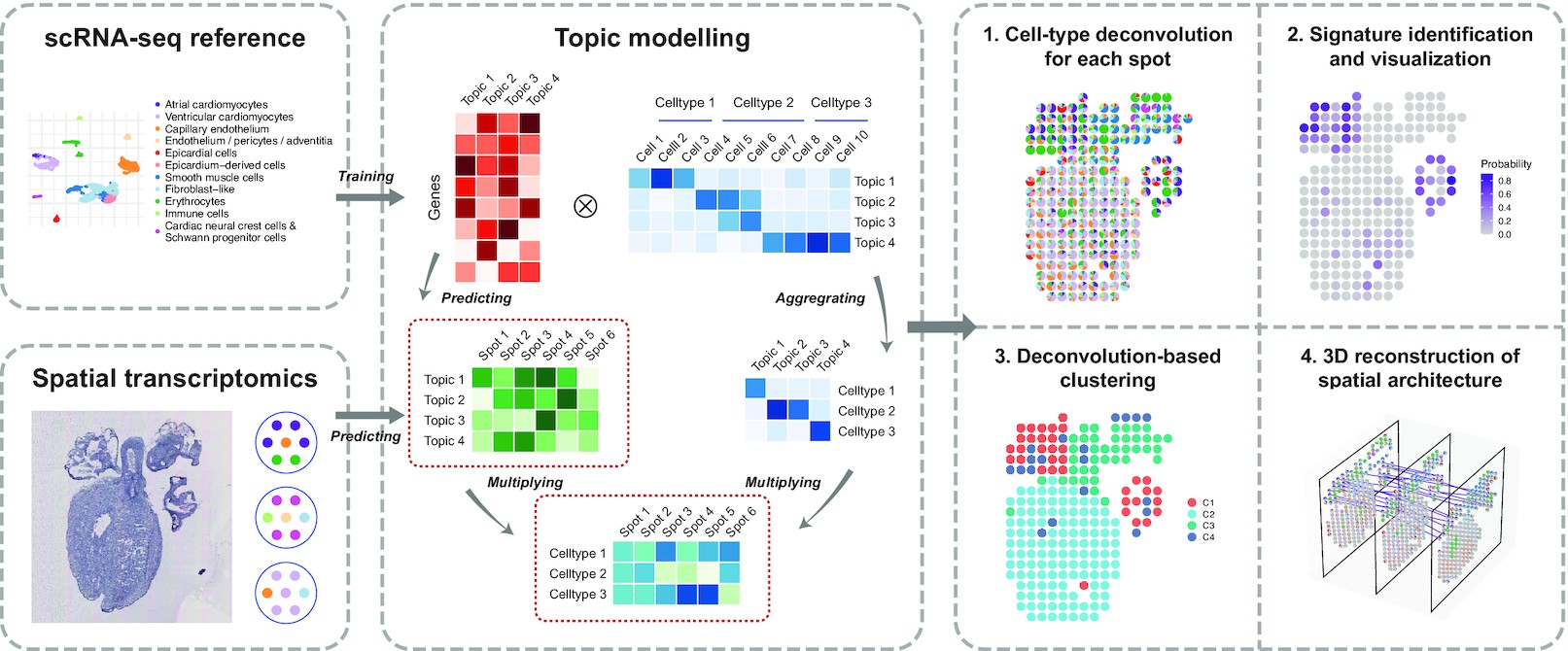
Schematic representation of the STRIDE workflow First, STRIDE estimates the gene-by-topic distribution and the topic-by-cell distribution from scRNA-seq. The topic-by-cell distribution is then summarized to the cell-type-by-topic distribution by Bayes’ Theorem. Next, the pre-trained topic model is applied to infer the topic distributions of each location in spatial transcriptomics. By combining cell-type-by-topic distribution and topic-by-location distribution, the cell-type fractions of each spatial location could be inferred. STRIDE also provides several downstream analysis functions, including signature detection and visualization, spatial domain identification and reconstruction of spatial architecture from sequential ST slides of the same tissue.