downtown Big Stone Gap, Wise County, Virginia (36.83606, -82.70552)” [USA]).
Cambarus manningiHobbs, 1981
= Cambarus (Hiaticambarus) manningiHobbs, 1981: 175, figs. 22c, 58e, 67, 68, 211 (“Little Cedar Creek (Coosa River basin) near school for deaf on outskirts of Cave Spring, Floyd County, Georgia” [USA]).
Cambarus miltusFitzpatrick, 1978b
= Cambarus (Lacunicambarus) miltusFitzpatrick, 1978b: 749, figs. 1–13 (“burrows along d’Olide Creek under old highway 98 bridge, 0.1 mi. (161 m) S of the junction of U.S. Highways 90, 98, and I-10 at Spanish Fort, Baldwin County, Alabama” [USA]).
Cambarus monongalensisOrtmann, 1905c: 395 (“Edgewood Park, Allegheney County, Pennsylvania” [USA] according to Hobbs, 1974b).
Cambarus nerteriusHobbs, 1964: 189; pl. 1 (“Matt’s Black Cave, 2 miles south of Renick, Greenbrier County, West Virginia” [USA]).
Cambarus nodosusBouchard & Hobbs, 1976
= Cambarus (Jugicambarus) nodosusBouchard & Hobbs, 1976: 8, fig. 3 (“small unnamed tributary of North Potato Creek (Hiwassee River system via Ocoee River) between 0.7 and 0.9 mile west of the Tennessee-North Carolina border on U.S. Highway 64, Polk County, Tennessee” [USA]).
Cambarus obeyensisHobbs & Shoup, 1947: 138; pl. 1 (“Big Hurricane Creek on the Monterey-Clark Range road at the Putnam-Cumberland County line in Tennessee” [USA]).
Cambarus obstipusHall, 1959: 221; pl. 1 (“Black Warrior River at Underwood’s Ferry, 8 miles downstream from Cordova, Walker County, Alabama” [USA]).
Cambarus ortmanniWilliamson, 1907: 754; pl. 35 (“Six-Mile Creek and Craven Ditch, tributary to Wabash River, above Bluffton, Wells County, Indiana” [USA) according to Hobbs, 1974b).
Cambarus parrishiHobbs, 1981
= Cambarus (Puncticambarus) parrishiHobbs, 1981: 263, figs. 21d, 89e, 99, 227 (“Hiwassee River, 2 miles north of the junction of Georgia Routes 17 and 66 on Route 17, approx. 7 miles southeast of Hiwassee” [= Towns County, Georgia, USA]).
Cambarus parvoculusHobbs & Shoup, 1947: 142; pl. 2 (“unnamed small clear swift spring-fed rocky stream tributary to Big Hurricane Creek in the southwest corner of Fentress County, Tennessee, northwest of Clark Range and south-southeast of Wilder, Fentress County” [USA]).
Cambarus pauleyiLoughman, Thoma, Fetzner & Stocker, 2015
= Cambarus (Jugicambarus) pauleyiLoughman, Thoma, Fetzner & Stocker, 2015: 534, figs. 5, 6 (“seepage stream adjacent to Moncove Lake State Park Playground, 2.0 km (1.3 mi) northwest of Roxalia, Monroe County, West Virginia (37.620745 N, -83.352988 W)” [USA]).
Cambarus pecki (Hobbs, 1967a)
= Procambarus peckiHobbs, 1967a: 2, figs. 1–12 (“McKinney Pit Cave (Alabama Cave Survey, no. A-620), about 2.5. miles west of Tuscumbia, Colbert County, Ala. (Sec. 10, T 4S, R12W)” [Alabama, USA]).
Cambarus polychromatusThoma, Jezerinac & Simon, 2005
= Cambarus (Tubericambarus) polychromatusThoma, Jezerinac & Simon, 2005: 326, fig. 1 (“banks and flood plain of Flat Creek, tributary of Hall Creek, Patoka River basin, at Co. Rd. 124S culvert crossing, Pike Co., Indiana (38.4019°N, 87.3066°W)” [USA]).
Cambarus pristinusHobbs, 1965: 268; pl. 1 (“White Oak Creek, a tributary to the Caney Fork of the Cumberland River, 3.9 miles east of the White-Cumberland County line and 0.1 miles south of US Rte. 70S” [Cumberland County, Tennessee, USA]).
Cambarus pyronotusBouchard, 1978
= Cambarus (Depressicambarus) pyronotusBouchard, 1978: 37, fig. 9 (“tributary of the Apalachicola River south of Indian Ridge, Torreya State Park, Liberty County, Florida” [USA]).
Cambarus reburrusPrins 1968: 458, figs. 1–11 (“small tributary to the Horsepasture River from Sapphire (= Fairfield) Lake off U.S. 64, 5.5 miles east of Cashiers, Jackson County, North Carolina” [USA]).
Cambarus reduncusHobbs, 1956a: 61, figs. 1–11 (“flood plain pools of Little River, 10.3 mi. W. of Winnsboro, Fairfield Co., S.C., on Rte. 22” [= Fairfield County, South Carolina, USA]).
Cambarus reflexusHobbs, 1981
= Cambarus (Depressicambarus) reflexusHobbs, 1981: 120, figs. 23c, 38a, 39h, 52, 203 (“Savannah River floodplain at U.S. Highway 301, Allendale County, South Carolina” [USA]).
Cambarus robustusGirard, 1852: 90 (“Humber River, near Toronto [Canada]”).
Cambarus rusticiformisRhoades, 1944a: 133, fig. 8 (“Little River, ½ mi. w. of Cadiz, Trigg County, Kentucky” [USA]).
Cambarus sciotensisRhoades, 1944b
= Cambarus bartoni sciotensisRhoades, 1944b: 96 (“limestone cliffs below O’Shaughnessy Dam, Scioto River, Sec. 3, Liberty Twp., Delaware County, Ohio” [USA]).
Cambarus scottiHobbs, 1981
= Cambarus (Puncticambarus) scottiHobbs, 1981: 238, figs. 21b, 89b, 92, 228 (“Clarks Creek, 1 mile north of Holland, Chattooga County, Georgia, on State Route 100” [USA]).
Cambarus setosus Faxon & Garman in Garman, 1889: 237; pl. 1, figs. 1, 2, 3, 7; pl. 2, fig. 1 (“Wilson’s Cave (Whisner Cave, 2 miles northwest of Sarcoxie, T.27N, R.29W, sec. 6], Jasper County, Missouri” [USA] according to Hobbs, 1974b).
= Cambarus ayersiiSteele, 1902: 18; pl. 5, fig. A; pl. 6, fig, 14 (“Fisher’s Cave, near Springfield, Missouri” [USA]).
Cambarus smilaxLoughman, Simon & Welsh, 2011
= Cambarus (Puncticambarus) smilaxLoughman, Simon & Welsh, 2011: 100, figs. 1, 2 (“West Fork of Greenbrier River in Breacher, 7.72 km (4.8 mi) from origin of Forest Service road 44 in Durbin, Pocahontas County, West Virginia, (38.60119°N, 79.82171°W)” [USA]).
Cambarus speciosusHobbs, 1981
= Cambarus (Hiaticambarius) speciosusHobbs, 1981: 181, figs. 22g, 58f, 69, 212 (“Talking Rock Creek at State Route 5, Pickens County, Georgia” [USA]).
Cambarus speleocoopiBuhay & Crandall, 2009
= Cambarus (Aviticambarus) speleocoopiBuhay & Crandall, 2009: 125, figs. 3, 4 (“Kellers Cave (Alabama Cave Survey, ACS#326, Marshall County)” [Alabama, USA]).
Cambarus sphenoidesHobbs, 1968: 262, figs. 1–11 (“tributary to Clear Creek (Emory River drainage), 11.2 miles north of Crossville, Cumberland County, Tennessee, on U.S. Rte. 127” [USA]).
Cambarus spicatusHobbs, 1956b: 116, figs. 1–11 (“Little River, 10.3 miles west of Winnsboro, South Carolina, Fairfield County, on St. Rte. 22” [USA]).
Cambarus stockeriThoma, 2011
= Cambarus (Tubericambarus) stockeriThoma, 2011: 319, fig. 1 (“south shore flood plain of Ramsey Branch (Blackburn Branch), a tributary of Coahulla Creek, Conasauga River basin, just upstream Hunt Road SE bridge crossing, Bradley County, Tennessee (35.04936°N, -84.86681°W)” [USA]).
Cambarus striatusHay, 1902b
= Cambarus latimanus striatusHay, 1902b: 437 (“Nashville, Tenn.” [Tennessee, USA]).
= Cambarus (Cambarus) floridanusHobbs, 1941a: 114, figs. 1, 4, 5, 8, 9, 16, 19, 22, 25, 31, 32) (“Cryptolabis Ravine, 12 miles west of Tallahassee on State Highway 19, Leon County, Florida” [USA]).
Cambarus strigosusHobbs, 1981
= Cambarus (Depressicambarus) strigosusHobbs, 1981: 134, figs. 23d, 39j, 56, 205 (“roadside ditch within 30 meters of Susan Smith Branch (tributary to Long Creek and the Broad River) west of State Route 17 on unnumbered county road, Wilkes County, Georgia” [USA]).
Cambarus subterraneusHobbs, 1993
= Cambarus (Jugicambarus) subterraneusHobbs, 1993: 719, figs. 1, 2a, b, e, k, o, p (“Twin Cave, Delaware County, Oklahoma (Choleta Quadrangle, T. 23N, R. 22E)” [USA]).
Cambarus tartarusHobbs & Cooper, 1972
= Cambarus (Jugicambarus) tartarusHobbs & Cooper, 1972: 51, figs. 1–12 (“Stansberry-January Cave System, 4 miles north of Colcord (T.21N, R.22E, Sec 11), Delaware County, Oklahoma, in the Spavinaw Creek drainage of the Arkansas River Basin” [USA]).
Cambarus tayloriLoughman, Henkanaththegedara, Fetzner & Thoma, 2017
= Cambarus (Puncticambarus) tayloriLoughman, Henkanaththegedara, Fetzner & Thoma, 2017: 482, figs. 9, 10 (“Fourmile Fork at Houston Road (KY 1114) crossing, 1.9 km (1.2 mi) southeast of Turkey, Breathitt County, 37.46333/-83.49893” [Kentucky, USA]).
Cambarus tenebrosusHay, 1902a
= Cambarus bartoni tenebrosusHay, 1902a: 232 (“Mammoth Cave, Kentucky” [USA]).
= Cambarus bartonii laevisFaxon, 1914: 391 (“Bloomington, Ind.” [Indiana, USA]).
= Cambarus (Cambarus) cahniRhoades, 1941: 146, fig. 36 (“Belgreen Cave, NW¼SW¼ sec. 12, T. 7 S., R. 13 W., Franklin County, Ala.” [Alabama, USA]).
= Cambarus bartoni ornatusRhoades, 1944a: 144, fig. 10 (“Ellis Branch 4 mi. W of Carrollton, Carrol County, Kentucky” [USA]).
Cambarus theepiensisLoughman, Foltz, Garrison & Welsh, 2013
= Cambarus (Puncticambarus) theepiensisLoughman, Foltz, Garrison & Welsh, 2013: 64, figs. 1, 2 (“left fork of Millers Branch, 2.2 miles (3.54 km) from CR 22/CR 27 intersection on CR 22, 0.05 mi (0.08 km) north of Crockett, Wayne County, West Virginia (38.23766ºN, -82.37685ºW” [USA]).
Cambarus thomaiJezerinac, 1993
= Cambarus (Tubericambarus) thomaiJezerinac, 1993: 536, fig. 4 (“roadside ditch on the property of the Union Elementary School at the intersection of State Route (St Rte) 79 and County Road (Co Rd) 18, Section 22, Perry Township, Coshocton County, Ohio (2.1 air km NW of West Carlisle; 5.6 air km SSE of New Guilford), 40°12ʹ4ʺN, 82°07ʹ50ʺW” [USA]).
Cambarus truncatusHobbs, 1981
= Cambarus (Depressicambarus) truncatusHobbs, 1981: 140, figs. 23b, 38f, 39k, m, 57, 206 (“roadside ditch 15.4 miles east of Irwinton, Wilkinson County, Georgia, on state Route 57” [USA]).
Cambarus tuckasegeeCooper & Schofield, 2002
= Cambarus (Jugicambarus) tuckasegeeCooper & Schofield, 2002: 372, fig. 1 (“North Carolina, Jackson County, Soco Creek off US 19 at US 441 Bus, SE of Cherokee (Swain County) (Whittier USGS 7.5ʹ quadrangle, UTM Zone 17, coordinates 290790E, 3927400N” [USA]).
Cambarus unestamiHobbs & Hall, 1969
= Cambarus (Depressicambarus) unestamiHobbs & Hall, 1969: 287, figs. 13–24 (“Daniel Creek, 2.5 miles west of Walker County line on State Route 143, Dade County, Georgia” [USA]).
Cambarus veitchorumCooper & Cooper, 1997a
= Cambarus (Aviticambarus) veitchorumCooper & Cooper, 1997a: 608, fig. 1 (“Alabama, Limestone County, subterranean stream in White Spring Cave, NW of Holland Gin (Tanner 7.5ʹ USGS Quadrangle, Sec. 11, T.5S, R.4W)” [USA]).
Cambarus veteranusFaxon, 1914
= Cambarus bartonii veteranusFaxon, 1914: 389; pl. 13, fig. 2 (“Indian Creek, Baileysville, Wyoming County, W. Va.” [West Virginia, USA]).
Cambarus williamiBouchard & Bouchard, 1995
= Cambarus (Glareocola) williamiBouchard & Bouchard, 1995: 2, figs. 1, 2b (“Brawleys Fork at Country Rd. 4401, 1.6 km southwest of Bradyville, Cannon County, Tennessee” [USA]).
Cambarus zophonastesHobbs & Bedinger, 1964: 11; pl. 1, figs. 1, 2, 4–11 (“Hell Creek Cave, Stone County, Arkansas (NE¼, NE¼. Sec. 30, T. 15 N, R. 10 W)” [USA]).
CreaserinusHobbs, 1973a
= Fallicambarus (Creaserinus) Hobbs, 1973a: 463 [type species Astacus fodiensCottle, 1863, by original designation; gender masculine].
Creaserinus burrisi (Fitzpatrick, 1987b)
= Fallicambarus (Creaserinus) burrisiFitzpatrick, 1987b: 433, figs. 1, 2a-d (“saturated sandy soil of hillside Sarracenia bog; T4N, R5W, E/2 Sec. 21, Greene County, Mississippi” [USA]).
Creaserinus byersi (Hobbs, 1941a)
= Cambarus (Cambarus) byersiHobbs, 1941a: 118, figs. 6, 10, 14, 17, 20, 23, 26, 27, 30 (“narrow swampy area along Phifer Creek, 5.5 miles northwest of Pensacola, Escambia County, Florida, near United States Highway 9” [USA]).
Creaserinus caesius (Hobbs, 1975)
= Fallicambarus (Creaserinus) caesiusHobbs, 1975: 24, fig. 7 (“roadside ditch at Hot Spring-Saline county line, Arkansas, on State Route 67” [USA]).
Creaserinus danielae (Hobbs, 1975)
= Fallicambarus (Creaserinus) danielaeHobbs, 1975: 28, fig. 8 (“roadside ditch 9.0 miles east of Ocean Springs, Jackson County, Mississippi, on U.S. Highway 90” [USA]).
Creaserinus fodiens (Cottle, 1863)
= Astacus fodiensCottle, 1863: 217 (“Upper Canada”; probably “Ontario, Canada” according to Hobbs, 1974b).
= Cambarus argillicolaFaxon, 1884: 115 (“Detroit, Michigan” [USA] according to Faxon, 1914).
= Cambarus UhleriFaxon, 1884: 116 (“swamp on Eastern Road near Felsbury, Somerset Co., Maryland” [USA] according to Faxon, 1914).
= Cambarus hedgpethiHobbs, 1948a: 224, fig. 17 (“lower middle part of the Aransas National Wildlife Refuge, Aransas County, Texas” [USA]).
Creaserinus gilpini (Hobbs & Robison, 1989)
= Fallicambarus (Creaserinus) gilpiniHobbs & Robison, 1989: 684, figs. 1q, 11 (“roadside seepage 3.1 mi south of southern junction of State Route 54 and U.S. Highway 79 at junction of latter with Pepperidge Road (T7S, R10W, Sec19), approximately 11 miles south of Pine Bluff and about 3 miles north of Cleveland County line, Jefferson County, Arkansas” [USA]).
Creaserinus gordoni (Fitzpatrick, 1987b)
= Fallicambarus (Creaserinus) gordoniFitzpatrick, 1987b: 439, figs. 2e–i, 3 (“DeSoto National Forest, Camp Shelby Military Reservation, T2N, R10W, Se/4 NE/4 SE/4 Sec. 5, Perry County, Mississippi” [USA]).
Creaserinus hortoni (Hobbs & Fitzpatrick, 1970)
= Fallicambarus hortoniHobbs & Fitzpatrick, 1970: 829, figs. 1–12 (“roadside ditch leading into a small tributary of Cypress Creek, 7.5. miles east of the Hardeman County line on State Route 57 (Hatchie River drainage), McNairy County, Tennessee” [USA]).
Creaserinus oryktes (Penn & Marlow, 1959)
= Cambarus oryktesPenn & Marlow, 1959: 197, figs. 1–14 (“roadside ditch at Alton, St. Tammany Parish, La.” [Louisiana, USA]).
DistocambarusHobbs, 1981
Distocambarus (Distocambarus) Hobbs, 1981
= Procambarus (Distocambarus) Hobbs, 1981: 301 [type species Procambarus (Distocambarus) devexusHobbs, 1981, by original designation; gender masculine].
Distocambarus (Distocambarus) crockeriHobbs & Carlson, 1983
= Distocambarus crockeriHobbs & Carlson, 1983: 421, fig. 1 (“roadside ditch 0.7 miles south of Parksville, McCormick County, South Carolina, on U.S. Highway 221” [USA]).
Distocambarus (Distocambarus) devexus (Hobbs, 1981)
= Procambarus (Distocambarus) devexusHobbs, 1981: 302, figs. 11j, 115–117, 234 (“marshy area under bridge within 200 meteres south of and in the flood plain of the Broad River on State Route 17, Wilkes County, Georgia” [USA]).
Distocambarus (Fitzcambarus) Hobbs, 1983
= Distocambarus (Fitzcambarus) Hobbs, 1983: 430 [type species Distocambarus (Fitzcambarus) carlsoniHobbs, 1983, by monotypy and original designation; gender masculine].
Distocambarus (Fitzcambarus) carlsoniHobbs, 1983: 430, fig. 1 (“swampy area bordering an unnamed tributary of the Saluda River about 1 mile north of State Route 81 on Route 106” [Anderson County, South Carolina, USA]).
Distocambarus (Fitzcambarus) hunteriFitzpatrick & Eversole, 1997: 272, fig. 1 (“runoff drainage just west of State Route 391 at junction of State Route 194; 34°05ʹ26.8ʺN 81°34ʹ88.1ʺW; Saluda River drainage, Saluda Co., South Carolina” [USA]).
Distocambarus (Fitzcambarus) youngineriHobbs & Carlson, 1985: 82, fig. 1 (“area adjacent to small woodland pool, about 50 m southwest of State Route 58 on Route 22 (11 airmiles due west of Newberry, Newberry County, South Carolina) (34°18ʹN, 81°48ʹW)” [USA]).
FallicambarusHobbs, 1969a
= FallicambarusHobbs, 1969a: 111 [type species Cambarus strawniReimer, 1966; by original designation; gender masculine].
= Procambarus (Tenuicambarus) Hobbs, 1972b: 12 [type species Procambarus tenuisHobbs, 1950a; by original designation; gender masculine)
Fallicambarus devastatorHobbs & Whiteman, 1987
= Fallicambarus (Fallicambarus) devastatorHobbs & Whiteman, 1987: 403, figs. 1, 2 (“prairie grassland at Angelina County Airport in Burke Community, about 5 miles (8 km) south of Lufkin, Angelina County, Texas” [USA]).
Fallicambarus dissitus (Penn, 1955)
= Cambarus dissitusPenn, 1955: 73, figs. 1–13 (“stream three miles east of Choudrant, Lincoln Parish, Louisiana” [USA]).
Fallicambarus harpiHobbs & Robison, 1985
= Fallicambarus (Fallicambarus) harpiHobbs & Robison, 1985: 1035, fig. 1 (“seepage area located 0.2 mile east of Glenwood, Pike County, Arkansas (Sec. 1, R. 24W, T. 5S) on U.S. Highway 70, on the property of Milburn Dillard” [USA]).
Fallicambarus houstonensisJohnson, 2008
= Fallicambarus (Fallicambarus) houstonensisJohnson, 2008: 1, figs. 1, 2, 3, 4a, c–e, 5, 6, 7, 8 (“powerline right of way near the junction of Rt. 105 and Truman Road, approximately 3 km (1.8 mi) ESE of Cleveland, Liberty County, Texas (30°20.122ʹ N 95°03.759ʹ W)” [USA]).
Fallicambarus jeanaeHobbs, 1973a
= Fallicambarus (Fallicambarus) jeanaeHobbs, 1973a: 463, fig. 1 (“seepage area, 1.8 miles east of the Clark County line, Hot Springs County, Arkansas,on State Route 84” [USA]).
= Fallicambarus (Fallicambarus) spectrumHobbs, 1973a: 469, fig. 2 (“roadside ditch, 2 miles east of Daisy, Pike County, Arkansas, on U.S. Highway 70” [USA]).
Fallicambarus kountzeaeJohnson, 2008
= Fallicambarus (Fallicambarus) kountzeaeJohnson, 2008: 13, figs. 11–17 (“grassy highway right of way in loblolly pine forest, Hwy. 69, 2.2 km (1.3 mi) north Rt. 1003, Hardin County, Texas (30°26.6ʹ N 94°23.1ʹ W)” [USA]).
Fallicambarus macneesei (Black, 1967)
= Cambarus macneeseiBlack, 1967: 173; figs. 1–12 (“roadside ditches along East McNeese Road, 1.8 miles west of intersection of East McNeese Road and Louisiana Highway 14, Lake Charles, Calcasieu Parish, Lousiana” [USA]).
Fallicambarus petilicarpusHobbs & Robison, 1989
= Fallicambarus (Fallicambarus) petilicarpusHobbs & Robison, 1989: 661, figs. 3, 4a (“roadside seepage 0.2 mile east of the Columbia County line on State Route 57, Union County, Arkansas (T16S, R18W, Sec 21)” [USA]).
Fallicambarus schusteriTaylor & Robison, 2016: 576, figs. 1, 2 (“roadside ditches along Co. Rd. 2190, 0.4 mi SW town of Haworth, McCurtain County, Oklahoma (33.8376, -94.6608)” [USA]).
Fallicambarus strawni (Reimer, 1966)
= Cambarus strawniReimer, 1966: 11, figs. 9–18 (“2.7 miles north of Dierks, Howard County, Arkansas, on State Highway 4” [USA]).
Fallicambarus tenuis (Hobbs, 1950a)
= Procambarus tenuisHobbs, 1950a: 194, figs. 1–12 (“six miles east of Page and just west of Oklahoma state line, Le Flore Co., Oklahoma” [USA]).
Fallicambarus wallsiJohnson, 2011a
= Fallicambarus (Fallicambarus) wallsiJohnson, 2011a: 59, figs. 1, 2a–h, 3, 4a–h, 5a–d (“roadside ditch and culvert pool, Rt. 1 3.5 km (2.2 miles) south intersection with Rt. 184, Sabine County, Texas (31.32498, -93.97711)” [USA]).
FaxonellaCreaser, 1933
= Faxonius (Faxonella) Creaser, 1933; 21 [type species Cambarus clypeatusHay, 1899, by monotypy; gender feminine].
Faxonella beyeri (Penn, 1950a)
= Orconectes (Faxonella) beyeriPenn, 1950a: 166, figs. 1–9 (“roadside ditch on U.S. Route 84, 2 miles northeast of Naborton, De Soto Parish, La.” [Louisiana, USA]).
Faxonella blairiHayes & Reimer, 1977: 1, figs. 1–7 (“woodland swamp approximately 100 yards W of U.S. Hwy. 259 on N side of the Little River, 7 mi S of Broken Box, McCurtain County, Oklahoma” [USA]).
Faxonella clypeata (Hay, 1899)
= Cambarus clypeatusHay, 1899: 122, fig. 2 (“Bay St. Louis, Mississippi” [USA]).
Faxonella creaseriWalls, 1968: 413, figs. 1–9 (“Louisiana, Caldwell Parish, roadside ditch 3.0 mi. N. of Grayson on U.S. Hwy. 165” [USA]).
FaxoniusOrtmann, 1905a
= FaxoniusOrtmann, 1905a: 97 [type species Astacus limosusRafinesque, 1817, by original designation; gender masculine].
= Orconectes (Billecambarus) Fitzpatrick, 1987a: 47 [type species Cambarus HarrisoniiFaxon, 1884, by original designation; gender masculine].
= Orconectes (Buannulifictus) Fitzpatrick, 1987a: 49 [type species Cambarus palmeriFaxon, 1884, by original designation; gender masculine].
= Orconectes (Crockerinus) Fitzpatrick, 1987a: 50 [type species Cambarus SanborniiFaxon, 1884, by original designation; gender masculine].
= Orconectes (Gremicambarus) Fitzpatrick, 1987a: 53 [type species Cambarus virilisHagen, 1870, by original designation; gender masculine].
= Orconectes (Procericambarus) Fitzpatrick, 1987a: 57 [type species Cambarus forcepsFaxon, 1884, by original designation; gender masculine].
= Orconectes (Rhoadesius) Fitzpatrick, 1987a: 58 [type species Cambarus sloanii Bundy in Forbes, 1876, by original designation; gender masculine].
= Orconectes (Tragulicambarus) Fitzpatrick, 1987a: 60 [type species Cambarus lanciferHagen, 1870, by original designation; gender masculine].
= Orconectes (Trisellescens) Bouchard & Bouchard, 1995: 18 [type species Orconectes etnieri Bouchard & Bouchard, 1976a, by original designation; gender masculine].
Faxonius acares (Fitzpatrick, 1965)
= Orconectes leptogonopodus acaresFitzpatrick, 1965: 87, figs. A–J (“stream tributary to Ouachita River, 6 mi. northwest of Mt. Ida, Montgomery County, Arkansas” [USA]).
Faxonius alabamensis (Faxon, 1884)
= Cambarus AlabamensisFaxon, 1884: 125 (“Second Creek, Waterloo, Lauderdale Co., Ala.” [Alabama, USA]).
Faxonius alluvius (Simon & McMurray, 2014)
= Orconectes (Crockerinus) alluviusSimon & McMurray, 2014: 354, figs. 1, 2 (“Indiana, Greene County: Plummers Creek, at CR 150 E bridge (Old Iron Mountain Road), tributary of West Fork White River, Wabash River basin, 2.66 mi SE Bloomfield, Richland Township, 39.994083N, -86.912754W” [USA]).
Faxonius barrenensis (Rhoades, 1944a)
= Orconectes rusticus barrenensisRhoades, 1944a: 125, fig. 6 (“Barren River, at Beech Bend, 2 mi. n. of Bowling Green, Warren County, Kentucky” [USA]).
Faxonius bisectus (Rhoades, 1944a)
= Orconectes bisectusRhoades, 1944a: 129, fig. 7 (“Brushy Fork, 1 mi. w. of Repton, Crittenden County, Kentucky” [USA]).
Faxonius burri (Taylor & Sabaj, 1998)
= Orconectes burriTaylor & Sabaj, 1998: 645; fig. 1 (“Wildcat Creek at Kentucky Hwy. 280, 12.6 km E Murray, Calloway County, Kentucky” [USA]).
Faxonius carolinensis (Cooper & Cooper, 1995)
= Orconectes (Procericambarus) carolinensisCooper & Cooper, 1995: 67, fig. 1 (“North Carolina, Jones County, Trent River (Neuse River basin) at State Road (SR) 1129 near junction SR1131, ca. 4.5 air mi (7.2 air km) NNE of Comfort (Philips Crossroads USGS Quadrangle, UTM coordinates 3882150/275010” [USA]).
Faxonius castaneus (Johnson, 2010)
= Orconectes (Gremicambarus) castaneusJohnson, 2010: 11, figs. 9, 10, 11, 12a–h, 13a–j (“Lake Brownwood near its spillway, Brown County, Texas (31.84319° N, 99.00236° W)” [USA]).
Faxonius causeyi (Jester, 1967)
= Orconectes causeyiJester, 1967: 518, figs. 1–12 (“Conchas Reservoir, San Miguel Co. (State Road 104), 32 mi NW of Tucumcari, New Mexico” [USA]).
Faxonius chickasawae (Cooper & Hobbs, 1980)
= Orconectes chickasawaeCooper & Hobbs, 1980: 29, fig. 10 (“Town Creek, 3.5 miles (5.6 km) southeast of Muldon, 3 miles (4.8 km) east of State Route 45W (CS: T 16S, R 7E, Sec 7 and 18), Monroe County, Mississippi” [USA]).
Faxonius compressus (Faxon, 1884)
= Cambarus compressusFaxon, 1884: 127 (“Second Creek, Waterloo, Lauderdale Co., Ala.” [Alabama, USA] according to Faxon, 1914).
Faxonius cooperi (Cooper & Hobbs, 1980)
= Orconectes cooperiCooper & Hobbs, 1980: 17, fig. 7. (“Brier Fork of the Flint River at U.S. Highway 231–431, about 2 miles (3.2 km) north of Meridianville (T 2S, R IE, Sec 7), Madison County, Alabama” [USA]).
Faxonius cristavarius (Taylor, 2000)
= Orconectes cristavariusTaylor, 2000: 144, fig. 14 (“Red River at Kentucky Highway 77, 5.6 km NE of Nada, Powell/Menifee County, Kentucky” [USA]).
Faxonius cyanodigitus (Johnson, 2010)
= Orconectes (Hespericambarus) cyanodigitusJohnson, 2010: 3, figs. 2, 3, 4, 5, 8 (“Pat Mayse Lake, Lamar County, Texas (33.84353° N, 95.54163° W)” [USA]).
Faxonius deanae (Reimer & Jester, 1975)
= Orconectes deanaeReimer & Jester, 1975: 17, figs. 1–8 (“Conchas Lake, located at the junction of the Conchas and South Camadian Rivers in San Miguel County, on State Road 104, approx. 32 miles NW of Tucumcari, New Mexico” [USA]).
Faxonius difficilis (Faxon, 1898)
= Cambarus difficilisFaxon, 1898: 656; pl. 65, figs. 1–4 (“McAlester, Pittsburg County, Oklahoma” [USA] according to Hobbs, 1974b).
Faxonius durelli (Bouchard & Bouchard, 1995)
= Orconectes (Procericambarus) durelliBouchard & Bouchard, 1995: 9, figs. 3, 4a (“Green River, off Tn Hwy 13, 2.4 km south of U.S. Hwy 64, Wayne County, Tennessee” [USA]).
Faxonius erichsonianus (Faxon, 1898)
= Orconectes erichsonianusFaxon, 1898: 659; pl. 64; figs. 7–12 (“Rip Roaring Fork, 5 miles northwest of Greeneville, Green County, Tennessee” [USA] according to Hobbs, 1974b).
= Cambarus spinosus gulielmiFaxon, 1914: 375 (“small stream flowing from a pond fed by the cave stream known as John Ross Spring, near Rossville, Walker Co., Georgia” [USA]).
Faxonius etnieri (Bouchard & Bouchard, 1976a)
= Orconectes etnieriBouchard & Bouchard, 1976a: 459, fig. 1 (“Robinson Creek at Tennessee State Highway 57 (Tennessee River system), Hardin County, Tennessee” [USA]).
Faxonius eupunctus (Williams, 1952)
= Orconectes eupunctusWilliams, 1952: 330; pl. 1, figs. 1–8 (“Eleven Point River at Riverton, Oregon County, Missouri” [USA]).
Faxonius forceps (Faxon, 1884)
= Cambarus forcepsFaxon, 1884: 133 (“Cyprus Creek, Lauderdale Co., Ala.” [Alabama, USA]).
Faxonius harrisonii (Faxon, 1884)
= Cambarus HarrisoniiFaxon, 1884: 130 (“Irondale, Washington County, Missouri” [USA] according to Hobbs, 1974b).
Faxonius hartfieldi (Fitzpatrick & Suttkus, 1992)
= Orconectes hartfieldiFitzpatrick & Suttkus, 1992: 70, fig. 1 (“Turkey Creek, about 6 mi (9.7 km) northeast of Coffeeville, 0.2 mi (0.3 km) east of State Route 32; T25N, R7E section 18, Yalobusha County, Mississippi” [USA]).
Faxonius hathawayi blacki (Walls, 1972)
= Orconectes difficilis blackiWalls, 1972: 454, figs. 3a–e, 4a (“Louisiana, Beauregard Parish, Bearhead Creek on La. St. Hwy. 109, 4 mi. SW Juanita” [USA]).
Faxonius hathawayi hathawayi (Penn, 1952)
= Orconectes (Orconectes) hathawayiPenn, 1952: 1; pl. 1, figs. 1–13 (“Spring Creek, 5.1 mi. east of Hineston (on Louisiana state highway 85), Rapides Parish, Louisiana” [USA]).
Faxonius hobbsi (Penn, 1950b)
= Orconectes hobbsiPenn, 1950b: 381, figs. 1–10 (“headwater creek of Bayou Lacombe at St. Tammany (6 miles north of Lacombe on Louisiana State Highway 187), St. Tammany Parish, La.” [Louisiana, USA]).
Faxonius holti (Cooper & Hobbs, 1980)
= Orconectes holtiCooper & Hobbs, 1980: 23, figs. 8, 9. (“Bogue Chitto Creek, 2.3 miles (3.7 km) west of Marion on State Route 14 (T 19N, R 7E, Sec 11), Perry County, Alabama” [USA]).
Faxonius hylas (Faxon, 1890)
= Cambarus hylasFaxon, 1890: 632 (“West Fork of Black River, Reynolds County, Missouri” [USA]).
Faxonius illinoiensis (Brown, 1956)
= Orconectes illinoiensisBrown, 1956: 163, figs. 1–9 (“Cypress Creek, 3¼ mi. south of Mt. Pleasant, Union County, Illinois” [USA]).
Faxonius immunis (Hagen, 1870)
= Cambarus immunisHagen, 1870: 71; pl. 1, figs. 101, 102; pl. 3, fig. 160; pl. 8, fig. b (“Lawn Ridge, Marshall County, Illinois” [USA] according to Hobbs, 1974b).
= Cambarus signiferHerrick, 1882: 253, fig. 7 [“Grass Lake, in Richfield, Hen. Co.” [Hennepin County, Minnesota, USA]).
= Cambarus immunis var. spinirostrisFaxon, 1884: 146 (“Obion Co., Tennessee” [USA]).
= Faxonius immunis pedianusCreaser, 1933: 14 (“Colorado, Denver County, reservoir at Englewood” [USA]).
Faxonius indianensis (Hay, 1896)
= Cambarus indianensisHay, 1896: 494, fig. 9 (“Patoka River, Patoka, Gibson County” [Indiana, USA] according to Hobbs, 1974b).
Faxonius jeffersoni (Rhoades, 1944a)
= Orconectes propinquus jeffersoniRhoades, 1944a: 123, fig. 5 (“tributary to Muddy Fork of Beargrass Creek, 2 mi. e. of Louisville corporation line, on USR-42, Jefferson County, Kentucky” [USA]).
Faxonius jonesi (Fitzpatrick, 1992)
= Orconectes (Gremicambarus) jonesiFitzpatrick, 1992: 780, fig. 1 (“Pawticfaw Creek at unnumbered hard-surfaced road, 3.1 mi (5.0 km) SSE of State Route 39; T10N, R16E, sec, 27/34, Kemper County, Mississippi” [USA]).
Faxonius juvenilis (Hagen, 1870)
= Cambarus juvenilisHagen, 1870: 66; pl. 1, figs. 29–33; pl. 3, fig. 157 (“Kentucky River, Little Hickman, Jessamine County, Kentucky” [USA] according to Hobbs, 1974b).
Faxonius kentuckiensis (Rhoades, 1944a)
= Orconectes kentuckiensisRhoades, 1944a: 122, fig. 4 (“Piney Creek, 3 mi. w. of Shady Grove, Crittenden County, Kentucky” [USA]).
Faxonius lancifer (Hagen, 1870)
= Cambarus lanciferHagen, 1870: 59; pl. 1, figs. 86, 87; pl. 3, fig. 159 (“Tallahatchie River at Rocky Ford, near the town of Etta, Union County, Mississippi” [USA] according to Penn, 1939).
= Cambarus faxoniiMeek, 1894: 1042, figs. 1, 2, 3, 4 (“St. Francis River at Greenway and Big Bay” [Arkansas, USA]).
Faxonius leptogonopodus (Hobbs, 1948b)
= Orconectes leptogonopodusHobbs, 1948b: 146, figs. 24–32 (“McKinney’s Creek, 4.7 miles northeast of Hatfield, Polk County, Arkansas, on U.S. Hy. 71” [USA]).
Faxonius limosus (Rafinesque, 1817)
= Astacus limosusRafinesque, 1817; 42 (“muddy banks of the Delaware, near Philadelphia” [Pennsylvania USA]).
= Astacus affinisSay, 1817: 168 (“the river Delaware” [USA]).
= Cambarus PealeiGirard, 1852: 87 (“Potomac, at Washington (D.C.)” [USA]).
Faxonius longidigitus (Faxon, 1898)
= Cambarus longidigitusFaxon, 1898: 653; pl. 62, figs. 6–9 (“Oxford Bend, White River, Arkansas” [USA]).
= Cambarus whitmaniSteele, 1902: 24; pl. 3, figs. C1–2; pl. 5, fig. B (“James River, Missouri” [USA]).
Faxonius luteusCreaser, 1933: 7; pl. 1, figs. 3, 4 (“Niangua River at mouth of Greasy Creek, 5 miles southeast of Buffalo, Dallas County, Missouri” [USA]).
Faxonius macrus (Williams, 1952)
= Orconectes nana macrusWilliams, 1952: 337; pl. 2, figs. 17–24 (“Spring River, 2 mi. SW Mt. Vernon, Lawrence County, Missouri” [USA]).
Faxonius maletae (Walls, 1972)
= Orconectes difficilis maletaeWalls, 1972: 456, figs. 2a–e, 4b (“Louisiana, Natchitoches Parish, Bayou Santabarb on La. St. Hwy. 117 (third branch north of Kisatchie)” [USA]).
Faxonius marchandi (Hobbs, 1948b)
= Orconectes marchandiHobbs, 1948b: 140, figs. 1, 2, 3, 4, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14 (“small, clear rocky stream of moderate current 3.2 miles southeast of Hardy, Sharp County, Arkansas, on U.S. Hy. 63 [USA]).
Faxonius margorectus (Taylor, 2002)
= Orconectes margorectusTaylor, 2002: 129, figs. 1, 2A (“Ferguson Creek at Kentucky Hwy. 70, 3.2 km E Smithland, Livingston County, Kentucky” [USA]).
Faxonius medius (Faxon, 1884)
= Cambarus mediusFaxon, 1884: 121 (“Irondale, Mo.” [Washington County, Missouri, USA]).
Faxonius meeki brevis (Williams, 1952)
= Orconectes meeki brevisWilliams, 1952: 348; pl. 3 (“stream approx. 5 mi. N Stillwell, on U.S. highway number 59, Adair County, Oklahoma” [USA]).
Faxonius meeki meeki (Faxon, 1898)
= Cambarus meekiFaxon, 1898: 658; pl. 65, figs. 5–9 (“Walnut Fork of Big Piney Creek, Swain, Newton County, Arkansas” [USA] according to Hobbs, 1974b).
Faxonius menaeCreaser, 1933: 5; pl. 1, figs. 9, 10 (“stream tributary to Irons Fork of Ouachita River at Mena, Polk County, Arkansas” [USA]).
Faxonius mirus (Ortmann, 1931)
= Cambarus (Faxonius) rusticus mirusOrtmann, 1931: 81 (“Hurricane Creek, Cumberland Springs, Moore County, Tennessee” [USA] according to Hobbs, 1974b).
Faxonius mississippiensis (Faxon, 1884)
= Cambarus MississippiensisFaxon, 1884: 123 (“Macon, Noxubee County, Mississippi” [USA] according to Faxon, 1914).
Faxonius nais (Faxon, 1885b)
= Cambarus NaisFaxon, 1885b: 140 (“Labette Co.” [Kansas, USA]).
= Cambarus pilosusHay, 1899: 121, fig. 1 (“Beloit, Mitchell County, Kansas” [USA]).
Faxonius nana (Williams, 1952)
= Orconectes nanaWilliams, 1952: 333; pl. 1, figs. 9–16 (as O. nana nana) (“Flint Creek, 5 mi. E Kansas, Delaware County, Oklahoma” [USA]).
Faxonius neglectus chaenodactylus (Williams, 1952)
= Orconectes neglectus chaenodactylusWilliams, 1952: 344; pl. 3, figs. 33–40 (“Whites Creek, 8 6/10 mi. SE Ava, Douglas County, Missouri” [USA]).
Faxonius neglectus neglectus (Faxon, 1885b)
= Cambarus neglectusFaxon, 1885b: 142 (“Mill Creek, Wabaunsee Co.” [Kansas, USA]).
Faxonius obscurus (Hagen, 1870)
= Cambarus obscurusHagen, 1870: 69; pl. 1, figs. 72–75; pl. 3, fig. 154 (“Genesee River, Rochester, Monroe County, New York” [USA]; lectotype designated by Fitzpatrick, 1967a: 162).
Faxonius occidentalis (Johnson, 2010)
= Orconectes (Buannulifictus) occidentalisJohnson, 2010: 19, figs. 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24 (“Guadalupe River @ Rt. 1376, Kendall County, Texas (29.95760° N, 98.71735° W)” [USA]).
Faxonius ozarkae (Williams, 1952)
= Orconectes ozarkaeWilliams, 1952: 339; pl. 2, figs. 25–32 (“Hackney Creek, 4 6/10 mi. WSW Stuart, Sharp County, Arkansas” [USA]).
Faxonius pagei (Taylor & Sabaj, 1997)
= Orconectes pageiTaylor & Sabaj, 1997: 263, figs. 1, 2 (“Morris Creek at Tennessee Hwy. 424, 0.5 km W jct. W/Tennessee Hwy. 114, 1.6 km NE Yuma, Carroll County, Tennessee” [USA]).
Faxonius palmeri creolanusCreaser, 1933
= Faxonius creolanusCreaser, 1933: 16; pl. 1, figs. 1–2 (“stream tributary to the Amite River, one-half mile north of Ethel, East Feliciana Parish, Louisiana” [USA]).
Faxonius palmeri longimanus (Faxon, 1898)
= Cambarus palmeri longimanusFaxon, 1898: 655; pl. 64, figs. 1–6 (“Red River, Arthur City, Lamar County, Texas” [USA] according to Hobbs, 1974b).
Faxonius palmeri palmeri (Faxon, 1884)
= Cambarus PalmeriFaxon, 1884: 124 (“brook running into the eastern side of Rod Foot Lake, near Idlewild Hotel, Obion Co., Tenn.” [Tennessee, USA]).
Faxonius pardalotus (Wetzel, Poly & Fetzner, 2005)
= Orconectes (Procericambarus) pardalotusWetzel, Poly & Fetzner, 2005: 59, figs. 1, 2, 3 (“Ohio River at Lock & Dam 53, 5 km NE of Olmsted, Pulaski Co., T15S, R2E, Sec. 18, NW 1/4, Lat.Long.: 37°12ʹ12ʺ/89°02ʹ29ʺ” [Illinois, USA]).
Faxonius perfectus (Walls, 1972)
= Orconectes perfectusWalls, 1972: 451, figs. 1A–E, 4C (“Alabama, Clarke Co., Satilpa Creek, 8.7 mi. E Grove Hill” [USA]).
Faxonius peruncus (Creaser, 1931)
= Cambarus (Faxonius) peruncusCreaser, 1931: 7; pl. 5 (“Little Creek, tributary to the St. Francis River, one mile northeast of Chloride, Iron County, Missouri” [USA]).
Faxonius placidus (Hagen, 1870)
= Cambarus placidusHagen, 1870: 65; pl. 1, figs. 7–79; pl. 3, fig. 158 (“Lebanon, Wilson County, Tennessee” [USA] according to Hobbs, 1974b).
Faxonius propinquus (Girard, 1852)
= Cambarus propinquusGirard, 1852: 88 (“Oswego, Oswego County, New York” [New York state, USA] according to Hobbs, 1974b).
= Cambarus propinquus typicusOrtmann, 1905a: 133 [no type locality designated].
= Orconectes iowaensisFitzpatrick, 1968: 507, figs. 1–10 (“Turkey River, 2½ mi S of Cresco, Howard Co., Iowa” [USA]).
Faxonius punctimanusCreaser, 1933: 1; pl. 1, figs. 5–6 (“Rubidoux Creek at Waynesville, Pulaski County, Missouri” [USA]).
Faxonius putnami (Faxon, 1884)
= Cambarus PutnamiFaxon, 1884: 131 (“Bear Creek, Grayson Springs, Grayson County, Kentucky” [USA] according to Hobbs, 1974b).
Faxonius quadruncusCreaser, 1933: 10; pl. 1, figs. 11–12 (“Stout’s Creek tributary to St. Francis River, between Ironton and Arcadia, Iron County, Missouri” [USA]).
Faxonius quinebaugensis (Mathews & Warren, 2008)
= Orconectes (Gremicambarus) quinebaugensisMathews & Warren, 2008: 374, fig. 1 (“Quinebaug River in Sturbridge, Massachusetts, at East Brimfield Dam” [Worcester County, Massachusetts, USA]).
Faxonius rafinesquei (Rhoades, 1944a)
= Orconectes rafinesqueiRhoades, 1944a: 116, fig. 1 (“Rough River, at Falls-of-Rough, Grayson-Breckenridge counties, Kentucky” [USA]).
Faxonius raymondi (Thoma & Stocker, 2009)
= Orconectes (Procericambarus) raymondiThoma & Stocker, 2009: 405, fig. 1 (“Ohio, Brown County, Pleasant/Union Townships, Straight Creek at Straight Creek Road (Old US 66) bridge at Center Point, 38°47ʹ56ʺN -83°53ʹ23ʺW” [USA]).
Faxonius rhoadesi (Hobbs, 1949)
= Orconectes rhoadesiHobbs, 1949: 19; pl. 3 (“Otter Creek between Granny White Pike and Hillsboro Pike, about seven miles south of Nashville, Davidson County, Tennessee” [USA]).
Faxonius ronaldi (Taylor, 2000)
= Orconectes ronaldiTaylor, 2000: 141, fig. 13 (“Mud River at Kentucky Highway 79, 4.0 km NE of Russellville, Logan County, Kentucky” [USA]).
Faxonius rusticus (Girard, 1852)
= Cambarus rusticusGirard, 1852: 88 (“The Ohio, at Cincinnati” [Ohio, USA]).
Faxonius sanbornii erismophorous (Hobbs & Fitzpatrick, 1962)
= Orconectes propinquus erismophorousHobbs & Fitzpatrick, 1962: 208, figs. 1–15 (“Crane Nest Creek at Pee Wee, Wirt County, West Virginia” [USA]).
Faxonius sanbornii sanbornii (Faxon, 1884)
= Cambarus SanborniiFaxon, 1884: 128 (“Oberlin, Lorain Co., Ohio” [USA]; lectotype designated by Fitzpatrick, 1967a: 157).
Faxonius saxatilis (Bouchard & Bouchard, 1976b)
= Orconectes saxatilisBouchard & Bouchard, 1976b: 439, fig. 1 (“Pigeon Creek at Oklahoma State Highway 63 (Red River basin via Kaimichi River system), LeFlore County, Oklahoma” [USA]).
Faxonius shoupi (Hobbs, 1948c)
= Orconectes shoupiHobbs, 1948c: 14, figs. 1–5, 15, 16 (“Mill Creek, tributary of Cumberland River, east of Oglesby near Antioch Pike, 10 miles south of Nashville, Davidson County, Tenn.” [Tennessee, USA]).
Faxonius sloanii (Bundy in Forbes, 1876)
= Cambarus sloanii Bundy in Forbes, 1876: 24 (“New Albany, Floyd County, Indiana” [USA] according to Hobbs, 1974b).
Faxonius spinosus (Bundy, 1877)
= Cambarus spinosusBundy, 1877: 173 (“Etowah, Oostanaula and Coosa Rivers, in the vicinity of Rome, Georgia” [USA]).
Faxonius stannardi (Page, 1985)
= Orconectes stannardiPage, 1985: 564, fig. 1 (“Little Wabash River at Secondary Road 719, 6 km NNW Louisville (T5N, R6E, Sec. 33SW), Clay County, Illinois” [USA]).
Faxonius stygocaneyi (Hobbs, 2001)
= Orconectes (Orconectes) stygocaneyiHobbs, 2001: 637, fig. 2 (“Mud Cave, Caney Mountain Conservation Area (Missouri Department of Conservation), Ozark County, Missouri, 36°41ʹ32ʺN 92°25ʹ47ʺW” [USA]).
Faxonius taylori (Schuster, 2008)
= Orconectes (Trisellescens) tayloriSchuster, 2008: 63, figs. 1, 2 (“Terrapin Creek at Tennessee State Route (SR) 69 crossing, approximately 1.4 km NE of Midway, Henry County, Tennessee (36.4984°N 88.4903°W) [USA]).
Faxonius texanus (Johnson, 2010)
= Orconectes (Buannulifictus) texanusJohnson, 2010: 31, figs. 25–29, 30a–o, 31a–h, 32, 33, 34 (“Trinity River just downstream of the spillway of the Lake Livingston dam, Polk County, Texas (30.62590° N, 95.00848° W)” [USA]).
Faxonius theaphionensis (Simon, Timm & Morris, 2005)
= Orconectes (Procericambarus) theaphionensisSimon, Timm & Morris, 2005: 44, figs. 2–12 (“Half Moon Springs at bridge at Indiana County Road 200 E, 2.57 km W of Chambersburg, Paoli Township, Orange County, Indiana; 38.5207348 °N 86.4229192° W” [USA]).
Faxonius transfuga (Fitzpatrick, 1966a)
= Orconectes transfugaFitzpatrick, 1966a: 178, figs. A–T (“Rogue River, 6 miles upstream from Grants Pass [Jackson County], Oregon” [USA]).
Faxonius tricuspis (Rhoades, 1944a)
= Orconectes tricuspisRhoades, 1944a; 117, fig. 2 (“Pete Light’s Spring, 3 mi. e. of Canton, Trigg County, Kentucky” [USA]).
Faxonius validus (Faxon, 1914)
= Cambarus validusFaxon, 1914: 382; pl. 7, figs. 3, 4, 8; pl. 13, fig. 1 (“Huntsville, Madison Co., Alabama” [USA]).
Faxonius virginiensis (Hobbs, 1951a)
= Orconectes virginiensisHobbs, 1951a: 122, figs. 1–10 (“Rowanty Creek, a tributary of the Nottoway River, Chowan River drainage, at the crossing of U.S. Highway 301, Sussex County, 4.8 (air) km south of Carson” [Virginia, USA] according to Stinson, 1997).
Faxonius virilis (Hagen, 1870)
= Cambarus virilisHagen, 1870: 63; pl. 1, figs. 23–28; pl. 2, figs. 128–132; pl. 3, fig. 155; pl. 8 (“Lake Superior”, restricted by Faxon, 1914).
= Cambarus wisconsinensis Bundy in Forbes, 1876: 4 (“Normal, Ill. and Racine, Wis.” [Illinois and Wisconsin, USA]).
= Cambarus debilis Bundy in Forbes, 1876: 24 (“Baraboo River, Ironton; Wisconsin River, Sauk City, Wisconsin” [USA]).
= Cambarus couesiStreets, 1877: 803 (“Red River of the North, near Pembina” [North Dakota, USA]).
Faxonius williamsi (Fitzpatrick, 1966b)
= Orconectes williamsiFitzpatrick, 1966b: 145, figs. 1–10 (“White River, 2.8 miles east of Pettigrew, Madison County, Arkansas” [USA]).
Faxonius wrighti (Hobbs, 1948d)
= Orconectes wrightiHobbs, 1948d: 85; pl. 3 (“Robinson Creek, State Highway 57, Hardin County, Tennessee” [USA]).
Faxonius yanahlindus (Taylor, Rhoden & Schuster, 2016)
= Orconectes yanahlindusTaylor, Rhoden & Schuster, 2016: 168, figs. 6, 7 (“Big Creek at State Road 99 bridge crossing, Limestone County, Alabama (34.8519°N, -87.0416°W NAD 83)” [USA]).
HobbseusFitzpatrick & Payne, 1968
= HobbseusFitzpatrick & Payne, 1968: 15 [type species Cambarus cristatusHobbs, 1955, by original designation; gender masculine].
Hobbseus attenuatusBlack, 1969: 193, figs. 1–12 (“roadside ditch adjacent to Noxapater Creek, on gravel road two miles north of State Route 395, six miles west of Noxapater, Winston County, Mississippi (R 11E, T 14N)” [USA]).
Hobbseus cristatus (Hobbs, 1955)
= Cambarus cristatusHobbs, 1955: 95, figs. 1–11 (“roadside ditch, 11.3 miles south of Macon on Route 45, Noxubee County, Mississippi” [USA]).
Hobbseus orconectoidesFitzpatrick & Payne, 1968: 17, figs. 1–12 (“woodland pool near Rock Hill community, about 4¼ mi. N of Starkville, Oktibbeha County, Mississippi (R14E T19N Sec. 1)” [USA]).
Hobbseus petilusFitzpatrick, 1977: 367, fig. 1 (“unnamed tributary of Patch Creek (Tombigbee River drainage), 11.8 km E of U.S. Highway 45 in Saltillo, on State Route 363” [Lee County, Mississippi, USA]).
Hobbseus prominens (Hobbs, 1966)
= Cambarus prominensHobbs, 1966: 110, figs. 1–10 (“roadside ditch, three miles west of Demopolis, Sumter County, Alabama, on U.S. Rte. 80” [USA]).
Hobbseus valleculus (Fitzpatrick, 1967b)
= Cambarus valleculusFitzpatrick, 1967b: 163, figs. 1–12 (“small creek, 6.8 mi. S junction of State Routes 15 and 12 (Ackerman) on State Route 15, Choctaw County, Mississippi” [USA]).
Hobbseus yalobushensisFitzpatrick & Busack, 1989: 637, fig. 1 (“Topashaw Creek, 3.8 airmi. (6.1 km) SW of Mantee (jct. of St. Rtes. 15 and 46), T21N, R11E, at the boundary of Secs. 2 and 11, Webster County, Mississippi” [USA]).
OrconectesCope, 1872
= OrconectesCope, 1872: 419 [type species Orconectes inermisCope, 1872; by subsequent designation in Fowler (1912); gender masculine].
= Orconectes (Hespericambarus) Fitzpatrick, 1987a: 54 [type species Orconectes inermisCope, 1872, by original designation; gender masculine].
Orconectes australis (Rhoades, 1941)
= Cambarus (Faxonius) pellucidus australisRhoades, 1941: 142, fig. 35 (“Shelta Cavern, SE¼ NE¼ sec. 17, T. 3S., R. 1 W., north of Huntsville, Madison County, Ala.” [Alabama, USA]).
Orconectes barriBuhay & Crandall, 2008
= Orconectes (Orconectes) barriBuhay & Crandall, 2008: 61, figs. 5, 6 (“Tonya’s Cave, on Route 200, 2.5 km south of Powersburg, Wayne County, Kentucky” [USA]).
Orconectes incomptusHobbs & Barr, 1972: 32, fig. 9 (“Cherry Cave, lat. 36°28ʹ09ʺN, long. 85°36ʹ28ʺW, Jackson County, Tennessee” [USA]).
Orconectes inermis inermisCope, 1872
= Orconectes inermisCope, 1872: 419, fig. 116 (“Wyandotte Cave” [Crawford County, Indiana, USA]).
Orconectes inermis testii (Hay, 1891)
= Cambarus pellucidus var. testiiHay, 1891: 149 (“Mayfield’s cave, SW¼NE¼SW¼ sec. 26, T. 9 N, R. 2 W., Monroe County, Indiana” [USA] according to Hobbs, 1974b).
= Cambarus pellucidus testiiHay, 1893: 285, pls. 44, 45, figs. 1–14. (“Mayfield’s cave, SW¼NE¼SW¼ sec. 26, T. 9 N, R. 2 W., Monroe County, Indiana” [USA] according to Hobbs, 1974b).
Orconectes packardiRhoades, 1944a
= Orconectes pellucidus packardiRhoades, 1944a: 121, fig. 3 (“Cumberland Crystal Cave, at Alpine, Pulaski County, Kentucky” [USA]).
Orconectes pellucidus (Tellkampf, 1844)
= Astacus pellucidusTellkampf, 1844: 684 (“Mammoth Cave, Edmonson County, Kentucky” [USA] according to Hobbs, 1974b).
= Cambarus typhlobiusJoseph, 1880: 202 (“Krain” [= Carniola, Slovenia] according to Holthuis, 1964a; in error, see Holthuis, 1964a).
= Cambarus coecusJoseph, 1881: 237 [nomen nudum].
= Cambarus stygiusJoseph, 1881: 241 [nomen nudum].
= Cambarus stygiusJoseph, 1882: 12 (“Reccafluss aus der Grotte von S. Kanzian bei Mataùn unweit Divazza” [= Reka River in St Canzian Cave, near Matavunje, not far from Divača, Slovenia] according to Holthuis, 1964a; in error, see Holthuis, 1964a).
Orconectes sheltaeCooper & Cooper, 1997b
= Orconectes (Orconectes) sheltaeCooper & Cooper, 1997b: 119, figs. 1, 2A (“Alabama, Madison County, Huntsville, Shelta Cave (Meridianville 7.5ʹ USGS Quadrangle, Sec. 27., T.3S, R.1W)” [USA]).
Palaeocambarus ††Taylor, Schram & Shen, 1999
= PalaeocambarusTaylor, Schram & Shen, 1999: 122 [type species Astacus licentiVan Straelen, 1928b, by original designation; gender masculine].
Palaeocambarus licenti †† (Van Straelen, 1928b)
= Astacus licentiVan Straelen, 1928b: 133; pl. 1 (“S.W. of Moukden, in Eastern Mongolia” [= SW of Shenyang, Liaoning Province, P.R. of China]).
= Astacus spinirostriusImaizumi, 1938: 176; pl. 22; pl. 23, figs. 9, 10, 12, 13 (“Niehhutzekow, near Lingyuan, Jehol” [= near Lingyuan City, Liaoning Province, P.R. of China]).
Procambarus †Ortmann, 1905b
= Cambarus (Cambarus) Ortmann, 1905a (nec Erichson, 1846): 96 [type species Astacus BlandingiiHarlan, 1830; by original designation; gender masculine].
= Cambarus (Procambarus) Ortmann, 1905b: 437 [type species Cambarus DiguetiBouvier, 1897, by subsequent designation of Fowler (1912); gender masculine].
= Cambarus (Paracambarus) Ortmann, 1906b: 1 [type species Cambarus (Paracambarus paradoxusOrtmann, 1906b, by monotypy; gender masculine].
= Cambarus (Ortmannicus) Fowler, 1912: 340 [replacement name for Cambarus (Cambarus) Ortmann, 1905a (nec Erichson, 1846)].
= Procambarus (Girardiella) Lyle, 1938: 76 [type species Cambarus HagenianusFaxon, 1884, by monotypy; gender feminine].
= Procambarus (Acucauda) Hobbs, 1972b: 5 [type species Procambarus fitzpatrickiHobbs, 1971a; by original designation; gender feminine].
= Procambarus (Austrocambarus) Hobbs, 1972b: 5 [type species Procambarus vazquezaeVillalobos F., 1954a; by original designation; gender masculine].
= Procambarus (Capillicambarus) Hobbs, 1972b: 6 [type species Cambarus hineiOrtmann, 1905d; by original designation; gender masculine].
= Procambarus (Hagenides) Hobbs, 1972b: 7 [type species Astacus advenaLe Conte, 1856; by original designation; gender masculine].
= Procambarus (Leconticambarus) Hobbs, 1972b: 7 [type species Cambarus barbatusFaxon, 1890; by original designation; gender masculine].
= Procambarus (Lonnbergius) Hobbs, 1972b: 8 [type species Cambarus acherontisLönnberg, 1895; by original designation; gender masculine].
= Procambarus (Mexicambarus) Hobbs, 1972b: 8 [type species Cambarus bouvieriOrtmann, 1909; by original designation; gender masculine].
= Procambarus (Pennides) Hobbs, 1972b: 10 [type species Procambarus natchitochaePenn, 1953a; by original designation; gender masculine].
= Procambarus (Remoticambarus) Hobbs, 1972b: 11 [type species Procambarus peckiHobbs, 1967a; by original designation; gender masculine].
= Procambarus (Scapulicambarus) Hobbs, 1972b: 11 [type species Cambarus paeninsulanusFaxon, 1914; by original designation; gender masculine].
= Procambarus (Villalobosus) Hobbs, 1972b: 12 [type species Procambarus riojaeVillalobos, 1944a; by original designation; gender masculine].
Procambarus ablususPenn, 1963: 121, figs. 1–10 (“Hatchie River, 12.1 miles E of Ripley (State hwy. 4), Tippah County, Mississippi” [USA]).
Procambarus acanthophorusVillalobos F., 1948: 175; pls. 1, 2 (“pequeña laguna situada en El Castillo, 4 Km. al oeste de Tuxpetec, Oax.” [= small lagoon at El Castillo, 4 km east of Tuxpetec, Oaxaca, Mexico]).
Procambarus acherontis (Lönnberg, 1895)
= Cambarus acherontisLönnberg, 1894: 127 (“subterranean rivulet about 30 feet from surface, Lake Brantley, Seminole County, Florida” [USA] according to Hobbs, 1974b; neotype designated in Hobbs, 1940a: 393; rejected by Hobbs, 1974b: 52).
= Cambarus acherontisLönnberg, 1895: 6, figs. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5b (“Lake Brantley, Orange County” [= Seminole County, Florida, USA]).
Procambarus achilliLópez, Mejía & Alvarez, 2003
= Procambarus (Villalobosus) achilliLópez, Mejía & Alvarez, 2003: 524, figs. 1, 2 (“Cascada del Arroyo de Atezca, 5 km NW from Molango, Hidalgo, Mexico”).
Procambarus acutissimus (Girard, 1852)
= Cambarus acutissimusGirard, 1852: 91 (“affluent of Mobile River in Kemper Co., Miss.” [Mississippi, USA]).
Procambarus acutus (Girard, 1852)
= Cambarus acutusGirard, 1852: 91 (“affluent of Mobile River in Kemper Co., Miss. [Mississippi, USA]).
= Cambarus stygius Bundy in Forbes, 1876: 3 (“Lake Michigan” [USA]).
Procambarus advena (Le Conte, 1856)
= Astacus advenaLe Conte, 1856: 402 (“Georgia inferiore”; restricted by Hobbs, 1974b to “2.5 miles west of Riceboro, Liberty County, Georgia” [USA]).
Procambarus alleni (Faxon, 1884)
= Cambarus AlleniFaxon, 1884: 110 (“St. John’s River, Hawkinsville, Orange Co., Fla. [Orange County, Florida, USA]).
Procambarus ancylusHobbs, 1958a: 164, figs. 13–24 (“Summerville, Dorchester County, S. C.” [South Carolina, USA]).
Procambarus angustatus (Le Conte, 1856)
= Astacus angustatusLe Conte, 1856: 401 (“Georgia inferiore” [= sandhills of southern Georgia [USA] according to Hobbs, 1981).
Procambarus apalachicolaeHobbs, 1942b: 55; pl. 3, figs. 26–30; pl. 17 (“roadside ditch in wire grass flatwoods, 11.1 miles west of Beacon Hill, U.S. Highway 98, Bay County, Florida” [USA]).
Procambarus atkinsoni (Ortmann, 1913)
= Cambarus (Procambarus) atkinsoniOrtmann, 1913: 414 (“tributarios del Río de los Indios, Isla de Pinos, Cuba”; lectotype (as lectoholotype) designated by Hobbs & Villalobos, 1964: 347, valid designation under Art. 74.5 (ICZN, 1999)).
Procambarus attiguusHobbs & Franz, 1992
= Procambarus (Ortmannicus) attiguusHobbs & Franz, 1992: 359, fig. 1 (“Silver Glen Springs, 9 mi (14.4 km) northwest of Astor Park, Marion County, Florida (SE ¼, NE ¼, SE ¼, Sec. 25 T.14S, R. 26E)” [USA]).
Procambarus barbatus (Faxon, 1890)
= Astacus penicillatusLe Conte, 1856 (nec Olivier, 1791): 401 (“2.5 miles west of Riceboro, Liberty County, Georgia” [USA]; neotype designated by Hobbs, 1974b: 50).
= Astacus barbatusFaxon, 1890: 621 (replacement name for Astacus penicillatusLe Conte, 1856 (nec Olivier, 1791)).
Procambarus barbigerFitzpatrick, 1978c
= Procambarus (Girardiella) barbigerFitzpatrick, 1978c: 69, figs. 37–52 (“Forrest, Scott County, Mississippi” [USA]).
Procambarus bivittatusHobbs, 1942b: 96; pl. 6, figs. 96–100; pl. 21 (“sloughs along the Escambia River on State Highway 62, Escambia County, Florida” [USA]).
Procambarus blandingii (Harlan, 1830)
= Astacus BlandingiiHarlan, 1830: 464 (“Camden, Kershaw County, South Carolina” [USA] according to Hobbs, 1974b).
Procambarus bouvieri (Ortmann, 1909)
= Cambarus (Cambarus) bouvieriOrtmann, 1909: 159, figs. 1, 2 (“petit riviêre torrentueuse à Uruapan, État de Michoacan, Mexique” [= small, fast-flowing river at Uruapan, Michoacán, Mexico]).
Procambarus braswelliCooper, 1998
= Procambarus (Ortmannicus) braswelliCooper, 1998: 82, fig. 1 (“North Carolina, Columbus County, Waccamaw River at NC 130 near Brunswick County line, 8.0 air km (5.6 air mi) SSE of Old Dock (Freeland USG quadrangle, UTM coordinates 3775210/726190E)” [USA]).
Procambarus brazoriensisAlbaugh, 1975
= Procambarus (Capillicambarus) brazoriensisAlbaugh, 1975: 1, fig. 1 (“ditch beside County Road 400, 0.1 mile SE of Missouri Pacific railroad and 0.25 mile SW of Brazos River, at S edge of Brazoria, Brazoria County, Texas” [USA]).
Procambarus caballeroiVillalobos, 1944b: 175; pls. 1, 2 (“riachuelos del Sur de Villa Juárez, Estado de Puebla” [= Xicotepec, Mexico]).
Procambarus capillatusHobbs, 1971b: 83, fig. 1(“drainage ditch adjacent to Burnt Corn Creek (Escambia River drainage) on State Route 41, northwest of Brewton, Escambia County, Alabama” [USA]).
Procambarus caritusHobbs, 1981
= Procambarus (Hagenides) caritusHobbs, 1981: 319, figs. 17d, 118b, 122, 123, 236 (“seepage area, 3.7 miles west of Glenwood, Wheeler County, on U.S. Highway 280” [Georgia, USA]).
Procambarus catemacoensisRojas, Alvarez & Villalobos, 2000
= Procambarus (Austrocambarus) catemacoensisRojas, Alvarez & Villalobos, 2000: 792, figs. 1, 2 (“Espagoya, Lake Catemaco (altitude 335 m), Municipio de Catamaco, Veracruz, Mexico (18°27ʹN, 95°6ʹW)”).
Procambarus cavernicolaMejía-Ortiz, Hartnoll & Viccon-Pale, 2003
= Procambarus (Austrocambarus) cavernicolaMejía-Ortiz, Hartnoll & Viccon-Pale, 2003: 392, figs. 1, 2 (“Cueva Gabriel, municipio de Acatlán de Pérez Figueroa, Oaxaca” [Mexico]).
Procambarus ceruleusFitzpatrick & Wicksten, 1998
= Procambarus (Girardiella) ceruleusFitzpatrick & Wicksten, 1998: 146, fig. 1 (“horse pasture on Riley Road, Reliance community, 0.7 mi (1.4 km) east of Farm to Market (FM on maps) Road 1179, east of Bryan, Brazos County, Texas, latitude and longitude approximately 30°45ʹN, 96°14ʹW” [USA]).
Procambarus chacalliLópez-Mejía, Alvarez & Mejía-Ortíz, 2004
= Procambarus (Villalobosus) chacalliLópez-Mejía, Alvarez & Mejía-Ortíz, 2004: 170, figs. 1, 2 (“nacimiento de Dejigui (altitude 1675 m), 4 km east of Huayacocotla, Municipio de Huayacocotla, Veracruz, Mexico (20°32ʹ6ʺN 98°26ʹ15ʺW)”).
Procambarus chaceiHobbs, 1958b: 5; pl. 2 (“Cedar Creek, three miles east of Lykes, Richland County, South Carolina, on U.S. Hy. 76” [USA]).
Procambarus citlaltepetlRojas, Alvarez & Villalobos, 1999
= Procambarus (Austrocambarus) citlaltepetlRojas, Alvarez & Villalobos, 1999: 398, figs. 2A–C, 3A–C, 4 (“Rincón de la Doncella Park (altitude 1400 m), Ciudad Mendoza, Municipio de Camerino Z. Mendoza, Veracruz (18°48ʹN 97°10ʹW)” [Mexico]).
Procambarus clarkii (Girard, 1852)
= Cambarus ClarkiiGirard, 1852: 91 “between San Antonio (Texas) and El Paso del Norte” [USA]).
Procambarus clemmeriHobbs, 1975
= Procambarus (Pennides) clemmeriHobbs, 1975: 19, fig. 6 (“tributary to the Jourdan River, 8.7 miles southeast of the Pearl River-Hancock County line on State Route 43 (4.3 miles northwest of the junction of routes 43 and 603 north of Kiln)” [Hancock County, Mississippi, USA]).
Procambarus cometesFitzpatrick, 1978c
= Procambarus (Girardiella) cometesFitzpatrick, 1978c: 74, figs. 53–71 (“field behind luxury mobile homes (T18N, R14E, SW¼, Sec. 3), Starkville, Oktibbeha County, Mississippi” [USA]).
Procambarus connusFitzpatrick, 1978c
= Procambarus (Girardiella) connusFitzpatrick, 1978c: 76, figs. 72–90 (“Carrollton, Carroll County, Mississippi” [USA]; misspelled as connos on p. 57).
Procambarus contrerasi (Creaser, 1931)
= Cambarus (Cambarus) contrerasiCreaser, 1931: 1; pls. 1, 2 (“tributary of the Rio Cazones near Agua Fria, 12 miles south of Miahuapan, State of Puebla, Mexico”).
Procambarus cubensis cubensis (Erichson, 1846)
= Astacus (Cambarus) cubensisErichson, 1846: 100 (“Cuba”).
= Cambarus consobrinusde Saussure, 1857a: 101 (“l’île de Cuba”).
Procambarus cubensis rivalis (Faxon in Rathbun, 1912)
= Cambarus cubensis rivalis Faxon in Rathbun, 1912: 459 (“mountain stream near San Diego de los Baños, in the Province of Pinar del Rio” [Cuba]).
Procambarus cuetzalanaeHobbs, 1982
= Procambarus (Villalobosus) cuetzalanaeHobbs, 1982: 39, fig. 1 (“Cueva de Tasalolpan, 5 km southwest of Cuetzalan, Puebla, in the Río Tecuantepec (tributary to Rio Tecolutla) watershed” [Mexico]).
Procambarus cuevachicae (Hobbs, 1941b)
= Cambarus blandingii cuevachicaeHobbs, 1941b: 1, fig. 1 (“La Cueva Chica, about one mile northeast of Pujal, San Luis Potosi, Mexico”).
Procambarus curdiReimer, 1975
= Procambarus (Girardiella) curdiReimer, 1975: 22, figs. 1–9 (“Navasota River, NE of Bryan on U.S. Highway 190, Brazos County, Texas” [USA]).
Procambarus delicatusHobbs & Franz, 1986
= Procambarus (Ortmannicus) delicatusHobbs & Franz, 1986: 509, figs. 1, 3d (“Alexander Springs, a tributary to the St. Johns River, about 9 km south of Astor Park, Lake County, Florida (Levy Grant 39, T 16S, R 27E; 19°04ʹ50ʺN, 29°04ʹ30ʺW)” [USA]).
Procambarus digueti (Bouvier, 1897)
= Cambarus DiguetiBouvier, 1897: 227 (“affluents du Rio Santiago, l’Etat de Jalisco” [Mexico]).
= Cambarus carinatusFaxon, 1898: 648; pl. 63 (“Guadalajara, Mexico”).
Procambarus dupratziPenn, 1953a: 1, figs. 1–7, 10–14 (“Attoyac Bayou, 5.6 miles southwest of Timpson (on U.S. highway 59), Shelby County, Texas” [USA]).
Procambarus echinatusHobbs, 1956c: 117, figs. 1–17 (“Salkehatchie River, 1.9 miles south of Barnwell, Barnwell County, S. C., on State Highway 3” [South Carolina, USA]).
Procambarus econfinaeHobbs, 1942b: 49; pl. 2, figs. 16–20; pl. 15 (“flatwoods in the northern part of Panama City, Bay County, Florida” [USA]).
Procambarus elegansHobbs, 1969b: 329, figs. 1–11, 24, 25 (“spillway from Corney Lake, an impounded tributary of the Ouachita River, Claiborne Parish, Louisiana” [USA]).
Procambarus enoplosternumHobbs, 1947a: 5, figs. 2, 5, 10, 12, 13, 18, 20, 23, 24, 25, 32 (“Rocky Creek, a small moderately flowing, clear, sand bottomed stream flowing between red hills six miles south of Lyons, Toombs County, Georgia, on U.S. Highway 1” [USA]).
Procambarus epicyrtusHobbs, 1958b: 1; pl. 1 (“South Ogeechee Creek, 6.8 miles south of Sylvania, Screven County, Georgia on U.S. Hy. 301 [USA]).
Procambarus erichsoniVillalobos, 1951: 384; pls. 5, 6, 7 (“Arroyos Puendo, Mamay y Bojoy, Tenango de Doria, Hidalgo” [Mexico]).
Procambarus erythropsRelyea & Sutton, 1975
= Procambarus (Ortmannicus) erythropsRelyea & Sutton, 1975: 8, figs. 1, 2 (“Sim’s Sink, 1 mi west of the junction of U.S. Hwys. 27 and 129, and 0.1 mi south of Hwy. 27, Suwannee Country, Florida (Sec. 24, T. 6S, R. 14E)” [USA]).
Procambarus escambiensisHobbs, 1942b: 46; pl. 2, figs. 11–15; pl. 14 (“about 100 yards east of the Perdido River on U.S. Highway 90, Escambia County, Florida” [USA]).
Procambarus evermanni (Faxon, 1890)
= Cambarus evermanniFaxon, 1890: 620 (“Escambia River at Flomaton, above Pensacola, Florida” [USA]).
Procambarus fallax (Hagen, 1870)
= Cambarus fallaxHagen, 1870: 45; pl. 1, figs. 103–105 (restricted by Hobbs, 1974b to “St. Johns River at Welaka, Putnam County, Florida” [USA]).
Procambarus fitzpatrickiHobbs, 1971a: 461, fig.1 (“roadside ditch at junction of State Rte. 67 and Woolmarket Road, just north of D’Iberville, Harrison County, Mississippi” [USA]).
Procambarus franziHobbs & Lee, 1976
= Procambarus (Ortmannicus) franziHobbs & Lee, 1976: 384, fig. 1 (“Orange Lake Cave, 0.4 mi S of junction of U.S. Hwy. 441 and State Route 318 off Hwy. 411 (T.12S, R.21E, Sec. 33/34), Marion County, Florida” [USA]).
Procambarus geminusHobbs, 1975
= Procambarus (Ortmannicus) geminusHobbs, 1975: 1, fig. 1 (“roadside pool (perhaps a streambed, but no flow was detected), 1.7 miles south of Taylor, Columbia County, Arkansas, on State Route 132” [USA]).
Procambarus geodytesHobbs, 1942b: 80; pl. 5, figs. 61–65; pl. 19 (“Orange Springs, in the northeastern part of Marion County, Florida” [USA]).
Procambarus gibbusHobbs, 1969b: 337, figs. 12–23 (“tributary to Muckalee Creek (Flint River drainage), 3.2 miles north of Americus on U.S. Hwy. 19, Sumter County, Georgia” [USA]).
Procambarus gonopodocristatusVillalobos, 1958: 279; pls. 1, 2, 3 (“Paso Largo, Veracruz, Km 411.2 de la carretera Martínez de la Torre, Nautla, 16 km NE Martínez de la Torre, Ver.” [Veracruz, Mexico]).
Procambarus gracilis (Bundy in Forbes, 1876)
= Cambarus gracilis Bundy in Forbes, 1876: 5 (“Normal, McLean County, Illinois” [USA] as restricted by Hobbs, 1974b).
Procambarus hagenianus hagenianus (Faxon, 1884)
= Cambarus HagenianusFaxon, 1884: 141 (“Charleston, South Carolina” [USA]; considered to be in error by Hobbs, 1974b).
Procambarus hagenianus vesticepsFitzpatrick, 1978c
= Procambarus (Girardiella) hagenianus vesticepsFitzpatrick, 1978c: 64, figs. 19–36 (“Egypt, Chickasaw County, Mississippi” [USA]).
Procambarus hayi (Faxon, 1884)
= Cambarus HayiFaxon, 1884: 108 (“Macon, Noxubee County, Mississippi” [USA] according to Hobbs, 1974b).
Procambarus hidalgoensisLópez-Mejía, Alvarez & Mejía-Ortiz, 2005
= Procambarus (Ortmannicus) hidalgoensisLópez-Mejía, Alvarez & Mejía-Ortiz, 2005: 558, figs. 2, 3 (“stream at Camino a Olotla, at 1375 m of altitude (20°38ʹ15ʺN, 98°38ʹ3ʺW), 2 km east of Tlanchinol, Hidalgo” [Mexico]).
Procambarus hinei (Ortmann, 1905d)
= Cambarus (Cambarus) hineiOrtmann, 1905d: 401, fig. 1 (“small freshwater pool, ¼ mile from Gulf Beach, near Cameron, Cameron Parish, Louisiana” [USA]).
Procambarus hirsutusHobbs, 1958a: 160, figs. 1–12 (“Salkehatchie River, 1.9 miles south of Barnwell, Barnwell County, S. C., on State Highway 3” [South Carolina, USA]).
Procambarus hoffmanni (Villalobos, 1944a)
= Paracambarus hoffmanniVillalobos, 1944a: 169; pl. 2 (“Vertedor de Demasía de la Presa de Necaxa” according to Villalobos, 1955 [Puebla, Mexico]).
Procambarus holifieldiSchuster, Taylor & Adams, 2015
= Procambarus (Girardiella) holifieldiSchuster, Taylor & Adams, 2015: 6, figs. 1, 2, 3 (“burrows along power line right of way on private property, 2.2 Km SE of junction State Route 5 and County Road 38, Perry County, Alabama (32.5435N; -87.3298W)” [USA]).
Procambarus horstiHobbs & Means, 1972: 401, fig. 2 (“Big Blue Springs (tributary to the Wacissa River), 2.2. miles south of the crossroads in the town of Wacissa, Jefferson County, Florida (SE ¼ NW ¼ Sec. 12, T. 2S, R. 3E)” [USA]).
Procambarus hortonhobbsiVillalobos, 1951: 402; pls. 10, 11 (“El Coyular, 7 km NE de La Unión, municipio de Zihuateutla, Puebla” [Mexico]).
Procambarus howellaeHobbs, 1952b: 167, figs. 1–14 (“spring-fed drainage ditch on the campus of Wesleyan College at Rivoli, Bibb County, Georgia” [USA]).
Procambarus hubbelli (Hobbs, 1940a)
= Cambarus hubbelliHobbs, 1940a: 406, fig. 19 (“roadside ditch in the flatwoods 1 mile east of Bonifay, Holmes County, Fla., on State Highway No. 1” [Florida, USA]).
Procambarus hybusHobbs & Walton, 1957: 39, figs. 1–12 (“roadside ditch, 1.7 miles north of Boligee, Greene County, Alabama, on U.S. Highway 11” [USA]).
Procambarus incilisPenn, 1962: 222, figs. 1–11 (“pool, 7.5 miles east of Edna, Jackson County, Texas, on state highway 111” [USA]).
Procambarus jaculusHobbs & Walton, 1957: 48, figs. 24–34 (“roadside ditch of Scott-Rankin County line on U.S. Highway 80, Rankin County, Mississippi” [USA]).
Procambarus kensleyiHobbs, 1990
= Procambarus (Girardiella) kensleyiHobbs, 1990: 583, figs. 2b, 3 (“roadside ditch on gentle slope 4.6 mi (7.4 km) NW of U.S. Highway 59 on Fann Road 2497, Angelina County, Texas” [USA]).
Procambarus kilbyi (Hobbs, 1940a)
= Cambarus kilbyiHobbs, 1940a: 410; fig. 20 (“small creek about 7 miles northwest of Blountstown, Calhoun County, Fla., on State Highway No. 6” [Florida, USA]).
Procambarus lagniappeBlack, 1968: 5, figs. 1–12 (“Pawticfaw Creek (tributary to Sucarnoochee Creek, in turn a tributary of Tombigbee River), 6.0 miles south of DeKalb, Kemper County, Mississippi, at Mississippi Highway 39” [USA]).
Procambarus latipleurumHobbs, 1942b: 52; pl. 3, figs. 21–25; pl. 16 (“roadside excavation and intermittent stream in flatwoods, 5.8 miles west of Weewahitchka on State Highway 52, Gulf County, Florida” [USA]).
Procambarus lecontei (Hagen, 1870)
= Cambarus LeConteiHagen, 1870: 47; pl. 1, figs, 15–16; pl. 2, fig. 145 (“Mobile County, Alabama” [USA] according to Hobbs, 1974b).
Procambarus leitheuseriFranz & Hobbs, 1983
= Procambarus (Ortmannicus) leitheuseriFranz & Hobbs, 1983: 323, fig. 1 (“Eagle’s Nest (= Lost Sink, Eagle Hole), 5.4 km northwest of the junction of U.S. Highway 19 and State Road 50 (NE¼, NE¼, SW¼, Sec. 21, T. 22S, R. 17E), Hernando County, Florida” [USA]).
Procambarus leonensisHobbs, 1942b: 114; pl. 8, figs. 121–125 (“sinkhole pond 3 miles southwest of Tallahassee, State Highway 19, Leon County, Florida” [USA] according to Hobbs, 1943a).
= Procambarus leonensisHobbs, 1943a: 49, figs. 1, 6, 7, 10, 12, 13, 14, 16, 17, 22, 26, 29, 31 (“sinkhole pond 3 miles southwest of Tallahassee, State Highway 19, Leon County, Florida” [USA]).
Procambarus lepidodactylusHobbs, 1947b: 25, figs. 1–12 (“Juniper Creek, one mile southwest of Patrick, Chesterfield County, South Carolina, on U.S. Highway 1” [USA]).
Procambarus lewisiHobbs & Walton, 1959: 39, figs. 1–12 (“roadside ditch 18.8 miles east of Montgomery, Macon Couty, Alabama, on Route 80” [USA]).
Procambarus liberorumFitzpatrick, 1978a
= Procambarus (Girardiella) liberorumFitzpatrick, 1978a: 533, figs. 1–14 (“Bentonville, Benton County, Arkansas; yard at 206 SW Seventh Street” [USA]).
= Procambarus (Girardiella) ferrugineusHobbs & Robison, 1988: 391, figs. 1, 2, 12 (“roadside ditch 10 miles (16 km) south of Lonoke on State Route 31, Lonoke County, Arkansas (T.1S, R. 8W, Sec. 6)” [USA]).
Procambarus litosternumHobbs, 1947a: 9, figs. 3, 4, 9, 11, 15, 16, 19, 21, 26, 29, 30 (“ sandbottomed stream flowing through swampy terrain five miles northeast of Swainsboro, Emanuel County, Georgia, on U.S. Highway 25” [USA]).
Procambarus llamasiVillalobos F., 1954a: 364; pls. 16, 17 (“Santa Rita, 47 km al E. de Escárega, Campeche” [Mexico]).
Procambarus lophotusHobbs & Walton, 1960: 123, figs. 1–11 (“roadside ditch, 3.4 miles northeast of Haynesville, Lowndes County, Alabama, on State Route 11” [USA]).
Procambarus lucifugus alachua (Hobbs, 1940a)
= Cambarus lucifugus alachuaHobbs, 1940a: 402, fig. 18 (“small cave, Hog Sink, about 10 miles west of Gainesville, Alachua County, Fla.” [Florida, USA]).
Procambarus lucifugus lucifugus (Hobbs, 1940a)
= Cambarus lucifugus lucifugusHobbs, 1940a: 398, fig. 17 (“Gum Cave, about 5 miles southwest of Floral City, Citrus County, Fla.” [Florida, USA]).
Procambarus lunzi (Hobbs, 1940b)
= Cambarus lunziHobbs, 1940b: 3, figs. 1–10 (“roadside ditch in the flatwoods, 1.4 miles southeast of Early Branch on State Highway 28, Hampton County, South Carolina” [USA]).
Procambarus luxusJohnson, 2011b
= Procambarus (Ortmannicus) luxusJohnson, 2011b: 59, figs. 1–5 (“canal and roadside ditch near Interstate 37 and County Road 17, San Patricio County, Texas (28.09435, -97.80987)” [USA]).
Procambarus lyleiFitzpatrick & Hobbs, 1971: 95, figs. 1–14 (“Shutispear Creek, 2.7 miles south of State Route 8 on State Route 9, Calhoun County, Mississippi” [USA]).
Procambarus machardyiWalls, 2006
= Procambarus (Girardiella) machardyiWalls, 2006: 260, figs. 1, 2 (“Fordney Creek, Walter B. Jacobs Memorial Nature Park, 4 km west and 1.6 km south of Blanchard, Caddo Parish, Lousiana, GPS coordinates: 32°34.221ʹN, 093°56.195ʹW” [USA]).
Procambarus mancusHobbs & Walton, 1957: 44, figs. 13–23 (“roadside ditch, 5.0 miles south of Meridian, Lauderdale County, Mississippi, on U.S. Highway 11” [USA]).
Procambarus marthaeHobbs, 1975
= Procambarus (Ortmannicus) marthaeHobbs, 1975: 6, fig. 2 (“sluggish stream, 2.3 miles west of the Alabama River on U.S. Highway 84, Monroe County, Alabama” [USA]).
Procambarus mayaAlvarez, López-Mejía & Villalobos, 2007
= Procambarus (Austrocambarus) mayaAlvarez, López-Mejía & Villalobos, 2007: 312, figs. 2, 3 (“salt-marsh 1 km from the coast, Sian Ka’an Nature Reserve, Municipio de Felipe Carrillo Puerto, Quintana Roo” [Mexico]).
Procambarus medialisHobbs, 1975
= Procambarus (Ortmannicus) medialisHobbs, 1975: 10, fig. 3 (“pool in roadside ditch, 0.6 mile south of Scotland Neck, Halifax County, North Carolina, on U.S. Highway 258” [USA]).
Procambarus mexicanus (Erichson, 1846)
= Astacus (Cambarus) MexicanusErichson, 1846: 99 [“El Mirador de Zacuapan, 8 km NE of Huatusco, Veracruz” [Mexico]; neotype (as neoholotype) designated by Villalobos F., 1954a: 312).
= Cambarus aztecusde Saussure, 1857b: 503 (“Tomatlá, dans les Terres chaudes”; “Veracruz, Mexico” according to Hobbs, 1974b).
Procambarus milleriHobbs, 1971c: 115, figs. 1–11, 16 (“well at Little Bird Nursery and Garden Store at 8427 Bird Road, Miami, Dade County, Florida (Sec. 15, Twp. 54S, R. 40E)” [USA]).
Procambarus mirandaiVillalobos F., 1954a: 355; pls. 13, 14 (“Cerro Hueca, 4 km SE Tuxtla Gutiérrez, Chiapas” [Mexico]).
Procambarus morrisiHobbs & Franz, 1991
= Procambarus (Lonnbergius) morrisiHobbs & Franz, 1991: 56, fig. 1 (“Devil’ s Sink, 152 m north of St. Rte. 20, 7.1 km west of Interlachen (junction of St. Rtes. 313 and 20), Putnam County, Florida (NE ¼, SE ¼, NW ¼, Sec.13, Twp. 10S, R. 23E)” [USA]).
Procambarus natchitochaePenn, 1953a: 5, figs. 8, 9, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19 (“tributary of Spring Creek at Melder (on Lousiana highway 85), Rapides Parish, Louisiana” [USA]).
Procambarus nechesaeHobbs, 1990
= Procambarus (Ortmannicus) nechesaeHobbs, 1990: 590, fig. 4 (“semi-permanent pool in roadside ditch on Farm Road 2497, 1.2 mi (1.9 km) SE of intersection with State Route 94, southwest of Lufkin, Angelina County, Texas” [USA]).
Procambarus nigrocinctusHobbs, 1990
= Procambarus (Girardiella) nigrocinctusHobbs, 1990: 576, figs. 1, 2a (“Jack Creek, a tributary of the Neches River, at State Route 94, about 3.0 mi (4.8 km) WSW of Lufkin Perimeter Route 287, Angelina County, Texas” [USA]).
Procambarus niveusHobbs & Villalobos 1964: 342, figs. 26–39 (“Cueva de Santo Tomás, Sierra de los Órganos, cerca de Ponce, Pínar del Río, Cuba”).
Procambarus nuecesHobbs & Hobbs, 1995
= Procambarus (Ortmannicus) nuecesHobbs & Hobbs, 1995: 54, fig. 1 (“tributary of the Nueces River 4.3 miles (6.9 km) south of Jourdanton at junction of State Routes 97 and 173, Atascosa County, Texas” [USA]).
Procambarus oaxacae oaxacaeHobbs, 1973b
= Procambarus (Austrocambarus) oaxacae oaxacaeHobbs, 1973b: 29, figs. 3, 4, 5 (“Cueva del Guano, 10 km NE Valle Nacional, Oaxaca, Mexico”).
Procambarus oaxacae reddelliHobbs, 1973b
= Procambarus (Austrocambarus) oaxacae reddelliHobbs, 1973b: 33, figs. 6, 7, 8 (“Cueva del Nacimiento del Río San Antonio, 10 km SSW Acatlán, Oaxaca, Mexico”).
Procambarus okaloosaeHobbs, 1942b: 100; pl. 7, figs. 101–105; pl. 22 (“intersection of State Highway 41 and U.S. Highway 90 at Milligan, Okaloosa County, Florida” [USA]).
Procambarus olmecorumHobbs, 1987a
= Procambarus (Austrocambarus) olmecorumHobbs, 1987a: 208, fig. 3 (“arroyo to Río Metlac near edge of Fortín de las Flores, Veracruz, Mexico”).
Procambarus orcinusHobbs & Means, 1972: 394, fig. 1 (“Gopher Sink, 3.1 miles southwest of Florida Road 61 and 0.2 miles east of Florida Road 369 (SW¼ NW¼ NE¼ Sec.16 T. 2S R. 1W), Leon County, Florida” [USA]).
Procambarus ortmannii (Villalobos, 1949)
= Paracambarus ortmanniiVillalobos, 1949: 331; pls. 1, 2 (“Los Estajos, 6 km NE of Zihuateutla, en un pequeño arroyito que corre por el lado derecho del camino que va al rancho El Mirador, Puebla” [Mexico]).
Procambarus ouachitaePenn, 1956: 100, figs. 1–17 (“tributary of the South Fork of the Saline River, 2.4 miles north of U.S. Highway 70 on a local road, 6.5 miles northeast of Hot Spring (7.7 miles south-southwest of Owensville), Garland County, Arkansas” [USA]).
Procambarus paeninsulanus (Faxon, 1914)
= Cambarus clarkii paeninsulanusFaxon, 1914: 369 (“three miles below Horse Landing, St. John’s River, Putnam County, Florida” [USA]).
Procambarus pallidus (Hobbs, 1940a)
= Cambarus pallidusHobbs, 1940a: 394, fig. 16 (“Warrens Cave, 11 miles northwest of Gainesville, Alachua County, Fla.” [Florida, USA]).
Procambarus paradoxus (Ortmann, 1906b)
= Cambarus (Paracambarus) paradoxusOrtmann, 1906b: 3, fig. 1 (“Tetela de Ocampo y La Cañada, 35 km northeast of Zacapoaxtla, Estado de Puebla, Mexico” according to Hobbs, 1974b).
Procambarus parasimulansHobbs & Robison, 1982
= Procambarus (Girardiella) parasimulansHobbs & Robison, 1982: 545, fig. 1 (“unnamed tributary to Prairie Bayou (Ouachita River basin), 10.2 miles east of Bismarck on State Route 84 (Sec. 35, R 19W, T 4S), Hot Spring County, Arkansas” [USA]).
Procambarus pearsei (Creaser, 1934)
= Cambarus (Ortmannicus) pearseiCreaser, 1934: 1, figs. 1, 2, 3 (“pond and ditch on Highway No. 22, south of Fayetteville, Cumberland County, North Carolina” [USA]).
Procambarus penniHobbs, 1951b: 273, figs. 1–11 (“Talisheek Creek, at Talisheek, St. Tammany Parish, a tributary of the Pearl River” [Louisiana, USA]).
Procambarus pentastylusWalls & Black, 2008
=Procambarus (Pennides) pentastylusWalls & Black, 2008: 50, figs. 1A–H, J, 2A–F, 3 (“Bearhead Creek on Louisiana Highway 389, 5.1 km E Fields, Beauregard Parish, Louisiana” [USA]).
Procambarus petersiHobbs, 1981
= Procambarus (Pennides) petersiHobbs, 1981: 442, figs. 12b, 173d, 176, 183b, 256 (“Rocky Comfort Creek (tributary to the Ogeechee River), 1.7 miles nort of Gibson, Glascock County, Georgia, on Route S2126 and 0.4 miles east on Chalker Smith Road” [Georgia, USA]).
Procambarus pictus (Hobbs, 1940a)
= Cambarus pictusHobbs, 1940a: 419, fig. 22 (“small, swift swamp stream about 2 miles southwest of Green Cove Springs, Clay County, Fla., on Highway No. 48” [Florida, USA]).
Procambarus pilosimanus (Ortmann, 1906b)
= Cambarus (Procambarus) pilosimanusOrtmann, 1906b: 6, fig. 2 (“probably Río Cahabón at Cobá, Province of Alta Verapaz, Guatemala” according to Hobbs, 1974b).
Procambarus planirostrisPenn, 1953b: 71, figs. 1–12 (“one mile south of Walker (on Louisiana Highway 336), Livingston Parish, Louisiana” [USA]).
Procambarus plumimanusHobbs & Walton, 1958
= Procambarus pearsei plumimanusHobbs & Walton, 1958: 8, figs. 1–13 (“roadside ditch 2.2 miles southeast of Havelock, Craven County, North Carolina on Hwy. 70” [USA]).
Procambarus pogumFitzpatrick, 1978c
= Procambarus (Girardiella) pogumFitzpatrick, 1978c: 83, figs. 91–108 (“Houston, Chickasaw County, Mississippi” [USA]).
Procambarus primaevus (Packard, 1880)††
= Cambarus primaevusPackard, 1880: 223 (“western border of Wyoming” [USA]; neotype designated by Feldmann et al., 1981: 797).
Procambarus pubescens (Faxon, 1884)
= Cambarus pubescensFaxon, 1884: 109 (“McBean Creek, south of Augusta, Richmond County, Georgia” [USA] according to Hobbs, 1974b).
Procambarus pubischelae deficiensHobbs, 1981
= Procambarus (Leconticambarus) pubischelae deficiensHobbs, 1981: 356, figs. 18d, 135, 241 (“roadside ditch, 3 miles south of Baxley, Appling County, Georgia, on U.S. Highway 1” [USA]).
Procambarus pubischelae pubischelaeHobbs, 1942b
= Procambarus pubichelaeHobbs, 1942b: 41; pl. 2, figs. 6–10; pl. 13 (“pond and roadside ditch 9.4 miles north (State Highway 82) of Lake City, Columbia County, Florida” [USA]).
Procambarus pycnogonopodusHobbs, 1942b: 117; pl. 8, figs. 126–130 (“roadside excavation and adjoining intermittent stream in the flatwoods 5.8 miles west of Wewahitchka on State Highway 52, Gulf County, Florida [USA] according to Hobbs, 1943a).
= Procambarus pycnogonopodusHobbs, 1943a: 53, figs. 3, 4, 8, 9, 11, 15, 19, 20, 21, 24, 25, 27, 28, 30, 32 (“roadside excavation and adjoining intermittent stream in the flatwoods 5.8 miles west of Wewahitchka on State Highway 52, Gulf County, Florida” [USA]).
Procambarus pygmaeusHobbs, 1942b: 83; pl. 5, figs. 66–70; pl. 20 (“about 16 miles north of Fargo on Georgia State Highway 89, Clinch County, Georgia” [USA]).
Procambarus raneyiHobbs, 1953b: 412, figs. 1–12 (“south fork of the Broad River, 1 mile south of Carlton on the Oglethorpe-Madison County line, Georgia (Savannah River drainage system)” [USA]).
Procambarus rathbunae (Hobbs, 1940a)
= Cambarus rathbunaeHobbs, 1940a: 414, fig. 21 (“near the Yellow River at Milligan, Okaloosa County, Fla., at intersection of State Highway No. 41 and U.S. Highway No. 90” [Florida, USA]).
Procambarus regalisHobbs & Robison, 1988
= Procambarus (Girardiella) regalisHobbs & Robison, 1988: 398, figs. 3, 4, 14 (“De Ann Cemetery, about 1 mile (.6 km) west of the junction of State Routes 19 and 24 on latter at western city limit of Prescott, Nevada County, Arkansas (T. 11S, R. 22W, Sec. 8)” [USA]).
Procambarus regiomontanusVillalobos F., 1954b
= Procambarus simulans regiomontanusVillalobos F., 1954b: 289; pls. 1, 2 (“5 km N de Monterrey, N. L.” [Nuevo León, Mexico]).
Procambarus reimeriHobbs, 1979
= Procambarus (Girardiella) reimeriHobbs, 1979: 804, fig. 1 (“roadside ditch about five miles northeast of Mena, Polk County, Arkansas, on unnumbered road to Iron Fork River” [USA]).
Procambarus riojae (Villalobos, 1944a)
= Paracambarus riojaeVillalobos, 1944a: 162; pl. 1 (“Huachinango, estado de Puebla, riachuelos tributarios del río Necaxa” [Mexico]).
Procambarus robertiVillalobos Figueroa & Hobbs, 1974
= Procambarus (Pennides) robertiVillalobos Figueroa & Hobbs, 1974: 3, fig. 2 (“ditch from La Media Luna, 4.8 miles (6.6 km) south of Río Verde (on highway to Pedro Montoya) and 2.5 miles (4 km) west on dirt road to Mina El Refugio, San Luis Potosí, Mexico”).
Procambarus rodrigueziHobbs, 1943b: 203; pl. 2 (“cave, four kilometres northwest of the hacienda at Potrero Viejo, Paraje Nuevo, Vera Cruz, Mexico”).
Procambarus rogersi campestrisHobbs, 1942b: 90; pl. 6, figs. 81–85 (about 12 miles south of Tallahassee, Leon County, Florida (Sec. 16–17, T.2S, R. 2W)” [USA] according to Hobbs, 1974).
Procambarus rogersi expletusHobbs & Hart, 1959: 179, figs. 27–39 (“seepage slope, 0.9 mile north of Clarksville, Calhoun County, Florida, on State Highway 73” [USA]).
Procambarus rogersi ochlockensisHobbs, 1942b: 89; pl. 5, figs. 76–80 (“7.3 miles west of Quincy, on U.S. Highway 90, Gadsden County, Florida (Sec. 1, T. 2N, R. 5W)” [USA according to Hobbs, 1974b).
Procambarus rogersi rogersi (Hobbs, 1938)
= Cambarus rogersiHobbs, 1938: 62, fig. 1 (“flat-woods four miles north of Blountstown on State Highway no. 6” [Florida, USA]).
Procambarus ruthveni (Pearse, 1911)
= Cambarus ruthveniPearse, 1911: 110 (“Cuatotolapam, Cantón de Acayucan, Veracruz, Mexico” according to Hobbs, 1974b).
Procambarus sbordoniiHobbs, 1978
= Procambarus (Austrocambarus) sbordoniiHobbs, 1978: 201, fig. 2 (“Cueva del Nacimiento de Rio S. Domingo, near the village of Bochil, at 1250 m” [Chiapas, Mexico]).
Procambarus seminolaeHobbs, 1942b: 142; pl. 10, figs. 166–170; pl. 24 [roadside excavation about nine miles northeast of Gainesville, on State Highway 13, Alachua County, Florida” [USA]).
Procambarus shermaniHobbs, 1942b: 61; pl. 3, figs. 36–40; pl. 18 (“about 12 miles southwest of Jay, Santa Rosa County, Florida, in the Escambia River swamp along McCaskill’s Mill Creek” [USA]).
Procambarus simulans (Faxon, 1884)
= Cambarus simulansFaxon, 1884: 112 (“Dallas, Texas” [USA] according to Hobbs, 1974b).
= Cambarus gallinusCockerell & Forter, 1900: 434, unnumbered text-figure (“Gallinas River at Las Vegas, New Mexico” [USA] according to Hobbs, 1974b).
= Cambarus baumgartneriHarris, 1901: 115 [nomen nudum].
Procambarus spiculifer (Le Conte, 1856)
= Astacus spiculiferLe Conte, 1856: 401 (“Athens, Clarke County, Georgia” [USA] according to Hobbs, 1974b).
Procambarus steigmaniHobbs, 1991b
= Procambarus (Girardiella) steigmaniHobbs, 1991b: 309, figs. 1, 2 (“Parkhill Prairie, a 52 acre tract of grassland in the Trinity River basin, 9.4 miles (15 km) north of U.S. Highway 380 off State Highway 36, Collin County, Texas (33°16ʹN 96°l8ʹW)” [USA]).
Procambarus strenthiHobbs, 1977b
= Procambarus (Scapulicambarus) strenthiHobbs, 1977b: 412, figs. 1, 2 (“small stream 15 mi (24 km) W of Ciudad Valles, San Luis Potosí, Mexico”).
Procambarus suttkusiHobbs, 1953c: 173, pl. 9 (“tributary of Claybank Creek, 2.0 miles west of Ozark, Dale County, Alabama, on Rt. 27 [Choctawhatchee River drainage]” [USA]).
Procambarus talpoidesHobbs, 1981
= Procambarus (Hagenides) talpoidesHobbs, 1981: 329, figs. 17e, 118d, e, 125, 126, 127, 238 (“Hogtown Creek just southwest of the junction of 13th (U.S. Highway 441) and Boundary streets in Gainesville, Alachua County, Florida” [USA]).
Procambarus texanusHobbs, 1971b: 87, fig. 2 (“Fish Hatchery near Smithville, Bastrop County, Texas” [USA]).
Procambarus teziutlanensis (Villalobos, 1947a)
= Paracambarus tezuitlanensisVillalobos, 1947a: 240; pl. 2; pl. 3, figs. 5–8 (“Chignautla, a 5 km. al Oriente de Teziutlán, Estado de Puebla” [Mexico]).
Procambarus tlapacoyanensis (Villalobos, 1947b)
= Paracambarus tlapacoyanensisVillalobos, 1947b: 537; pl. 1, 2 (“Cañada de Tomata, Tlapacoyan, Veracruz” [Mexico]).
Procambarus toltecaeHobbs, 1943b: 198; pl. 1 (“stream about five miles north of Tomazunchale, at Palitla, San Luis Potosi, Mexico”).
Procambarus troglodytes (Le Conte, 1856)
= Astacus troglodytesLe Conte, 1856: 400 (“Georgia oryzaceis” [= rice fields in Georgia, USA]).
= Astacus fossarumLe Conte, 1856: 401 (“in fossis Georgia inferioris” [= ditches in lower Georgia]).
= Astacus maniculatusLe Conte, 1856: 401 (“in fossis Georgia inferioris” [= ditches in lower Georgia]).
Procambarus truculentusHobbs, 1954: 111, figs. 1–13 (“seepage area 11 miles north of Lyons in Emanuel County, Georgia, on U.S. Highway 1” [USA]).
Procambarus tulaneiPenn, 1953c: 163, figs. 1–12 (“unnamed tributary of Bayou D’Arbonne, 4 miles west of Dubach (on Louisiana Highway 288), Lincoln Parish, La.” [Louisiana, USA]).
Procambarus vazquezaeVillalobos F., 1954a: 328; pls. 7, 8 (“Playa Norte de la Laguna de Catemaco, Ver.” [Veracruz, Mexico]).
Procambarus veracruzanusVillalobos F., 1954a: 323; pls. 5, 6 (“Presidio, 30 km. SE Córdoba, Veracruz. Cuenca del río Papaloapan” [Mexico]).
Procambarus verrucosusHobbs, 1952c: 212, fig. 82 (“tributary of Caleba Creek (Alabama River system), 3.9 miles south of Tuskegee, Macon County, Ala., on U.S. Highway 29” [Alabama, USA]).
Procambarus versutus (Hagen, 1870)
= Cambarus versutusHagen, 1870: 51; pl. 1, figs. 55–58; pl. 2, fig. 150 (“Spring Hill, Mobile County, Alabama” [USA] according to Hobbs, 1974b).
Procambarus viaeviridis (Faxon, 1914)
= Cambarus viae-viridisFaxon, 1914: 370; pl. 5 (“St. Francis River, Greenway, Clay Co., Arkansas” [USA]).
Procambarus villalobosiHobbs, 1969c: 41, fig. 2 (“Cueva del Agua, 75 km al oeste de Valles, San Luis Potosí, Mexico”).
Procambarus vioscai payneiFitzpatrick, 1990
= Procambarus (Pennides) vioscai payneiFitzpatrick, 1990: 259, fig. 1 (“Big Black River at State Route 9, approx. 1 mile (1.6 km) S of Eupora, Choctaw-Webster counties, Mississippi” [USA]).
Procambarus vioscai vioscaiPenn, 1946
= Procambarus vioscaiPenn, 1946: 27, fig. 1 (“Big Creek at Fishville, about 3 miles east of Pollock, Grant Parish, La.” [Louisiana, USA]).
Procambarus williamsoni (Ortmann, 1905b)
= Cambarus (Procambarus) williamsoniOrtmann, 1905b: 439, figs. 1, 2, 3 (“about 4 to 5 miles due south of the town of Izabal, south of Rio Malagua, Los Amates, Province of Izabal, Guatemala”).
Procambarus xilitlaeHobbs & Grubbs, 1982
=Procambarus (Scapulicambarus) xilitlaeHobbs & Grubbs, 1982: 45, fig. 1 (“Hoya de las Guaguas, 10 kilometers south-southwest of Aquismón, and very near the town of Xilitla, San Luis Potosí, Mexico”).
Procambarus xochitlanaeHobbs, 1975
= Procambarus (Villalobosus) xochitlanaeHobbs, 1975: 16, fig. 5 (“Cueva de Los Camarones (Río Tecolutla Basin), 3 km northwest of Xochitlán, Puebla” [Mexico]).
Procambarus youngiHobbs, 1942b: 131; pl. 9, figs. 146–150; pl. 23 (“Guard House Branch, about one mile west of Weewahitchka on State Highway 52, Gulf County, Florida” [USA]).
Procambarus zapoapensisVillalobos F., 1954a
= Procambarus ruthveni zapoapensisVillalobos F., 1954a: 347; pls. 11, 12 (“Zapoapan de Cabaña, 11 km S. SE. de Catemaco, Veracruz. Cuenca del Río Papaloapan” [Mexico]).
Procambarus zihuateutlensisVillalobos, 1951: 394; pls. 8, 9 (“Arroyo de Tlatentiloyan, Los Estajos, municipio de Zihuateutla, Puebla” [Mexico]).
Procambarus zonangulusHobbs & Hobbs, 1990
= Procambarus (Ortmannicus) zonangulusHobbs & Hobbs, 1990: 608, fig. 1 (“Dishman Road at Tram Road north of Meeker, Jefferson County, Texas (30°7ʹN, 94°15ʹW)” [USA]).
TroglocambarusHobbs, 1942a
= TroglocambarusHobbs, 1942a: 345 [type species Troglocambarus maclaneiHobbs, 1942a, by original designation; gender masculine].
= TroglocambarusHobbs, 1942b: 146 [type species Troglocambarus maclaneiHobbs, 1942a, by monotypy; gender masculine].
Troglocambarus maclaneiHobbs, 1942a: 345; pls. 1, 2 (“Squirrel Chimney, a small cave about 11 miles north-west of Gainesville, Alachua County, Florida (Sec. 21, Twp. 9S, R. 18E)” [USA]).
=Troglocambarus maclaneiHobbs, 1942b: 146; pls. 1; 10, figs. 171–175 (“Squirrel Chimney” [Florida, USA]).
Family CambaroididaeVillalobos, 1955
= Cambaroidinae Villalobos, 1955: 7.
CambaroidesFaxon, 1884
= AstacusPallas, 1772: 81 [type species Astacus DauricusPallas, 1772, by monotypy; gender masculine; suppressed under the plenary powers for the purposes of the Law of Priority and the Law of Homonymy in Direction 12, see Anonymous, 1955].
= Astacus (Cambaroides) Faxon, 1884:150 [type species Astacus japonicusDe Haan, 1841 [in De Haan, 1833–1850], by subsequent designation in Faxon (1898); gender masculine].
Cambaroides dauricus (Pallas, 1772)
= Astacus dauricusPallas, 1772: 81 (“Siberia”).
= Astacus leptorhinusFischer de Waldheim, 1836: 467; pl. 5 (“rivière Chila en Daourie” [= Shilka River, Dauria, Russian Far East]).
Cambaroides japonicus (De Haan, 1841 [in De Haan, 1833–1850])
= Astacus japonicusDe Haan, 1841 [in De Haan, 1833–1850]: 164; pl. 35, fig. 9 (“central-western Aomori Prefecture, Honshu” [Japan] according to Kawai & Fitzpatrick, 2004; lectotype designated by Yamagushi & Baba, 1993: 233).
= Cambaroides neglectusSkorikov, 1907: 116 [nomen nudum].
Cambaroides koshewnikowiBirstein & Vinogradov, 1934
= Cambaroides dauricus koshewnikowiBirstein & Vinogradov, 1934: 56, fig. 23E (“freshwater part of the Tatar Straits (Tatarskiy Proliv), Amur Liman near Pronge” [Russian Far East; translated from the original]).
Cambaroides schrenckii (Kessler, 1874)
= Astacus SchrenckiiKessler, 1874: 363 (“Ussri River, Amur River and Kidzi” [Russian Far East]; lectotype designated by Kawai & Tudge, 2008: 159).
= Cambaroides schrenckii sachalinensisBirstein & Vinogradov, 1934: 57 (“Sakhalin Island, in rivers flowing to Amur Liman” [Russian Far East; translated from the original]).
= Austropotamobius pallipes bispinosusKaraman, 1961: 12 (“Amorsee, Tatanz” [? = lake in the Amur Basin, Russian Far East]; lectotype designated by Holthuis, 1964a: 47).
Cambaroides similis (Koelbel, 1892)
= Astacus (Cambaroides) similisKoelbel, 1892: 651, figs. 1–11 (“Kyonggi-do Province, South Korea”; lectotype designated by Kawai & Min, 2005: 785).
Cambaroides wladiwostokiensisBirstein & Vinogradov, 1934
= Cambaroides wladiwostokiensisBirstein & Vinogradov, 1934: 56, fig. 23C, D (“Peter the Great Bay basin (“Zaliv Petra Velikogo”), affluents of Muda-Dzian River” [Russian Far East; translated from the original).
Family Cricoidoscelosidae ††Taylor, Schram & Shen, 1999
Cricoidoscelosus ††Taylor, Schram & Shen 1999
= CricoidoscelosusTaylor, Schram & Shen 1999: 130 [type species Cricoidoscelosus aethusTaylor, Schram & Shen 1999, by original diagnosis and monotypy; gender masculine].
Cricoidoscelosus aethusTaylor, Schram & Shen 1999: 130, figs. 3, 7, 8 (“Ling-yuan County, Liaoning Province” [P.R. China]).
Superfamily Parastacoidea †Huxley, 1879
Family Parastacidae †Huxley, 1879
= Parastacidae Huxley, 1879: 771.
= Austroastacidae Clark, 1936: 8.
= Euastacidae Riek, 1959: 255.
= Astacoidinae Starobogatov, 1996: 23.
= Parastacoidinae Starobogatov, 1996: 24.
Aenigmastacus ††Feldmann, Schweitzer & Leahy, 2011
= AenigmastacusFeldmann, Schweitzer & Leahy, 2011: 3211 [type species Aenigmastacus crandalliFeldmann, Schweitzer & Leahy, 2011 by original designation; gender masculine].
Aenigmastacus crandalli †† Feldmann, Schweitzer & Leahy, 2011: 322, figs. 1–4 (“McAbee beds of the Kamloops Group at the McAbee locality, 50°47.181ʹ N, 121°08.568ʹ W, east from Cache Creek, British Columbia, Canada”).
AstacoidesGuérin-Méneville, 1839
= AstacoidesGuérin-Méneville, 1839: 109 [type species Astacoides GoudotiiGuérin-Méneville, 1839, by monotypy; gender masculine].
Astacoides betsileoensisPetit, 1923
= Astacoides madagascariensis var. betsileoensisPetit, 1923: 219 (“vicinity of Fianarantsoa, Madagascar” according to Hobbs, 1987b).
Astacoides caldwelli (Spence Bate in Sclater, 1865)
= Astacoides GoudotiiGuérin-Méneville, 1839: 109 (“Madagascar”; lectotype designated by Holthuis, 1964b: 314; suppressed for the Purposes of the Principle of Priority but not the Principle of Homonymy and placed on the Official Index of Rejected and Invalid specific Names in Zoology in Opinion 519, see Anonymous, 1958b).
= Astacus caldwelli Spence Bate in Sclater, 1865: 469; pl. 27 (“Madagascar, vicinity of Antananarivo”).
Astacoides crosnieriHobbs, 1987b: 27, figs. 2a, b, 3c, 4, 6a, 10e, 11d, 12, 13e, 14, 15, 16 (“Marais d’Ampamaherana, situé ã 25 km de Fianarantsoa sur la ligne de Chemin de fer, Fianarantsoa-Manakara, Madagascar”).
Astacoides granulimanusMonod & Petit, 1929
= Astacoides madagascariensis var. granulimanusMonod & Petit, 1929: 22, figs. 1E, 4C, F, H, J, 6E, 7D–I, 8C–D, 9 (partim) (“Forêt d’Ikongo, Vinanitelo, Madagascar”; lectotype designated by Hobbs, 1987b: 36).
Astacoides hobbsiBoyko, Ravoahangimalala, Randriamasimanana & Razafindrazaka, 2005: 43, fig. 1 (“Andranofotsiorana, effluent of Ranomadio river, 20°19ʹS, 47°39ʹE, Fianarantsoa province, Madagascar”).
Astacoides madagascarensis (H. Milne Edwards & Audouin, 1839)
= Astacus madagascarensis H. Milne Edwards & Audouin, 1839: 152 (“Madagascar”, probably “vicinity of Tananarive” according to Hobbs, 1987b; lectotype designated by Holthuis, 1964b: 311).
= Astacoides madagascariensis var. madagascariensisMonod & Petit, 1929: 12, figs. 1C, 1bis, I–F, 4G, O, P, 5F, 6A–C, 8E, F (“Manjakatompo (Ankaratra); Sambaina (prov. du Vakianankaratra); région d’Antsirabe (province du Vakinankaratra); Vakinankaratra” [Madagascar]).
= Astacoides madagascariensis var. brevirostrisMonod & Petit, 1929: 18, figs. 1A, 1bis F, H, 3D, 4D, M, N, 5A, C–E, 5bis, 6D, 8A, B (“environs de Tananarive; marché de Tananarive; ruisseau de Tananarive” [Madagascar]).
Astacoides petitiHobbs, 1987b: 31, figs. 3e, 6b, 10b, 12, 13f, 14, 17, 18 (“Fond de la valée d’Isaka (= Isaha?), Madagascar”).
Astacopsis †Huxley, 1879
= AstacopsisHuxley, 1879: 764 [type species Astacus franklinii Gray in Eyre, 1845, by monotypy; gender feminine].
Astacopsis franklinii † (Gray in Eyre, 1845)
= Astacus Franklinii Gray in Eyre, 1845: 409; pl. 3, fig. 1 (“Van Diemen’s Land” [= Tasmania, Australia]; lectotype (as lectoholotype) designated by Riek, 1969: 898).
= Astacopsis fluviatilisRiek, 1969: 912, fig. 16A (“Hobart Creek, Hobart” [Tasmania, Australia]).
Astacopsis gouldiClark, 1936: 35; pl. 7, fig. 28 (“Circular Head, Tas.” [Tasmania, Australia]; lectotype (as type) designated by Riek, 1969: 898).
Astacopsis tricornisClark, 1936: 36; pl. 1, fig. 7; pl. 7, fig. 29 (“Tasmania: Lake St. Clair” [Australia]; lectotype (as type) designated by Clark, 1939: 121, see Lew Ton & Poore, 1987).
CheraxErichson, 1846
= CheraxErichson, 1846: 88 [type species Astacus (Cheraps) PreissiiErichson, 1846, by monotypy; gender masculine; accepted as the Valid Original Spelling and placed on the Official List of Generic Names in Zoology in Opinion 519, see Anonymous, 1958b].
= CherapsErichson, 1846: 101 [considered to be an Invalid Original Spelling for CheraxErichson, 1846 and placed on the Official Index of Rejected and Invalid Names in Zoology in Opinion 519, see Anonymous, 1958b].
= AstaconephropsNobili, 1899: 244 [type species Astaconephrops AlbertisiiNobili, 1899, by monotypy; gender masculine].
= ParachaerapsSmith, 1912: 161 [type species Astacus bicarinatus Gray in Eyre, 1845, by monotypy; gender masculine].
Cherax albertisii (Nobili, 1899)
= Astaconephrops AlbertisiiNobili, 1899: 244 (“Katau” [= Katau River, Papua New Guinea]).
= Cherax divergensHolthuis, 1950: 3, fig. 1 (“Upper Fly River, 5 miles below Palmer Junction, Western Division of Papua, latitude 5°58ʹ S., longitude 141° 28ʹ E.” [Papua New Guinea]).
Cherax albidusClark, 1936: 28; pl. 1, fig. 4; pl. 6, fig. 24 (“Nurrabiel” [Victoria, Australia]; lectotype designated by Lew Ton & Poore, 1987: 23).
Cherax austiniCoughran, Dawkins, Hobson & Furse, 2012: 47, fig. 2 (“Whitsunday Islands National Park, southeastern corner of Whitsunday Island, Queensland; 20°17ʹ50ʺS 149°02ʹ51ʺE” [Australia]).
Cherax barrettiClark, 1941a: 31; pl. 10, fig. 1 (“Wessel Island, Japanese Creek” [Northern Territory, Australia]).
Cherax bicarinatus (Gray in Eyre, 1845)
= Astacus bicarinatus Gray in Eyre, 1845: 410; pl. 3, fig. 2 (“Port Essington, N.T.” [Northern Territory, Australia]; lectotype (as lectoholotype) designated by Riek, 1969: 899).
Cherax boschmaiHolthuis, 1949: 322; pl. 6, fig. 1; pl. 9, fig. 4 (“Paniai Lake” [Papua Province, Indonesia]).
Cherax boesemaniLukhaup & Pekny, 2008
= Cherax (Astaconephops) boesemaniLukhaup & Pekny, 2008: 331, figs. 1–5 (“Indonesia, Western Irian Jaya, Kais River Drainage, at the shorelines of the Ajamaru Lakes” [= Ayamaru Lakes, West Papua Province]).
Cherax buitendijkaeHolthuis, 1949: 315; pl. 4, fig. 3; pl. 5, fig. 1; pl. 9, fig. 1 (“Paniai Lake” [Papua Province, Indonesia]).
Cherax cainiiAustin & Ryan, 2002: 360, figs. 2, 3, 4 (“Scott R., Brennan Bridge, Scott R. Road, 12 km northeast of Augusta, southwestern Western Australia” [Australia]).
Cherax cairnsensisRiek, 1969: 914 (“near Anderson St., Cairns, N. Qld.” [Queensland, Australia]).
Cherax cartalacoolahShort, 1993: 55, figs. 1, 2, 3, 4A, B (“Cape Flattery, second creek south of headland, 14°59.2ʹS 145°20.2ʹE” [Queensland, Australia]).
Cherax cidCoughran, Dawkins, Hobson & Furse, 2012: 51, fig. 3 (“unnamed stream flowing into Cid Harbour, Whitsunday Islands National Park, western side of Whitsunday Island, Queensland; 20°15ʹ31ʺS 148°57ʹ04ʺE” [Australia]).
Cherax communisHolthuis, 1949: 319; pl. 5, fig. 3; pl. 7, fig. 3; pl. 9, fig. 3 (“Paniai Lake” [Papua Province, Indonesia]).
Cherax crassimanusRiek, 1967a: 119, fig. 5d; pl. 3B (“Beedelup Falls, Pemberton area, W. A.” [Western Australia, Australia]).
Cherax cuspidatusRiek, 1969: 913, fig. 15F (“20 miles south of Port Macquarie, N.S.W.” [New South Wales, Australia]).
Cherax depressusRiek, 1951: 375, figs. 7–9 (“Mt. Coot-tha, Brisbane” [Queensland, Australia]).
Cherax destructorClark, 1936: 26; pl. 1, figs. 3, 5; pl. 5, fig. 23 (“ponds in University grounds, Melbourne, Vic.” [Victoria, Australia]; lectotype designated by Lew Ton & Poore, 1987: 23).
= Cherax davisiClark, 1941a: 33; pl. 10, fig. 3 (“New South Wales: Dumaresq Creek, Armidale” [Australia]).
= Cherax esculusRiek, 1956: 6 (“Peel River at Nundle, N.S.W.” [New South Wales, Australia]).
Cherax dispar crassusRiek, 1951: 372 (“Caboolture, Queensland” [Australia]).
Cherax dispar disparRiek, 1951
= Cherax disparRiek, 1951: 371, figs. 2, 3 (“Sandy Creek, Moorooka, Brisbane” [Queensland, Australia]).
Cherax dispar elongatusRiek, 1951: 372, fig. 4 (“Lake McKenzie, Fraser Island, Queensland” [Australia]).
Cherax gherardiiPatoka, Bláha & Kouba, 2015a
= Cherax (Astaconephrops) gherardiiPatoka, Bláha & Kouba, 2015a: 527, figs. 1–3 (“surrounding tributary streams to Ajamaru (also Ayamaru or Aiamaru) Lakes, West Papua, Indonesia (GPS S1°16ʹ23.18ʺ E132°12ʹ21ʺ)”).
= Cherax (Astaconephrops) gherardiaePatoka, Bláha & Kouba, 2015b: 830 [unjustified emendation under Art. 32.5.1
Cherax glaberRiek, 1967a: 120, fig. 5f; pl. 4B (“12 miles north of Augusta, W.A.” [Western Australia, Australia]).
Cherax gladstonensisRiek, 1969: 915 (“Gladstone, Qld.” [Queensland, Australia]).
Cherax holthuisiLukhaup & Pekny, 2006
= Cherax (Cherax) holthuisiLukhaup & Pekny, 2006: 101, figs. 1–4 (“Indonesia, Western Irian Jaya [= West Papua province], Kais River Drainage, at the shorelines of the Aitinjo Lake, situated about 25 km southeast of Ajamaroe”).
Cherax leckiiCoughran, 2005a: 191, figs. 2, 3 (“ephemeral tributary of Koreelah Creek (dry sclerophyll), Koreelah National Park, northeastern N.S.W.; 28°16.932ʹS 152°28.578ʹE” [New South Wales, Australia]).
Cherax longipesHolthuis, 1949: 317; pl. 5, fig. 2; pl. 9, fig. 2 (“Meijepa, Tigi Lake” [Papua Province, Indonesia]).
Cherax lorentzi aruanusRoux, 1911
= Cheraps aruanusRoux, 1911: 88, figs. 1–3 (“Ngaigouli, Pobdjetour (Trangan); Seltouli and Manoumbai (Kobroor), Arou” [=Aru Islands, Maluku Province, Indonesia]).
Cherax lorentzi lorentziRoux, 1911
= Cheraps lorentziRoux, 1911: 97, figs. 4, 5 (“near Mapar, Manikion District, N.W. New Guinea, W. of Geelvink Bay, 1°42ʹS, 133°50ʹE” [West Papua Province, Indonesia], lectotype designated by Holthuis, 1949: 305).
Cherax minorHolthuis, 1996
= Cherax (Astaconephrops) minorHolthuis, 1996: 361, figs. 1, 2 (“Sungai Kurao, Wurigelebur, Irian Jaya, 3°47ʹS 138°42ʹE” [Papua Province, Indonesia]).
Cherax misolicusHolthuis, 1949: 307; pl. 7, fig. 1; pl. 8, fig. 3 (“Misool, off N.W. New Guina, 1°40ʹ–2°4ʹS 129°44ʹ–130°30ʹE, in small rivulet” [West Papua Province, Indonesia]).
Cherax monticolaHolthuis, 1950: 7, figs. 2–4 (“Ibele River, 15 km northeast of Habbema Lake, altitude 2250 m, latitude 4°S, longitude 138°44ʹ E” [Papua Province, Indonesia]).
Cherax muridoHolthuis, 1949: 313; pl. 4, fig. 2; pl. 8, fig. 6 (“Paniai Lake” [Papua Province, Indonesia]).
Cherax neopunctatusRiek, 1969: 913 (“Coffs Harbour, N.S.W.” [New South Wales, Australia]).
Cherax nucifragaShort, 1991: 115, figs. 1–4 (“Palm Springs, near Channel Pt, Northern Territory, 13°11ʹS, 130°10.5ʹE” [Australia]).
Cherax pallidusHolthuis, 1949: 311; pl. 4, fig. 1; pl. 8, fig. 5 (“Paniai Lake” [Papua Province, Indonesia]).
Cherax paniaicusHolthuis, 1949: 324; pl. 6, fig. 2; pl. 9, fig. 5 (“Paniai Lake” [Papua Province, Indonesia]).
Cherax papuanusHolthuis, 1949: 309; pl. 2, fig. 2; pl. 8, fig. 4 (“Lake Marguerite (= Lake Kutubu), Papua, 6°22ʹS, 143°17ʹE” [Papua New Guinea]).
Cherax parvusShort & Davie, 1993: 70, figs. 1–4 (“O’Leary Ck, tributary of the Tully R. above Koombooloomba Dam, 17°50.7ʹS, 145°37.7ʹE” [Queensland, Australia]).
Cherax peknyiLukhaup & Herbert, 2008
= Cherax (Cherax) peknyiLukhaup & Herbert, 2008: 213, figs. 1, 2, 3A–G (“Tamu Creek, Fly River Drainage,, 7°34ʹ S 141°03ʹ E, Western Province, PNG” [Papua New Guinea]).
Cherax plebejus (Hess, 1865)
= Astacoides plebejusHess, 1865: 164; pl. 7, fig. 17 [“Sydney”; presumed to be in error by Riek (1967a) who considers the type series to come from “Albany area, Western Australia” [Australia]).
= Chaeraps intermediusSmith, 1912: 168; pl. 24, fig. 2; pl. 27, fig. 34 (“Western Australia” [Australia]).
Cherax preissii (Erichson, 1846)
= Astacus (Cheraps) PreissiiErichson, 1846: 101 (“near Albany” [Western Australia, Australia]; neotype designated by Riek (1951: 377).
= Cheraps preissii var. angustusMcCulloch, 1914: 231; pl. 32 (“near Albany” [Western Australia, Australia]; lectotype (as holotype) designated by Riek, 1951: 377, valid designation under Art. 74.5 (ICZN, 1999)).
Cherax pulcherLukhaup, 2015
= Cherax (Astaconephrops) pulcherLukhaup, 2015: 2, figs. 1–5 (“Hoa Creek, Teminabuan region, Kepala Burung (Vogelkop) Peninsula, West Papua, Indonesia”).
Cherax punctatusClark, 1936: 29; pl. 1, fig. 6; pl. 6, fig. 25 (“Queensland: Coorari” [Australia]).
Cherax quadricarinatus (von Martens, 1868)
= Astacus quadricarinatusvon Martens, 1868: 617 (“Cap York” [= Cape York, Queensland, Australia]).
Cherax quinquecarinatus (Gray in Eyre, 1845)
= Astacus quinque-carinatus Gray in Eyre, 1845: 410; pl. 3, fig. 3 (“Western Australia, near Swan River” [Australia]).
= Cherax glabrimanusRiek, 1967a: 117, fig. 5c; pl. 3A (“10 miles south of Yallingup, W.A.” [Western Australia, Australia]).
= Cherax neocarinatusRiek, 1967a: 118 (“10 miles east of Blackwood River, Western Australia” [Australia]).
Cherax rhynchotusRiek, 1951: 377, fig. 12 (“Mapoon, Queensland” [Australia]).
Cherax robustusRiek, 1951: 376, fig. 10 (“Lake Birrabeen, Fraser Island” [Queensland, Australia]).
Cherax rotundusClark, 1941a: 34; pl. 10, fig. 2 (“Queensland: Muddy River, Severn” [Australia]).
Cherax setosusRiek, 1951
= Cherax rotundus setosusRiek, 1951: 385 (“Booral, Karuah River, Port Stephens, N.S.W.” [New South Wales, Australia]).
Cherax snowdenLukhaup, Panteleit & Schrimpf, 2015: 4, figs. 1–5. (“Oinsok River Drainage, Sawiat District, Kepala Burung (Vogelkop) Peninsula, West Papua, Indonesia”).
= Cherax (Cherax) subterigneusPatoka, Bláha & Kouba, 2015b: 831, figs. 1–5 (“Kais River drainage, at the shoreline of Aitinjo Lake, about 20–25 km southeast of Ajamaru Lakes, West Papua (GPS 1°25ʹ55.895ʺS 132°22ʹ55.996ʺE)” [Indonesia]).
Cherax solusHolthuis, 1949: 326; pl. 6, fig. 3; pl. 9, fig. 6 (“Meijepa, Tigi Lake” [Papua Province, Indonesia]).
Cherax tenuimanusSmith, 1912
= Chaeraps tenuimanusSmith, 1912: 166; pl. 22; pl. 27, fig. 30 (“Margaret River, Western Australia” [Australia]).
Cherax urospinosusRiek, 1969: 916 (“Indooroopilly, Brisbane, Qld.” [Queensland, Australia]).
Cherax warsamsonicusLukhaup, Eprilurahman & von Rintelen, 2017: 154, figs. 1–5 (“unnamed creek draining into Warsamson River, north of Sorong City, 0°49ʹ16.62ʺS 131°23ʹ3.34ʹE, West Papua, Indonesia”).
Cherax wasselliRiek, 1969: 914 (“Bridge Spring, between Rocky R. and Scrubby C., Cape York, Qld.” [Queensland, Australia]).
EngaeusErichson, 1846
= Astacus (Engaeus) Erichson, 1846: 102 [type species Astacus (Engaeus) fossorErichson, 1846, by subsequent designation in Clark (1936); gender masculine].
= PseudengaeusClark, 1936; 47 [type species Pseudengaeus strictifronsClark, 1936, by original designation; gender masculine].
= AustroastacusClark, 1936: 51 [type species Engaeus hemicirratulusSmith & Schuster, 1913, by original designation; gender masculine].
Engaeus affinisSmith & Schuster, 1913: 120, figs. 23, 24, 25, 26 (“Warburton, Vic.” [Victoria, Australia] according to Riek, 1969).
= Engaeus villosusClark, 1936: 44; pl. 1, fig. 10; pl. 9, fig. 36 (“Victoria: Acheron River flats, near Marysville” [Australia]).
Engaeus australisRiek, 1969: 905, fig. 14D (“Lilly Pilly Gully, Wilson’s Promontory, Vic.” [Victoria, Australia]).
Engaeus cisternariusSuter, 1977: 78, figs. 1–3 (“in Nothofagus cunninghamii rainforest, at a tributary of the Dip River, north-western Tasmania, grid reference (G.R) 7915635505” [Australia]).
Engaeus cunicularius (Erichson, 1846)
= Astacus (Engaeus) cuniculariusErichson, 1846: 102 (“Vandiemensland” [Tasmania, Australia]).
Engaeus curvisuturusHorwitz, 1990: 498, fig. 18 (“Yarra R. plains and slightly up the hill-slope, near bridge over Yarra R. at Warburton, GR 8022; 879 210” [Victoria, Australia]).
Engaeus cymus (Clark, 1936)
= Austroastacus cymusClark, 1936: 53, fig. 2 (“Victoria: Dondangadale (between Myrtleford and Whitfield)” [Australia]).
= Engaeus parvulusRiek, 1951: 386 (“Blundells, Condor Creek, A.C.T.” [Australian Capital Territory, Australia]).
Engaeus disjuncticusHorwitz, 1990: 544, fig. 29 (“small tributary of Rubicon R, due E. of Elizabeth Town on Weetah Rd, N. Tas.” [Tasmania, Australia]).
Engaeus fossor (Erichson, 1846)
= Astacus (Engaeus) fossorErichson, 1846: 102 (“Tasmania” [Australia]; lectotype designated by Horwitz, 1990: 442).
= Engaeus ignotusClark, 1939: 124; pl. 13, fig. 8–8b (“Smithton” [Tasmania, Australia]).
Engaeus fultoniSmith & Schuster, 1913: 126 (“Fern Tree Gully and Cape Otway Forest, Victoria” [Australia]).
Engaeus granulatusHorwitz, 1990: 556, fig. 31 (“Browns Ck, upstream from road, at the mouth of creek, E. of Port Sorell, Tas.” [Tasmania, Australia]).
Engaeus hemicirratulusSmith & Schuster, 1913: 123, figs. 34, 35, 37, 38 (“Thorpdale; Warragul, Moyarra (near Oultrim); Kongwak (near Jumbanna), Gippsland” [Victoria, Australia]).
= Engaeus jumbunnaRiek, 1969: 905, fig. 14E (“Kongwak, near Jumbunna, south Gippsland, Vic.” [Victoria, Australia]).
Engaeus karnangaHorwitz, 1990: 465, fig. 11 (“ swamp at Lilly Pilly Gully, Wilsons Promontory, Vic., GR 8020: 864 347” [Victoria, Australia]; in error, considered to be “Moyarra near Oultrim [= Outtrim]” [Victoria, Australia] by Lew Ton & Poore, 1987).
Engaeus laevis (Clark, 1941a)
= Geocharax laevisClark, 1941a; 35; pl. 10, fig. 4 (“Victoria: Bunyip” [Australia]).
Engaeus lenganaHorwitz, 1990: 566, fig. 33 (“seepage with pipe outlet at beach, near campsite/boat launch on E. coast of Rocky Cape, in National Park, GR 8016: 743 750” [Tasmania, Australia]).
Engaeus leptorhynchusClark, 1939: 122; pl. 13, figs. 6–6b (“Pioneer Mine, Derby” [Tasmania, Australia]).
Engaeus lyelli (Clark, 1936)
= Geocharax lyelliClark, 1936: 32, fig. 1 (“Gisborne, Vic.” [Victoria, Australia]; lectotype (as type) designated by Riek, 1969: 880).
Engaeus mairenerHorwitz, 1990: 550, fig. 30 (“small creek in tea-tree swamp, off Big Hill Rd, 1 km E. of Lefroy, NE. Tas., GR 8215: 985 495” [Tasmania, Australia]).
Engaeus mallacootaHorwitz, 1990: 573, fig. 34 (“Double Ck along Nature Trail, in Croajingolong Natl Pk, on Genoa-Mallacoota Rd, E. Vic., GR 8822: 373 426” [Victoria, Australia]).
Engaeus martigenerHorwitz, 1990: 578, fig. 35 (“upper reaches of Fotheringate Ck, at Strzelecki Peaks, Flinders Is., GR 8517: 913 493” [Tasmania, Australia]).
Engaeus merosetosusHorwitz, 1990: 470, fig. 12 (“tributary of Waurn Ponds Ck in cleared paddock below dam, 2 km N. of Mt. Moriac in W. Vic.” [western Victoria, Australia]).
Engaeus nulloporiusHorwitz, 1990: 561, fig. 32 (“tea-tree swamp, 1.5 km S. of 3-way corner (Frankford, Glengarry, Birralee) of road, N. Tas.” [northern Tasmania, Australia]).
Engaeus orientalisClark, 1941a: 39; pl. 10, fig. 8 (“Victoria: Cann River Valley; Scanlon’s Creek; Orbost” [Australia]).
Engaeus orramakunnaHorwitz, 1990: 583, fig. 36 (“tributary of Pipers R on Lilydale Rd, about 3 km S. of Lilydale, NE. Tas., GR 8315: 181 307” [north-eastern Tasmania, Australia]).
Engaeus phyllocercusSmith & Schuster, 1913: 122, figs. 30, 31, 36 (“Narracan River, Thorpdale, Trafalgar” [Victoria, Australia]).
Engaeus quadrimanusClark, 1936: 41; pl. 8, fig. 32 (“Warragul” [Victoria, Australia]; lectotype designated by Horwitz, 1990: 455).
= Engaeus marmoratusClark, 1941a: 39; pl. 10, fig. 7 (“Victoria: South Buchan” [Australia]).
Engaeus rostrogaleatusHorwitz, 1990: 588, fig. 37 (“Ryton Junction on Midland Highway, about 30 km due S. of Morwell, Eastern Strzelecki Ranges, Vic., GR 8120: 453 354” [Victoria, Australia]).
Engaeus sericatusClark, 1936: 40; pl. 8, fig. 34 (“Victoria: Croydon” [Australia]).
Engaeus spinicaudatusHorwitz, 1990: 594, fig. 38 (“plain at second crossing of Surveyors Ck after Scottsdale on Old Waterhouse Rd, NE. Tas., GR 8415: 504 517” [north-eastern Tasmania, Australia]).
Engaeus sternalis (Clark, 1936)
= Pseudengaeus sternalisClark, 1936: 48; pl. 9, fig. 41 (“Warragul, Vic.” [Victoria, Australia]; lectotype (as type) designated by Riek, 1969: 889).
Engaeus strictifrons (Clark, 1936)
= Pseudengaeus strictifronsClark, 1936: 47; pl. 9, fig. 40 (“Victoria: Portland” [Australia]).
Engaeus tayateaHorwitz, 1990: 599, fig. 39 (“small tributary of Pearly Brook near bridge on Pearly Brook Rd, about 8 km due W. of Mt Horror, NE. Tas., GR 8415: 539 539” [northeastern Tasmania, Australia]).
Engaeus tuberculatusClark, 1936: 43; pl. 9, fig. 39 (“Victoria: Sherbrook Falls; Dandenong; Warburton” [Australia]).
= Engaeus connectusRiek, 1969: 906, fig. 14F (“2 miles south of Powelltown, Laver’s Creek, on Noojee Road, Vic.” [Victoria, Australia]).
Engaeus urostrictusRiek, 1969: 904, fig. 14C (“Dandenong Creek, at Alpine Road, Vic.” [Victoria, Australia]).
Engaeus victoriensisSmith & Schuster, 1913: 121, figs. 27, 28, 29, 32, 33 (“Dandenong Ranges, Vic.” [Victoria, Australia] according to Riek, 1969; lectotype (as type) designated by Riek, 1969: 879; considered lost by Lew Ton & Poore, 1987).
Engaeus yabbimunnaHorwitz, 1994: 439, fig. 1 (“Burnie Park, from burrow in seepage area in gully of Shorewell Creek below Oldacre Falls (GR 8015 068 551)” [Tasmania, Australia]).
EngaewaRiek, 1967a
= EngaewaRiek, 1967a: 106 [type species Engaewa subcoeruleaRiek, 1967a, by original designation; gender feminine].
Engaewa pseudoreductaHorwitz & Adams, 2000: 670, figs. 7C, 8B, 9B (“Asutralia: Western Australia, near Osmington, north-east of Margaret Riv.”).
Engaewa reductaRiek, 1967a: 108, fig. 3 (“Block 1041, ½ mile c. north of Quindalup Common, near Dunsborough, W. A.” [Western Australia, Australia]).
Engaewa similisRiek, 1967a: 110, fig. 4 (“Augusta, W. A.” [Western Australia, Australia]).
Engaewa subcoeruleaRiek, 1967a: 107, fig. 2; pl. 1 (“Inlet River, 15 miles north-west of Walpole, W. A.” [Western Australia, Australia]).
Engaewa walpoleaHorwitz & Adams, 2000: 673, figs. 10A–J (“Australia, Western Australia, The Knoll Scenic Drive, Walpole”).
EuastacusClark, 1936
= EuastacusClark, 1936: 10 [type species Cancer serratusShaw, 1794 (nec Forskål, 1775), by original designation; gender masculine].
= EuastacoidesRiek, 1956: 4 [type species Euastacoides setosusRiek, 1956, by original designation; gender masculine].
Euastacus angustusFurse, Dawkins & Coughran, 2013: 107, fig. 3. (“unnamed tributary, Border Ranges National Park, northeastern New South Wales; 28°S 153°E” [Australia]).
Euastacus armatus (von Martens, 1866)
= Astacus armatusvon Martens, 1866: 35 (“Murray River, Australia”).
= Euastacus elongatusClark, 1941b: 12; pl. 1 (“Victoria: Echuca, Murray River” [Australia]).
Euastacus australasiensis (H Milne Edwards, 1837 [in H. Mine Edwards, 1834–1840])
= Astacus australasiensisH Milne Edwards, 1837 [in H. Mine Edwards, 1834–1840]: 332; pl. 24, figs. 1–5 (“Sydney area, New South Wales” [Australia] according to Morgan, 1997).
= Astacoides nobilisDana, 1852: 526; pl. 33, fig. 3a–b (“New South Wales?” [Australia]).
Euastacus balanensisMorgan, 1988: 1, figs. 3, 4 (“Qld, tributary of Davies Ck., Lamb Range, Atherton Tableland, (17°03ʹS, 145°37ʹE)” [Queensland, Australia]).
Euastacus bidawalusMorgan, 1986: 19, figs. 10, 11 (“Vic., Chandlers Ck., near junction with Cann R., 27 km north of Cann River, (37°20ʹS., 149°13ʹE.)” [Victoria, Australia]).
Euastacus bindalMorgan, 1989: 555, fig. 2 (“upper North Creek, Mt. Elliot, (19°30ʹS, 146°58ʹE), NEQ” [NE Queensland, Australia]).
Euastacus binzayediFurse, Dawkins & Coughran, 2013: 105, fig. 2. (“unnamed tributary/gully in Lamington National Park, southeast Queensland; 28°S 153°E” [Australia]).
Euastacus bispinosusClark, 1941b: 22; pl. 7 (“Victoria: Glenelg” [Australia]; lectotype (as holotype) designated by Morgan, 1986: 24).
Euastacus brachythoraxRiek, 1969: 912, fig. 16F (“Brown Mt., N.S.W.” [New South Wales, Australia]).
Euastacus clarkaeMorgan, 1997: 30, figs. 13, 14 (“NSW Tributary of Cockerawombeeba Creek, tributary of Forbes River, north of Birdwood, (31°11ʹS 152°22ʹE)” [New South Wales, Australia]).
Euastacus claytoniRiek, 1969: 909, fig. 16D (“Maclaughlin R., N.S.W.” [New South Wales, Australia]).
Euastacus crassusRiek, 1951
= Euastacus nobilis crassusRiek, 1951: 383 (“small stream at Bendora, A.C.T.” [Australian Capital Territory, Australia]).
Euastacus dalagarbeCoughran, 2005b: 362, fig. 4 (“minor gully feeding Brindle Creek (rainforest), Border Ranges National Park, northeastern N.S.W.; 28°22.789ʹS 153°04.334ʹE” [New South Wales, Australia]).
Euastacus dangadiMorgan, 1997: 42, figs. 19, 20 (“NSW Stockyard Creek, downstream of Cedar Park in Ingalba State Forest, north of Kempsey, (30°53ʹS 152°48ʹE)” [New South Wales, Australia]).
Euastacus dharawalusMorgan, 1997: 46, figs. 21, 22 (“NSW, Fitzroy Falls, stream above Falls” [New South Wales, Australia]).
Euastacus diversusRiek, 1969: 908 (“30 miles north of Orbost, Vic” [Victoria, Australia]).
Euastacus eungellaMorgan, 1988: 8, figs. 5, 6 (“Qld, tributary of Cattle Ck (North Branch), near Mt Dalrymple, Eungella National Park, west of Mackay, (21°02ʹS 148°37ʹE)” [Queensland, Australia]).
Euastacus fleckeri (Watson, 1935)
= Astacopsis fleckeriWatson, 1935: 233; pl. 34 (“Root’s Creek, near Mt. Carbine, in the Mt. Molloy district, about 80 miles west of Cairns” [Queensland, Australia]).
Euastacus gamilaroiMorgan, 1997: 50, figs. 23, 24 (“NSW Hanging Rock (near Nundle)” [New South Wales, Australia]).
Euastacus girurmulaynCoughran, 2005b: 365, fig. 5 (“Tuntable Creek, above falls, Nightcap National Park, northeastern N.S.W.; 28°33.234ʹS 153°17.785ʹE” [New South Wales, Australia]).
Euastacus gumarMorgan, 1997: 53, figs. 25, 26 (“NSW Gorge Creek, Richmond Range State Forest, on Gorge Creek-Sextonville Road, (28°45ʹS 152°42ʹE)” [New South Wales, Australia]).
Euastacus guruhgiCoughran, 2005b: 366, fig. 6 (“Korrumbyn Creek, adjacent to visitor carpark (rainforest), Mount Warning National Park, northeastern N.S.W.; 28°23.875ʹS 153°16.893ʹE” [New South Wales, Australia]).
Euastacus guwinusMorgan, 1997: 57, fig. 27 (“NSW Tianjara Creek above Falls, tributary Shoalhaven River, near Tianjara, (35°07ʹS 150°20ʹE)” [New South Wales, Australia]).
Euastacus hirsutus (McCulloch, 1917)
= Astacopsis serratus var. hirsutusMcCulloch, 1917: 238 (“Belmore Falls Creek, which runs into the Kangaroo River, New South Wales” [Australia]).
= Euastacus keirensisRiek, 1969: 910, fig. 16C (“Mt. Keira, south coast of New South Wales” [Australia]).
Euastacus hystricosusRiek, 1951: 380 (“Yabba Creek, Yabba, Queensland” [Australia]).
Euastacus jagabarCoughran, 2005b: 368, fig. 7 (“tributary to Sheepstation Creek, Border Ranges National Park, northeastern N.S.W.; 28°23.900ʹS 153°01.500ʹE” [New South Wales, Australia]).
Euastacus jagaraMorgan, 1988: 44, figs. 24, 25 (“Qld, Flaggy Ck., 3,000 ft, Mistake Mts. via Laidley” [Queensland, Australia]).
Euastacus kershawi (Smith, 1912)
= Astacopsis kershawiSmith, 1912: 160; pls. 19, 20 (“Vic., Moe River, Gippsland” [Victoria, Australia]; lectotype (as holotype) designated by Riek, 1969: 894; lectotype designation by Morgan (1986: 38) invalid, see Lew Ton & Poore, 1987).
Euastacus maccaiMcCormack & Coughran, 2008: 472, figs. 2, 3A (“ephemeral wet area within the drainage of Uriamukka Creek, a tributary of the Nowendoc River, which joins the Manning River, New South Wales” [Australia]).
Euastacus maidae (Riek, 1956)
= Euastacoides maidaeRiek, 1956: 5 (“upper reaches of Currumbin Creek, south-east Queensland” [Australia]).
Euastacus mirangudjinCoughran, 2002: 26, figs. 2–4 (“Iron Pot Creek, an upper tributary of the Richmond River, approximately 30 kn NW of Kyogle (28°28ʹ30”S 152°45ʹE)” [New South Wales, Australia]).
Euastacus monteithorumMorgan, 1989: 558, fig. 3 (“Beauty Spot 98 (Queensland Department of Forestry), headwaters of Kroombit Creek, Kroombit Tops, (24°22ʹS 151°00ʹE), central Q.” [Queensland, Australia]).
Euastacus morganiCoughran & McCormack, 2011: 18, figs. 1, 2 (“Australia, New South Wales, tributary of Little Nymboida River, upstream of Eastern Dorrigo Way road crossing near Lowanna, on periphery of Bindarri National Park, rainforest, 30.2288°S 152.9203°E”).
Euastacus neodiversusRiek, 1969: 908 (“National Park, Wilson’s Promontory, in stream of E. slope of Sealers Cover track” [Victoria, Australia] according to Lew Ton & Poore, 1987).
Euastacus neohirsutusRiek, 1956: 3 (“twenty miles west of Dorrigo, N.S.W.” [New South Wales, Australia]).
= Euastacus aquilusRiek, 1969: 911 (“near Point Loukout, New England National Park, N.S.W.” [New South Wales, Australia]).
Euastacus pilosusCoughran & Leckie, 2007: 309, figs. 2, 3B, 6 (“lower reaches of Flaggy Creek, a short distance upstream of its junction with the Cataract River, approximately 3 km north of Sandy Hill and the Bruxner Highway, and 13 km west/northwest of Drake” [New South Wales, Australia]).
Euastacus polysetosusRiek, 1951: 384 (“Tubrabucca Creek, Hunter River, Barrington Tops, N.S.W.” [New South Wales, Australia]).
Euastacus reductusRiek, 1969: 907, fig. 16B (“Upper Allyn R., below the southern end of Barrington Tops, N.S.W.” [New South Wales, Australia]).
= Euastacus alienusRiek, 1969; 907 (“Bulahdelah Mt., near Stroud, N.S.W.” [New South Wales, Australia]).
Euastacus riekiMorgan, 1997: 79, figs. 37, 38 (“NSW Snowy River Bridge, Mount Kosciusko” [New South Wales, Australia]).
Euastacus robertsiMonroe, 1977: 65; pl. 19 (“Horan’s Creek, Mt. Finnigan National Park, NE.Q.” [Queensland, Australia]).
Euastacus setosus (Riek, 1956)
= Euastacoides setosusRiek, 1956: 4 (“Mt. Glorious, Q.” [Queensland, Australia]).
Euastacus simplexRiek, 1956: 2 (“fifteen miles N. of Armidale, N.S.W.” [New South Wales, Australia]).
Euastacus spinichelatusMorgan, 1997: 87, figs. 41, 42 (“NSW Fenwicks Creek, tributary of Hastings River on Oxley Highway south of Yarrowitch, (31°18ʹS 151°59ʹE)” [New South Wales, Australia]).
Euastacus spinifer (Heller, 1865)
= Cancer serratusShaw, 1794 (junior homonym of Cancer serratusForskål, 1775): 21; pl. 8 (“New Holland”; presumed to be Sydney, New South Wales [Australia] by Davie, 2002).
= Astacoides spiniferHeller, 1865: 102; pl. 9 (“Neuholland”, presumed to be Sydney region [Australia] by Ahyong, 2014).
= Astacopsis paramattensisSpence Bate, 1888: 202; pl. 27, fig. 1 (“Paramatta River, Sydney, Australia”).
= Astacopsis sydneyensisSpence Bate, 1888: 204; pl. 27, fig. 2 (“Sydney, Australia”).
= Euastacus spinosusRiek, 1956: 2; pl. 1 (“upper reaches of Hastings River, N.S.W.” [New South Wales, Australia]).
= Euastacus clydensisRiek, 1969: 911 (“Clyde R., near Brooman” [New South Wales, Australia]).
Euastacus sulcatusRiek, 1951: 379 (“Binna Burra, Lamington National Park, Queensland” [Australia]).
= Euastacus cunninghamiRiek, 1951: 379 (“western slopes of Cunningham’s Gap, Queensland” [Australia]).
Euastacus suttoniClark, 1941b: 18; pl. 5 (“Queensland: Wyberba” [Australia]).
Euastacus urospinosus (Riek, 1956)
= Euastacoides urospinosusRiek, 1956: 5 (“Obi Obi Creek, Maleny, Q.” [Queensland, Australia]).
Euastacus valentulusRiek, 1951: 380 (“upper reaches of Currumbin Creek” [Queensland, Australia]).
Euastacus vesperMcCormack & Ahyong, 2017: 557, figs. 1B–D, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 (“Cudgegong River, Coricudgy Road, New South Wales, 32°52.009ʹS, 150°18.295ʹE” [Australia]).
Euastacus woiwuruMorgan, 1986: 43, figs. 20, 21 (“Vic., Dobsons Ck. near Alpine Road Crossing, Dandenong Mountains east of Melbourne” [Victoria, Australia]).
Euastacus yangaMorgan, 1997: 99, figs. 46–48 (“NSW Double Creek, tributary Boyne Creek near Pigeon Rouse, west of Ulladulla, (35°22ʹS 1500 15ʹE)” [New South Wales, Australia]).
Euastacus yarraensis (McCoy, 1888)
= Astacopsis serratus var. yarraensisMcCoy, 1888: 225; pl. 160 (“Yarra and its numerous affluents flowing southwards into the sea of the south coast of the colony” [Victoria, Australia]).
Euastacus yigaraShort & Davie, 1993: 75, figs. 6–8 (“O’Leary Ck., 17°50.7ʹS, 145°37.7ʹE” [Queensland, Australia]).
GeocharaxClark, 1936
= GeocharaxClark, 1936: 31 [type species Geocharax gracilisClark, 1936, by original designation; gender masculine].
= ParastacoidesClark, 1936: 48 [type species Astacus tasmanicusErichson, 1846, by original designation; gender masculine].
Geocharax falcataClark, 1941a: 36; pl. 10, fig. 5 (“Fyans Creek, south of divide of Grampians” [Victoria, Australia] according to Lew Ton & Poore, 1987; lectotype (as type) designated by Riek, 1969: 891).
Geocharax tasmanicus (Erichson, 1846)
= Astacus tasmanicusErichson, 1846: 94 (“Vandiemensland”; probably far northwest Tasmania [Australia] according to Hansen & Richardson, 2006).
= Geocharax gracilisClark, 1936: 31; pl. 1, fig. 8; pl. 6, fig. 26 (“Victoria: Gellibrand River, south of Colac” [Australia]).
GramastacusRiek, 1972
= GramastacusRiek, 1972: 385 [type species Gramastacus insolitusRiek, 1972, by original designation; gender masculine].
Gramastacus insolitusRiek, 1972: 386, figs. 2, 16, 19, 21, 24 (“8 km SW. of Moyston, western Victoria” [Australia]).
= Gramastacus gracilisRiek, 1972: 386, figs. 17, 20, 22 (“Dwyer’s Creek, Grampians, western Victoria” [Australia]).
Gramastacus lacusMcCormack, 2014; 56, figs. 1–3 (“Boomeri swamp behind Boomeri camp ground, off Old Gibber Road, Myall Lakes National Park, 32.50910°S 152.32143°E” [New South Wales, Australia]).
Lammuastacus ††Aguirre-Urreta, 1992
= LammuastacusAguirre-Urreta, 1992: 819 [type species Lammuastacus longirostrisAguirre-Urreta, 1992, by original designation; gender masculine].
Lammuastacus longirostris †† Aguirre-Urreta, 1992: 819, figs. 4–7 (“headwaters of Arroyo Las Bayas, lower member of the Ñirihuau Formation, Oligocene” [Patagonia, Argentina]).
OmbrastacoidesHansen & Richardson, 2006
= OmbrastacoidesHansen & Richardson, 2006: 733 [type species Parastacoides leptomerusRiek, 1951, by original designation; gender masculine].
Ombrastacoides asperrimanusHansen & Richardson, 2006: 738, fig. 7 (“Australia: Tasmania: at Birchs Inlet, Landing Creek quarry”).
Ombrastacoides brevirostrisHansen & Richardson, 2006: 740, fig. 8 (Australia: Tasmania: at Birches Inlet, Landing Creek quarry”).
Ombrastacoides decemdentatusHansen & Richardson, 2006: 743, fig. 9 (“Australia: Tasmania: roadside seepage at The Needles, Strathgordon Road”).
Ombrastacoides denisoniHansen & Richardson, 2006: 745, fig. 10 (“Australia: Tasmania: McDougalls Road at crossing of Little Denison River”).
Ombrastacoides dissitusHansen & Richardson, 2006: 747, fig. 11 (“Australia: Tasmania: plain east of junction of Leprena track with Catamaran River, Lune River”).
Ombrastacoides huonensisHansen & Richardson, 2006: 749, fig. 12 (“Australia: Tasmania: plain west of Scotts Peak Road near Harlequin Hill”).
Ombrastacoides ingressusHansen & Richardson, 2006: 752, fig. 13 (“Australia: Tasmania: floodplain of small creek at east side of Victoria Pass, Lyell Highway”).
Ombrastacoides leptomerus (Riek, 1951)
= Parastacoides leptomerusRiek, 1951: 387 (“Lake Lilla and outlet stream, Cradle Mt., Tasmania” [Australia]).
= Parastacoides setosimerusRiek, 1951: 386 (“Mt. Rufus, Tasmania” [Australia]).
Ombrastacoides parvicaudatusHansen & Richardson, 2006: 754, fig. 14 (“Australia: Tasmania: creek near King River, Lyell Highway”).
Ombrastacoides professorumHansen & Richardson, 2006: 757, fig. 15 (“Australia: Tasmania: Allens Creek, Crotty Road”).
Ombrastacoides pulcher (Riek, 1967b)
= Parastacoides pulcherRiek, 1967b: 1006, fig. 6 (“Lake Pedder, south-western Tasmania” [Australia]).
Palaeoechinastacus ††Martin, Rich, Poore, Schultz, Austin, Kool & Vickers-Rich, 2008
= PalaeoechinastacusMartin, Rich, Poore, Schultz, Austin, Kool & Vickers-Rich, 2008: 288 [type species Palaeoechinastacus australianusMartin, Rich, Poore, Schultz, Austin, Kool & Vickers-Rich, 2008, by monotypy; gender masculine].
Palaeoechinastacus australianus †† Martin, Rich, Poore, Schultz, Austin, Kool & Vickers-Rich, 2008: 288, fig. 2A–C (“Otway group (Albian) at Dinosaur Cove, Cape Otway, Victoria, Australia”).
Paranephrops †White, 1842
= ParanephropsWhite, 1842: 79 [type species Paranephrops planifronsWhite, 1842, by monotypy; gender masculine].
Paranephrops fordycei †† Feldmann & Pole, 1994: 163, figs. 2–6 (“roadside cutting adjacent to Bannock Burn, some 800 m upstream from its confluence with the Kawarau River (grid ref. NZMS 260, F41/088625, New Zealand Geological Society Fossil Record Number F41/f214)” [New Zealand]).
Paranephrops planifronsWhite, 1842: 79 (“River Thames, New Zealand”).
= Paranephrops tenuicornisDana, 1852: 527 (“freshwater streams of New Zealand, about the Bay of Islands”).
Paranephrops zealandicus (White, 1847)
= Astacus ZealandicusWhite, 1847: 123 (“New Zealand”).
= Astacoides tridentatusWood-Mason, 1876: 4 (“New Zealand”).
= Paranephrops horridusMiers, 1876: 73 [nomen nudum].
= Paranephrops setosusHutton, 1873: 402 (“stream near Invercargill, Province of Otago; and the river Avon, near Christchurch, Canterbury” [New Zealand]).
= Paranephrops neo-zelanicusChilton, 1889: 249; pl. 10 [partim] (“South Island generally, excepting north-western portion; Stewart Island” [New Zealand]).
ParastacusHuxley, 1879
= ParastacusHuxley, 1879: 771 [type species Astacus pilimanusvon Martens, 1869, by subsequent designation in Faxon (1898); gender masculine].
Parastacus brasiliensis brasiliensis (von Martens, 1869)
= Astacus Brasiliensisvon Martens, 1869: 16; pl. 2, fig. 2 (“Sowohl bei Porto Alegre selbst, in einem Bache an dem Berge hinter der Stadt, als weiter im Binnenlande in der Region des Urwaldes bei Rödersberg” [= near Porto Alegro and the rainforest region near São Leopoldo, Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil]).
Parastacus brasiliensis pomatensisFontoura & Conter, 2008: 29, fig. 1. (“Brazil, Rio Grande do Sul, São Francisco de Paula, Pró Mata, Garapiá stream (29°29.371ʹS; 50°13.800ʹW)”).
Parastacus caeruleodactylusRibeiro, Buckup, Gomes & Araujo, 2016: 311, figs. 6, 7, 8d, 9 (“Brazil, Rio Grande do Sul, Morrinhos do Sul (29°17ʹ13.7ʺS; 49°54ʹ53.42ʺW)”).
Parastacus defossusFaxon, 1898: 686; pl. 67, figs. 3, 4 (“Montevideo, Uruguay”).
Parastacus fluviatilisRibeiro, Buckup, Gomes & Araujo, 2016: 305, figs. 3, 4, 5e, f (“Brazil, Rio Grande do Sul, São José dos Ausentes, Apuaê-Inhandava Basin, Silveira River (28°35ʹ54.45ʺS; 49°59ʹ1.36ʺW)”).
Parastacus laevigatusBuckup & Rossi, 1980: 677, figs. 18–20 (“Joinville (Estrada da Cidra, Chácara dos Ipès), Santa Catarina, Brasil”).
Parastacus nicoleti (Philippi, 1882)
= Astacus NicoletiPhilippi, 1882: 624 (“Chile; Valdivia”).
Parastacus pilimanus (von Martens, 1869)
= Astacus pilimanusvon Martens, 1869: 15; pl. 2, fig. 1 (“Porto Alegre; Sta Cruzim obern Flussgebiet des Rio Pardo, eines Zuflusses des Jacuhy” [= Brazil, Rio Grande do Sul, Porto Alegre and Santa Cruz do Sul, in the upper basin of the Rio Pardo, a tributary of the Rio Jacuí]).
Parastacus pugnax (Poeppig, 1835)
= Astacus pugnaxPoeppig, 1835: 314 (“Talcahuano, Chile”; neotype designated by Hobbs, 1989: 80).
= Astacus chilensisH. Milne Edwards, 1837 [in H. Milne Edwards, 1834–1840]: 333 (“les côtes de Chili” [= Chilean coast]).
= Parastacus hassleriFaxon, 1898: 687; pl. 70, figs. 1–3 (“Talcahuano, Chile”).
Parastacus saffordiFaxon, 1898: 683; pl. 68 (“Montevideo, Uruguay”).
Parastacus tuerkayiRibeiro, Huber, Schubart & Araujo, 2017: 3, figs. 1, 2, 3, 4E–G (“Brazil, Santa Catarina, Penha, Beto Carreiro World (26°48ʹ10ʺS 48°37ʹ02ʺW)”).
Parastacus varicosusFaxon, 1898: 685; pl. 69 (“Colima, Mexico”; considered to be in error by Riek, 1971).
SamastacusRiek, 1971
= SamastacusRiek, 1971: 134 (type species Astacus spinifronsPhilippi, 1882, by original designation; gender masculine).
Samastacus spinifrons (Philippi, 1882)
= Astacus spinifronsPhilippi, 1882: 627. (“Llico i de Valdivia” [= Llico and Valdivia, Chile]).
= Astacus bimaculatusPhilippi, 1894: 378 [no type locality indicated].
= Parastacus agassiziiFaxon, 1898: 690; pl. 70, figs. 4, 5 (“Talcahuano, Chile”).
SpinastacoidesHansen & Richardson, 2006
= SpinastacoidesHansen & Richardson, 2006: 758 [type species Parastacoides insignisClark, 1939, by original designation; gender masculine].
Spinastacoides catinipalmusHansen & Richardson, 2006: 764, fig. 18 (“Australia: Tasmania: Indiana Creek, 500 m up road from Warners Landing, Lower Gordon River”).
Spinastacoides inermis (Clark, 1939)
= Parastacoides inermisClark, 1939: 126; pl. 13, fig. 10–10b (“Adamson’s Peak” [Tasmania, Australia]).
= Parastacoides sternalisRiek, 1967b: 1002, fig. 4 (“North-east of Mt. Bowes, south-western Tasmania” [Australia]).
Spinastacoides insignis (Clark, 1939)
= Parastacoides insignisClark, 1939: 126; pl. 13, fig. 11–11b (“Melaleuca Creek, southwestern Tasmania” [Australia]).
TenuibranchiurusRiek, 1951
= TenuibranchiurusRiek, 1951: 381 [type species Tenuibranchiurus glypticusRiek, 1951, by original designation; gender masculine].
Tenuibranchiurus glypticusRiek, 1951: 382, fig. 13 (“Caloundra, Queensland” [Australia]).
VirilastacusHobbs, 1991a
= VirilastacusHobbs, 1991a: 802 (type species Parastacus araucaniusFaxon, 1914, by original designation; gender masculine).
Virilastacus araucanius (Faxon, 1914)
= Parastacus araucaniusFaxon, 1914: 353; pl. 4 (“Corral, Chile”).
Virilastacus jaraiRudolph & Crandall, 2012: 262, figs. 2–5 (“homestead in the “Quinta El Porvenir” sector (37°26ʹ39.84ʺS, 72°18ʹ37.12ʺW), 1.5 km northeast of the town of Los Ángeles, in southern Chile, Biobío región”).
Virilastacus retamaliRudolph & Crandall, 2007: 503, figs. 2–5 (“geogenous peatland in the “Los Kakaknes” homestead of Rucapihuel in the Coastal Cordillera, province of Osorno, southern Chile”).
Virilastacus rucapihuelensisRudolph & Crandall, 2005: 767, figs. 2–5 (“Rucapihuel, province of Osorno, Chile”).
Nomina dubia
Astacus (Cambarus) WiegmanniErichson, 1846: 99 (“Mexiko” [= Mexico]).
Nomina nuda
Austropotamobius italicus meridionalisFratini, Zaccara, Barbaresi, Grandjean, Souty-Grosset, Crosa & Gherardii, 2005: 115.
Austropotamobius pallipes rhodanicusStarobogatov, 1996: 12 [stated to be a replacement name for Austropotamobius pallipes pallipes var. rhodanicus Laurent & Suscillon 1962; an original name combination which does exist according to Manganelli et al., 2006].
Cambarus (Cambarus) lobdelliLyle, 1938: 76.
Cambarus (Faxonius) creaseriLyle, 1938: 76.
Cambarus (Girardiella) hagenianus carriLyle, 1938: 76.
Cambarus (Girardiella) hagenianus evansiLyle, 1938: 76.
Cambarus (Girardiella) hagenianus forestaeLyle, 1938: 76.
Cambarus (Ortmannicus) cookaeLyle, 1938: 76.
Cambarus (Ortmannicus) evictusLyle, 1938: 76.
Cambarus schmittiPenn, 1941: 8.
Incertae sedis
Enoploclytia porteriMiller & Ash, 1988: 275, figs. 2, 3 (“Late Carnian (Upper Triassic), Petrified Forest National Park, Arizona” [USA]).
Unavailable names
Procambarus fallax forma virginalisMartin, Dorn, Kawai, van der Heiden & Scholtz, 2010: 114.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We thank the US National Science Foundation EF-0531762 and DEB-1301820 and the Biodiversity Synthesis Center (http://synthesis.eol.org/) for partial funding of this effort. Martyn E. Y. Low (Lee Kong Chian Natural History Museum, Singapore) provided much appreciated help in tracking down obscure references as well as providing nomenclatorial opinions on several species. Arthur Anker aided with finding and translating Russian and Ukranian literature, whilst James W. Fetzner Jr. and Sancia van der Meij helped with other obscure literature. David Stern was instrumental in providing some helpful phylogenetic analyses to help work through certain taxonomic issues and his assistance in the development of figures 1 and 2 is gratefully acknowledged. Chris Lukhaup is gratefully acknowledged for allowing us to use his excellent photos. We are thankful to Peter Castro, Susie Adams, Fred Schram, and two anonymous reviewers for their careful reading of our manuscript and many helpful suggestions.
REFERENCES