-
PDF
- Split View
-
Views
-
Cite
Cite
Ran Nir-Paz, Itamar Grotto, Israel Strolov, Asher Salmon, Michal Mandelboim, Ella Mendelson, Gili Regev-Yochay, Absence of in-flight transmission of SARS-CoV-2 likely due to use of face masks on board, Journal of Travel Medicine, Volume 27, Issue 8, December 2020, taaa117, https://doi.org/10.1093/jtm/taaa117
Close - Share Icon Share
While there are many reports of patients who were either severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) or coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) active patients flying in the last epidemic, there is no evidence to support viral transmission during flights. Recently, it was reported that in flights arriving from endemic areas to Greece and Brunei, asymptomatic rate was as high as 3–5%.1,2 Recently potential transmission during a flight in Africa was suggested.3 Thus, it would be important to anticipate the risk of such travel. On 20 February Israel repatriated 11 citizens form the Diamond Princesses cruise ship in Japan back to Israel. Those 11 patients had at least 1 negative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) for SARS-Cov-2 before flight boarding. A total of six were women and five men with age ranging from 42 to 76 (median of 70). All were transferred in a dedicated bus directly from the ship to the aircraft. The equipment was a charter Bombardier Galaxy 6000 commercial aircraft. Flight staff included three pilots and one steward, who were instructed to wear filtering facepiece (FFP2) masks. The crew had minimal interaction with passengers that was mainly in the distribution of the meals. This aircraft have two outflow valves that alternate between, and one air mixture unit (https://www.academia.edu/31466052/Global_Express_Integrated_Air_Management_System).
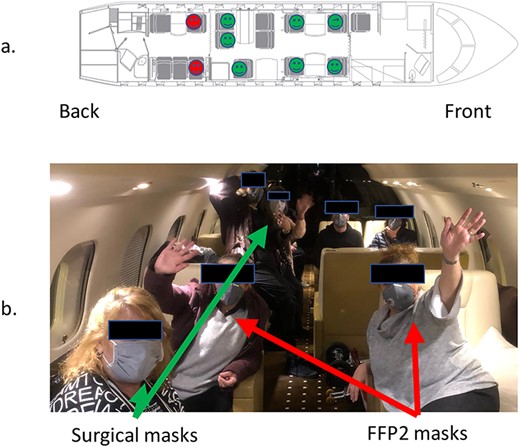
Upon arrival to Israel all 11 citizens were retested, and two were found to be positive for SARS-COV-2. One was a 76-year-old male, and the other was a 62-year-old woman who was also positive by viral cultures 4 days after arrival (see xsSupplementary Table S1). Both were spouses of COVID-19 patients admitted to hospitals in Japan. Therefore, we assume that those two acquired the virus before plane boarding and were infective during flight. Both of them remained asymptomatic after the flight. While on the plane (see sitting scheme on Figure 1), all passengers were instructed to have surgical masks and to replace it every 3 hours for the duration of the flight. Few were using FFP2 masks with unidirectional valve instead. During the 13.5 hours flight, the passengers were allowed to take off masks for eating and drinking. Based on history taken, most of the passengers took off masks during two meals served for ~15 min each. On board, the passengers were moving within the cabin freely, many have kept masks on, and were using the restrooms on the back of the aircraft. Upon arrival to Israel all passengers were put into compulsory isolation for 14 days due to their presence on the Diamond Princess. All passengers that tested negative upon arrival were found to be negative on six consecutive tests during the 14 days of quarantine, even after being in close proximity during the flight with the two positive COVID-19 patients. During the SARS epidemic, there were few reports suggesting transfer of SARS from infected passengers to others during flights.4 However, a later study5 suggested a rather low risk of transmission. An additional study from Singapore supported low transmission during flights,6 which was confirmed in serological and virus spread simulation studies.7 Those studies led World Health Organization (WHO) to a conclusion that the risk of SARS transmission in airplanes is rather low (https://www.who.int/csr/sars/travel/airtravel/en/).
(a) Interior of aircraft and sitting of passengers. The positive (red) passengers were in the back part of the aircraft wearing FFP2 masks. Negative are marked with green and crew with yellow. (b) Surgical masks used by passengers are demonstrated by green arrows, and red arrows shows FFP2 masks
Our information of this long-haul flight may support claims of low risk of transmission of SARS-COV-2 during flights. Although our example may underestimate the risk of transmission due to the use, by some of the passengers, of higher standard masks (N95). Yet, the very close proximity and contact for a long duration and at least for some part of the flight uncovered their face, may further suggest that the observations of low risk of SARS transmission holds true for COVID-19. Since experimentations aircraft viral transmission may be complicated and not applicable to all types of equipment, the WHO recommendations for SARS may be used for air travel on situations where COVID-19 patients are present with the modification of using masks.
Author contribution
R.N.P contributed to writing, data collection/analysis, interpretation and revision. I.G. contributed to data collection, revision and critical review. I.S and A.S. contributed to data collection. M.M. contributed to data collection and revision. E.M. contributed to data collection, interpretation and revision. G.Y.R. contributed to data collection/analysis interpretation and revision.
Funding
No funding was received for this work.
Conflict of interest
None declared.